Pharmacology Exam 1/3
Chapter 1
Pharmacology: the study of medicines
Drugs have three uses
Therapeutic
Preventative
Diagnostic
Pharmacognosy: the study of the natural origin of drugs and the effects of natural drugs
Hypocrites first proposed that disease was due to natural causes as opposed to some gods
Galen said that there is both a cause and a cure when someone gets sick
Asia is commonly about preventative medicine
Paracelsus supported the use of individual drugs
Valerious Cordis published dispensaries in Germany
Types of Herbal Medicine
preventative
folk
problematic
Homeopathy: body heals thyself
Genetic engineering: artificially ‘cutting’ and ‘splicing’ DNA into an organism’s DNA
Generally used for recombinant DNA technology
Used in agriculture, medicine, reproduction
Drug Categories
Prescription RX
Must be ordered by a licensed practitioner
Over the Counter
Can be sold by retail outlets/pharmacies
No prescription required
Narcotic/controlled
Must be ordered by a licensed practitioner
Many rules and regulations
Health Canada
To help Canadians maintain and improve their health
Promotes well being of Canadians
Policies and Procedures re:
Safe and nutritious food
Keep people informed e.g health threats
Regulations
NAPRA National Association of Pharmacy Regulatory Authorities
Health Canada
Schedules
Schedule I= Rx
Schedule II= OTC sold by a pharmacist
Schedule III= OTC sold only in pharmacy
unscheduled= sold in outlet
narcotic/controlled substances
Drug Approval Process
Develop substance
Isolate & Purify Substance
Administer tissue cultures/small animals
Lab & Animal Studies
Clinical Trials
Evidence submitted to TPD
Drug Review by TPD
Risk/Benefits weighed
Marketing authorization granted or denied
After Approval
Distributors must report
Info about serious s/e
Info re failure to produce effects
New safety info
TPD monitors (therapeutic product directorate)
adverse events
investigations complaints
maintains post-approved surveillance
manages recalls
Special Access Program
Administered by TPD
specified MD
specified patient (quandary care)
Chapter 2
Drug actions
Homeostasis: the stability of the organism
Achieved by control and feedback mechanisms
|
|---|
Messengers and receptors
Messenger produced by cell → Messenger sent into extracellular fluid → Messenger reaches target cell → messenger binds with a receptor on the cell surface → effect produced
Specificity: the property of a receptor site that enables it to bind to a specific chemical messenger
Affinity: the strength by which a particular messenger binds to the receptor site
Mechanisms of drug action
Agonist: a drug that triggers the same response as an endogenous chemical messenger
Enhances the natural reaction to the messenger
Antagonist: a drug that blocks the action of an endogenous chemical messenger
Inhibits natural reaction
When they block action they may…
Directly inactivate the receptor
Bind to the receptor in a competitive fashion
Agonists stimulate receptors
Antagonists block receptors
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics: the study of the activity of a drug within the body over some time
A-absorption
the process by which a drug enters the circulatory system
typically orally; disintegrate then release the drug into the GI tract for dissolution
factors affecting absorption | impact & example consideration route | considerations |
|---|---|---|
route of administration | affects the drug’s systematic effects e.g oral, iv, the transdermal | oral route provides systemic absorption. IV skips absorption. Transdermal is a slow and steady |
dosage form | affects rate due to form e.g. coated tablets disintegration tablets coated | coated tablets take longer. oral tablets instantly dissolve in saliva |
D- distribution
M- metabolism
E- elimination
Chapter 5-Topical Medications
Integumentary System
The tissue that covers the body including skin, nails, and hair
Protects the body from exposure to harmful pathogens and harsh substances
Helps regulate body temperature
Skin
the body’s largest organ
3 layers
Epidermis
Dermis
Subcutaneous tissue
Epidermis
Top layer
Forms new cells and sheds old, dead cells
Produces nails, hair, glands
Interspersed with melanocytes- the color of your skin
Dermis
Second layer
Composed of connective tissue, capillaries, and nerves
Location of sebaceous glands (waxy substance) and sweat glands
Subcutaneous tissue
Third layer
Connects dermis to underlying organs and tissues
Sun Exposure and Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet A radiation damages the skin
UVA 1&2- suntan region
Ultraviolet B
burn
Characteristics of effective sunscreen
SPF of >30
protect against UVA and UVB
types of cancer
Actinic keratosis
Basal cell carcinoma
Melanoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Intrinsic aging
Loss of collagen and elastin in the dermis
Less oil production
Shrinking of subcutaneous tissue
Thinning and sagging of skin
A natural process that can be delayed but not stopped
Extrinsic aging
Caused by external factors such as sun exposure, air pollutants, smoking, skin irritation
Lesions caused by external factors, genetic predisposition, or a combination of both
DNA mutation resulting in benign tumors, precancerous conditions, skin cancer
ABCDEs of skin cancer
Asymmetry
Border
Color
Diameter
Evolution
Drug Regimens and Treatments
Sunscreens
partially block UV radiation
Many reduce UVB rays whiles allowing UVA rays through.
