QMS - DMAIC Process
REMEMBER: Try to add notes not included in AI summary
Definition
DMAIC (duh-MAY-ick): A structured, five-step problem-solving procedure.
Goal
Solve root causes of quality and process problems.
Outcome
Establish best practices for long-lasting and replicable solutions.
Understanding Root Causes
Symptoms
Visible outcomes of the problem.
The Problem
The gap from the goal or standard.
Causes
Underlying issues that are not immediately obvious.
Root Causes Scenario
Symptoms of High Product Defects
Increased defective products.
Surge in customer complaints.
High return rates.
Identifying the Problem
Current defect rate is 5%, while the goal is 1% or less.
Root Causes Identified
Machine calibration issues.
Inadequate training of operators.
Use of low-quality materials from a new supplier.
Test Your Understanding
Service Business Example
Problem: Customers unhappy with slow service.
Identifying Symptoms
Frequent complaints about bugs in software updates.
DMAIC Overview
Applicability
Associated with Six Sigma but also applicable in lean projects.
Key Objectives
Identify opportunities, analyze data, develop solutions, and manage improvement.
Tollgates
Definition
Checkpoints for project teams to present findings to stakeholders.
Six Sigma Organizational Structure
Leadership Team
Executive responsible for approving projects.
Project Champion
Facilitates project identification and resource allocation.
Identifies Black Belts and team members
Part-time role
Black Belts
Team leaders focused on project execution.
Spend 100% of their time on SS projects
Green Belts
Assist Black Belts and lead smaller projects.
Master Black Belt
Full-time technical leader and mentor.
Team Members
Tools Used in DMAIC
Key Tools
Project charter, process maps, cause-and-effect analysis, hypothesis tests, and control plans.
Projects in Six Sigma
Project Characteristics
Must drive significant improvements and align with corporate goals.
Initial Projects
Often opportunistic, targeting current problems.
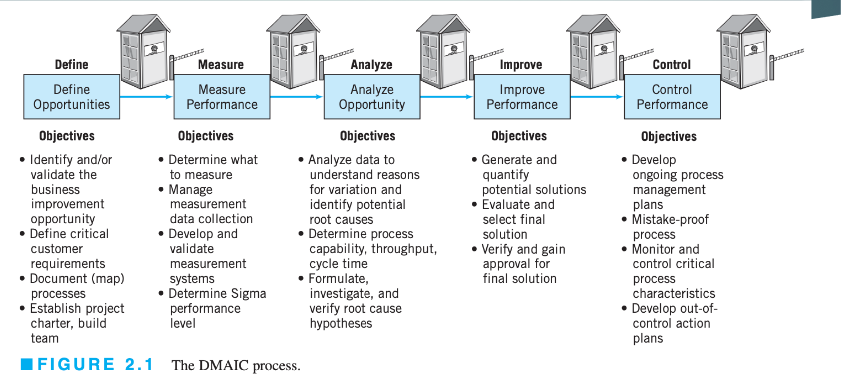
The Define Step
Objective
Identify valuable project opportunities and ensure alignment with customer needs.
Key Deliverable: Project Charter
Outlines scope, metrics, benefits, team roles, resources, and milestones.
This should be completed within 2-4 days
SIPOC Diagram
Visual mapping of Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers.
Tollgate Review Questions
Focus on problem statement, stakeholder identification, project scope, and action plan.
The Measure Step
Objective
Establish current baseline performance through data collection on quality, cost, and throughput or cycle time.
Key Variables
KPIVs (Key Process Input Variables)
Critical inputs that directly impact the process's performance and outcomes
For example: Materials, human resources, equipment, environmental conditions, process steps
KPOVs (Key Process Output Variables).
Measurable results that reflect the process’s effectiveness
For example: Product quality, customer satisfaction levels, cycle time or throughput time, cost efficiency, delivery performance
Data Collection Strategies
Historical data and observational studies.
Key Activities
Defining baseline performance, evaluating measurement systems, and updating project charter.
The Analyze Step
Objective
Determine cause-and-effect relationships and sources of variability.
Sources of Variability
Common causes (inherent variability): These are systemic in nature and difficult to isolate
Special causes (specific disruptions): These are identifiable and it is possible to take immediate action for them
Key Tools
Control charts, statistical hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and FMEA.
Tollgate Review Preparation
Present targeted opportunities and ensure project alignment with customer CTQs.
The Improve Step
Objective
Develop and implement solutions to address root causes.
Key Actions
Process redesign and bottleneck reduction, mistake-proofing (Poka-Yoke), and designed experiments.
Tollgate Review Considerations
Document problem solutions, pilot test results, and risk management plans.
The Control Step
Objective
Ensure improvements are sustained over time.
Key Elements
Handing off improved processes, developing a control plan, and scheduling follow-up validations.
Tollgate Review Considerations
Confirm project results, ensure monitoring systems are in place, and summarize lessons learned.