Organic Chemistry: How to Name Organic Compounds.
SOURCES: IB CHEMISTRY TEXTBOOK, 4.1.1 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY BASIC CONCEPTS BOOKLET
PLEASE NOTE: These notes are just on naming organic compounds, not on organic chemistry. For organic chemistry flashcards, see here: https://knowt.com/flashcards/0f1ef27c-5d81-46b1-8bed-a22f87ada005
Definitions:
Molecular formula;
The actual number of atoms in a formula (intergers).
e.g. Butane, C4H10
Empirical formula;
The smallest interger ratio of atoms in a compound.
e.g. Butane, C2H5
General formula;
An algebraic formula to find the molecular formula of any member of a homologous series.
e.g. Alkane, CnH2n+2
Structural formula;
Minimal structure displayed, but still showing the atomic arrangement.
e.g. Butane, CH3CH2CH2CH3 or CH3(CH2)2CH3
Skeletal formula;
A simplified formula made by removing the hydrogen atom depictions and rplacing the carbons with dots, and joining them up to form a zig-zag.
e.g. Butane, /\/
Displayed formula;
A type of structural representation that shows all the atoms and the bonds between them.
e.g. Butane; (There’s no way to make it smaller)
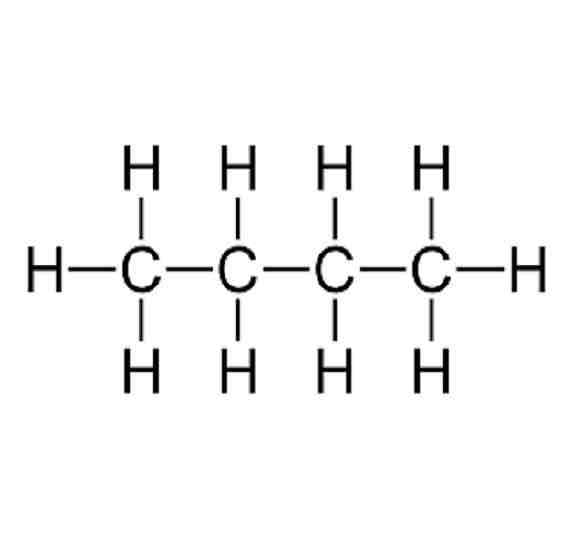
Homoloogous series;