A common ingredient is PABA
para amino benzoic acid
Sun Protection Factor
Estimates how much longer a person can be in the sun and not burn
Measures mostly UVB-blocking activity; therefore, a person may still get exposed to UVA radiation
medication | Therapeutic uses | cautions and considerations |
|---|---|---|
Benzocaine (Lanacane) | Relieve sunburn | Associated with |
Hydrocortisone (Cortaid, | decreases | Risk of allergic contact |
Silver sulfadiazine | Prevents infection in | Caution in sulfonamide |
Photosensitivity
Increased sensitivity of the eyes and skin to light
Risk increases with drugs in certain classes
Watch for computer prompts and warn patients to avoid sun exposure.
Classes of drugs include ACE inhibitors, antibiotics ((doxycycline, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, sulfonamides), antidepressants(phenothiazines), antihistamines, antipsychotics, cardiovascular drugs(statins, enalapril, diltiazem), chemotherapeutic agents, diuretics( furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide), hypoglycemic(glipizide, glyburide), NSAIDs(Ibuprofen, ketoprofen, naproxen, celecoxib)
Define
integumentary: skin, hair, nails,
dermatology- the branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of skin disorders.
keratolytic-a type of medical treatment to remove warts, calluses and other lesions in which the epidermis produces excess skin.
astringent- contraction, closes your pours
antiseptic-prevents the growth of organisms/ diseases
antibiotic- medication inhibits or stops the growth
antipruritic- anti itching
emollient- help soften or soothe the skin
Demulcent- relieves the inflammation on the skin
Disinfectant-a chemical that destroys bacteria
Bactericidal- capable of killing bacteria
Bacteriostatic- inhibits the growth of bacteria
Debridement- removing damaged tissue and foreign objects from a wound
Granulation- healing of a serious wound
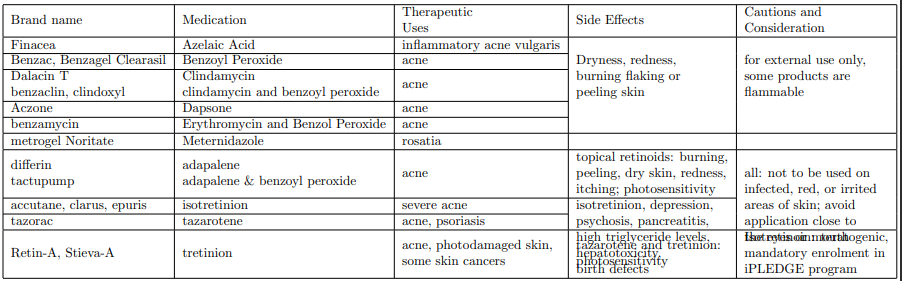
Acne, Wrinkles, Rosacea
Acne: overproduction of sebum is often caused by hormonal changes
Pimples,
blackheads,
whiteheads,
deep cysts in serious cases
Wrinkle
line or crease in the skin
promoted by sun exposure, smoking, lighter skin, heredity
Rosacea: chronic inflammatory disorder is seen in adults
redness, visible surface blood vessels, raised bumps
face only
excess sebum production
triggered by stress, temperature, hot drinks, exercise, spicy food, alcohol, products which irritate the skin, sunlight
Drug Therapy for acne, wrinkles, and rosacea
acne
cleanse twice a day
OTC products
topical prescription products
oral prescription products
Wrinkles
retinoids
Rosacea
identify and avoid triggers
topical agents
antibiotics
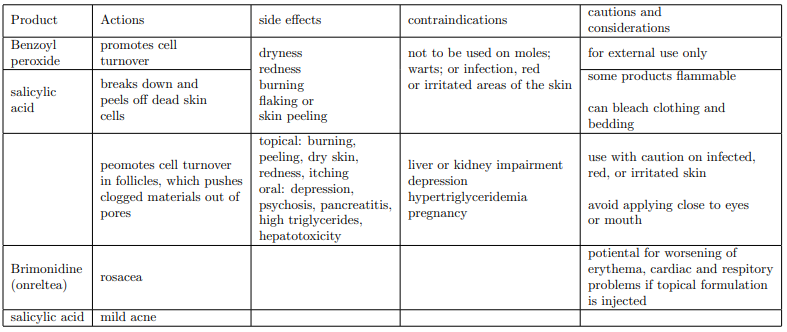
dermatitis
pruritis, inflamed skin that can be caused by a variety of factors
symptoms include areas of redness, dry flaky skin, raised or bumpy skins pruritis
psoriasis
an immunologic condition
manifests as well-defined plaques that are raised, silvery or white
can appear anywhere on the body and may be very small or quite large
exacerbated by stress and environmental factors
Topical Corticosteroids
anti-inflammatories
cortisone; steroids
for many types of skin
many forms
potency (fluorinated=stronger)
Rx and OTC
end in “sone” and “olone”
Hair Loss
androgenic alopecia
referred to as male-pattern baldness
affects men and women
hair follicles shrink, producing finer hair
Alopecia areata
a chronic inflammatory condition affecting hair follicles
may cause areas of complete hair loss
Antihistamines
inhibit inflammation, redness, and itching
work if histamine is released
antipruritic
Combination: Caladryl (calamine + diphenhydramine)
Skin Infections
bacterial infections
impetigo
caused by S. aureus or Streptococcus
superficial, highly contagious; common in an early childhood
erysipelas- don’t worry about
A form of cellulitis that spreads rapidly through the skin
folliculitis
Inflammation of a hair follicle, surrounding tissue not affected
Furuncle
Begins in a sebaceous gland and associated hair follicle; more extensive and deep than folliculitis
Carbuncle
a coalescent mass of infected follicles; deeper than a furnicle
Fungal infection
candidiasis
Caused by Candida albicans; lesions in the vagina and mouth
ringworm
caused by a microscopic fungus
infects the skin or nails
spreads outward as the center heals, leaving a ring
Yeast Infection
cause: candida albicans
treated the same as fungal infections
Fungal Skin Infections
ringworm (tinea corporis)
athlete’s foot (tinea pedis ic)
jock itch (tinea crudis)
nails (onychomycosis)
Viral infections
Herpes simplex virus (HSV
HSV type 1 associated with cold sores
HSV type 2 associated with genital infection
Herpes Zoster
Chicken Pox (Vaccine- varicella – Varivax)
Shingles ( Vaccine – varicella life and non-live –Zostavax and Shingrix)
Wart
The epidermal tumor is caused by a virus
Viruses may lie dormant and later cause reinfection
Topical Salicylic acid preparations, i.e Compound W, Duoplant
External Parasites
human lice
wingless parasitic insects that feed on human blood
spread by direct contact with infested person’s head, body, or personal items
symptoms of infestation is itching
types | description |
|---|---|
body lice | -Live on clothing and moist areas of the body |
Head lice | -Lives on scalp and hair-Feed on blood from the scalp which produces itching |
Pubic lice | -Live in the pubic area |
types of lice:
body lice
Shower or bathe, and apply 20-30g of cream or lotion to the whole body; then wash off in 24 hours
repeat once a week
head lice
Massage two ounces of less of cream or lotion into premoistened hair for four minutes, and rinse out
repeat once a week
pubic lice
Apply a thin layer of cream or lotion that extends to the thighs, trunk, and axillary regions; wash off in 24 hours.
repeat once a week
Scabies
type of mite
Female burrows in epidermis secretes substances that disintegrate the skin, then feeds on the skin
Intense itching at night caused by increased activity of mitese, feeding, and deposition of feces.
Lesions are slightly elevated, wavy grayish-white burrows.
Lesions often seen in webs between fingers
Drug Therapy for Scabies
permethrin
adults
apply to the skin from neck to feet
infants and older adults
apply to the scalp and face
everyone
wash off 8-12 hours later
Crotamiton (Eurax)
cream for the intense itching
Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Use of Disinfectants
instruments
Best to use two separate agents with different mechanisms of action
treats infections in the mouth and on the body
The oral cavity is difficult to disinfect because very few drugs adhere to the mucosal lining long enough to overcome bacteria
Types of Disinfectants
Povidone-iodine (Betadine)- wounds
Zinc oxide (Desitin)- diaper rash
Chlorhexidine gluconate (Peridex, Perichlor, Periogard)- antibacterial dental rinse
Decubitus Ulcers
Are caused by contact pressure applied to the area of the skin. It happens when patients are confined to beds or wheelchairs. The skin is meant to skin if not the skin will become thin. It is common near bony areas such as the tailbone, heels, hips, spine, and elbows. How to prevent it? Turn patients in every 2 hours. Apply for skin protection. Using air beds. Ensure good hydration and nutrition.
Treatments for Ulcers
debridement
Removes dead, crusted, or contaminated tissue around a wound to promote healing
can be painful so pain medication is given prior
Positioning
Reposition bedridden patients every 2 hours
Prevents new wounds from developing
Prevents existing wounds from getting worse
24-hour care is required if they are unable to move independently
Burns
causes
heat and thermal injury
electrical and chemical sources
determinants of prognosis
severity
how deep the damage is
% of body surface affected
Determined by dividing the body into major sections
Drug Regimens and Treatments for Burns
cooling and cleaning
cool water
A mixture of refrigerated and room-temperature saline
Water-soaked gauze pads cooled in the refrigerator
Blisters
not to be drained or popped
Drug Regimens and Treatments for Burns:
Silver Sulfadiazine
Protects non-superficial wounds from bacterial infection. Side effects are skin discoloration, skin rash, and a burning sensation. Contraindications are pregnancy and infants under 2 months. Cautions and considerations would be allergies Careful wound care and monitoring of tissue necrosis
Burns and Skin Ulcers
mechanism for healing
debridement
granulation
drainage
debridement
dead tissue is removed
new tissue forms at the base
Granulation
when the lumpy, pink tissue containing new connective tissue and capillaries form around the edges of a wound
Drainage
Other Drugs
drugs to absorb exudates
Duoderm
Drug for debridement
collagenase (Santyl)
Drugs for granulation
polyurethane foam dressing (eg, Allevyn)
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
aloe gel
Has wound-healing, antibacterial, and antifungal properties
In concentrated form, used for treating mild psoriasis and burn-wound healing
Needs to be applied three times a day for up to four weeks
Concentrations in many lotions and oils are not sufficient to do more than moisturize
Clove Oil
An antiseptic used on exposed dentin when combined with zinc oxide or zinc acetate
Lanolin, Cocoa Butter, Vegetable or Seed Oils
Added as moisturizers to creams and lotions
Keep skin hydrated and soft
Vitamins A, D, and E
Emollients added to moisturizers to promote skin health and healing
Chapter 16
The Immune System, Bacterial Infections, Fungal Infections, and Drug Therapy
Anatomy and Physiology of the Immune System
The immune system helps the body fight infection
Organs of the immune system and their functions
The bone marrow produces white blood cells which
fight infection.The thymus produces T lymphocytes.
The lymph nodes trap microbes, and the lymph vessels carry the fluid of the lymphatic system to cleanse body tissues.
The spleen removes microbes from the blood.
Immune System
bodies built-in defense mechanisms against pathogens
made of specialized cells, tissues, and organs
cells of the Immune System
leukocytes: white blood cells
agranulocytes: don’t contain granules in the cytoplasm
Granulocytes: contain granulates in the cytoplasm
Monocytes: circulate in the blood; move into infected tissue
macrophages: mature; ingest invaders
lymphocytes: detect specific pathogens; support immunity
Types of immunity
innate immunity
present from birth
first line of defense that is quick to fight pathogens
forms of innate immunity
integumentary and GI system, which forms a barrier between the body’s interior and outside pathogens
Phagocytic leukocytes, which break down pathogens
Eosinophils, leukocytes, neutrophils
The complement system, which consists of enzymes and proteins
histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandins
Infectious Diseases
define
Disorders caused by pathogenic organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or protozoa
Infectious Disease Prevention
handwashing
using soap and water to wash hands
hand hygiene
Cleaning hands using alcohol-based products that do not require water
Universal precautions
Personal safety standards to protect against accidental exposure to pathogens
Includes personal protective equipment
Sanitizing
Bacterial Infections
Bacteria: single-celled organisms
can be found on the skin, in the mouth, in the gastrointestinal tract
cause disease when they grow uncontrollably or enter the bloodstream
Pathogenic bacteria: can cause an infection
Bacterial Infection: bacterial growth in body tissues can cause tissue damage
symptoms of bacterial infection
Fever of >101 degrees Fahrenheit and white blood cell count of >12,000/mm^3
Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
oxygen requirement | -aerobic bacteria need oxygen to live--anaerobic bacteria can survive without oxygen |
bacterial shape | -cocci are spherical-bacilli are rod-shaped-spirochetes are spiral-shaped arrangement |
arrangement | clusters, repair thickness |
the thickness of cell walls | - Gram-positive bacteria have a thick cell wall that absorbs crystal violet- gram-negative bacteria have a thin cell wall that does not absorb crystal violet |
Antibiotic Selection
antibiotic: a chemical substance with the ability to kill or inhibit bacterial growth
factors considered in an antibiotic selection
type of pathogen suspected
antibiotic’s spectrum of activity
location of the pathogen
identifying bacteria and selecting a drug treatment
sample or swab taken is taken from the parties
the sample is grown in a laboratory culture
culture and sensitivity tests performed
a broad spectrum is effective against multiple organisms
Empirical treatment: using medication to treat a patient before the specific microorganism causing the infection is identified
nosocomial infection: acquired while a patient is in a hospital or nursing home
bactericidal agent kills the invading agent
bacteriostatic agent: inhibits the growth of bacteria
clinical and microbiologic responses are used to evaluate the outcome
Antibiotic Side Effects and Dispensing Issues
Parenteral antibiotics should be mixed exactly as directed
drug may cause adverse effects if not done correctly
The counting tray should be swabbed with alcohol after counting oral antibiotics
most antibiotics are taken on an empty stomach, but some should be taken with food
Antibiotics may decrease the effectiveness of birth control pills
Antibiotics should be given around the clock
Antimicrobial Resistance
antibiotic resistance: is the ability of bacteria to develop defense mechanisms that resist or inactivate antibiotics used
preventing resistance
prescribing antibiotics only when necessary
using auxiliary labels that remind patients to complete the entire course of antibiotics
Storage and Liquid Antibiotics
storage requirement
some antibiotics must be refrigerated
some antibiotics may be stored at room temperature
technicians may discuss this information with the patient
Medication Flavors
technicians may suggest and change flavors
the flavored medication increases adherence in children
Ophthalmic Antibiotics
manufacturing requirements
same pH as the eye
sterility
Dispensing Issues
often rejected due to expense
need to inform the prescriber of alternatives
STIs and Drug Treatment
Sexually Transmitted Infections: genital-system infections transmitted by sexual activity
They were formally known as STDs and general diseases
preventing STIs
no sex
wait until marriage
use a condom
Chlamydia
caused by chlamydia trachomatis
often asymptomatic
typically occurs with gonorrhea
potential for reinfection if a partner is not treated
Gonorrhea
caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Symptoms: painful urination and discharge of pus from the penis, abdominal pain due to pelvic inflammatory disease
Long-term complications include sterility in patients with a penis.
Risk of systemic infections in any patient if untreated
Occurs frequently with chlamydia
Syphilis
stages | Description |
|---|---|
primary-stage infection | -chancre at the site of infection which heals in weeks-fluid from chancre highly infectious-if not treated, will progress to the secondary stage |
secondary-stage Infection | -skin rash, patchy hair loss, malaise, mild fever-symptoms subside, the disease becomes latent |
Late or tertiary-stage infection | -occurs after at least 10 years-rubbery tissue masses in organs and deafness, blindness, CNS lesions, perforation of the roof of the mouth |
Other Sexually Transmitted Infections
infection | description |
|---|---|
nongonococcal urethritis | -Caused by catheters, chemical agents, or sexual transmission-Genital discharge, burning while urinating, itching-May progress to PID in patients with a uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, or ovaries |
Gardnerella vaginitis | -Characterized by vaginal discharge and odor-Caused by an interaction between the organism and anaerobic bacteria in the vagina-Frothy discharge, fishy odor, vaginal pH of 5 to 6 |
trichomonas vaginalis | -Bacteria found in individuals of any sex-Potential for infection if vaginal acidity is disturbed-Profuse, yellowish, or light cream-colored discharge with a disagreeable odor that irritates, burning, and itching |
Medications and their use
medication | infection |
|---|---|
azithromycin | certain stages of syphilis, gonococcal infections |
ceftriaxone | penicillinase-producing bacteria |
doxycycline | lymphogranuloma venereum, which is caused by chlamydia trachomatis |
metronidazole | Gardnerella, vaginalis |
tetracycline and erythromycin | chlamydia |
penicillin G benzathine | syphilis, especially during the primary stage |
Fungi and Diseases
fungus: Single-celled eukaryotic organism
mushrooms, yeasts, mold
They are different from green plants since they lack chlorophyll and reproduce using spores
They are different from animal cells and bacteria by having rigid cell walls
they are different from human cells since human cell membranes contain cholesterol and fungi’s cell membranes contain ergosterol
Infectious Disease Treatment
Fungal Infections
Dermatophytes are fungal infections of the skin
Candidiasis causes vaginal yeast infections and oral thrush
not all fungi cause infections
states of immunodeficiency
drug therapy
poor nutrition
IV catheters
Some cancers
Human immunodeficiency virus
Antifungal medication polyenes azoles, echinocandins, misc
drug regimens and treatment for fungal infections: antifungal drugs
Fighting Parasitic and Protozoal Infections
Infectious Disease Treatment
parasitic and protozoal infections
Parasites are organisms that live off a host
protozoa are single-celled organisms that usually cause infections through oral-fecal route
Giardiasis is an intestinal infection caused by protozoa and is carried in bird droppings, deposited in water or on vegetation
Common Parasitic and Protozoan Organisms and Infections
Therapy often combines 2 or 3 drugs
quinine
hydroxychloroquine-Plaquenil
doxycycline
tetracycline
clindamycin
atovaquone- Malarone
Mefloquine-Lariam
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
echinacea: used to treat the common cold, RTIs, and vaginal yeast infections
reduces the severity and length of symptoms
variable concentrations in the products availably
no standard dose established
must be used multiple times a day and started at the first signs of infections
Zinc
used to enhance wound healing and prevent wound-associated infections
no well-established dose
Garlic: used for immune system stimulation and prevention of infections
used topically for dermatophyte infections
side effect of oral garlic dermatitis or burns
drug interaction for garlic: anticoagulants
Ginseng: used for several conditions including prevention of infection
has been shown to reduce the length of cold sores and the risk of recurrence
side effects are headaches
drug interaction with ginseng: warfarin
Vitamin C: used to boost the immune system and for its antioxidant effects
side effects of high doses are diarrhea, upset stomach, kidney stones
Immune System, Viral Infections, and Drug Therapy
17.1 Viruses and Viral Infections
Virus
an infectious agent smaller than a bacterium, not a whole-cell organism
Individuality consists virus particle is a virion
Consists of a core of DNA or RNA surrounded by a capsid
must attach itself to a host cell to replicate
Ways that viruses spread
direct contact, ingestion of contaminated food or water, inhalation of airborne particles, exposure to contaminated body fluids or equipment
Viruses and Viral Infections
virus
a minute infectious agent smaller than a bacterium
consists of segments of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coating or capsule
requires host cells to reproduce
Stages of Viral Infection
Attachment: Virion attaches to cell receptors
Penetration: virion penetrates the cell and escaped into the cytoplasm
uncoating: virion sheds capsid and presents DNA or RNA to the cell nucleus
Replication and Assembly: Virion DNA or RNA causes cells to produce new viral particles
release: duplicated viruses are released from the host cell
Significant Viral Infection
Influenza: symptoms include malaise, myalgia, headache, chills, fever
Patients at risk for complications include the elderly; patients with cardiovascular disease, renal disease, diabetes, and respiratory conditions; immunocompromised patients.
Annual vaccinations are recommended for those at risk for complications.
Hepatitis: inflammation of the liver
various types referred to as hepatitis A through G
severity range from benign to serious
HIV: considered a chronic disease
regimens of at least three drugs
important to monitor for drug interactions
Classification of Viral Infections
Viral Duration and Severity
An acute viral infection quickly resolves.
Chronic viral infection has a long course with periods of remission.
A slow viral infection maintains a progressive course over months or years.
The extent of Viral Infection
A local viral infection affects tissues of a single system.
A generalized viral infection has spread to other tissues.
Latent Viruses
A virus that lies dormant
after infection and then later becomes activeExamples: herpesviruses
and HIV
Virus and Host-Cell Interaction
Immunoglobin
A type of antibody produced by host cell B lymphocytes
An immunoglobulin that matches a viral protein may prevent the virus from attaching to a cell or may destroy the virus.
Interferon
Induces production of proteins that may disrupt viral replication or prevent spread to uninfected cells
Vaccination
description
Exposing a patient to a component of a virus or an altered viral strain to produce antibodies
When later exposed to the actual virus, the infection does not develop because natural defenses have been primed.
Viral Mutations
It makes effective vaccine production difficult.
An example is the influenza vaccine which must be reformulated each year
Chapter 17.2 Antiviral Agents (Nonretroviral)
challenges of treating viral infection
Viruses use host’s cellular processes to function and replicate.
Medications which block the virus life cycle are often toxic to the patient.
The similar challenge presented by chemotherapy agents for cancer
Antiviral Drugs
formulated to seek out a virus and prevent its replication without interfering with normal host function
Therapeutic Uses of Antiviral Drugs
Herpesvirus Infections
Herpes Simplex 1 (HSV-1)
Herpes Simplex 2 (HSV-2)
Varicella-zoster (chicken pox/ shingles)
cytomegalovirus (human herpesvirus 5)
Influenza
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
Antiherpes Agents
Work Wise: Ganciclovir and Valganciclovir are considered hazardous drugs, so it is essential to follow handling precautions as outlined in the pharmacy’s workplace policies and procedures
Anti-Influenza Agents
Other Antiviral Agents
HIV/AIDS and Antiretroviral
Define
retrovirus: uses RNA as its genetic material
Reverse transcriptase: The enzyme retroviruses use to become part of the host’s DNA
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): A retrovirus that attaches to receptors on the surface of CD4 cells
It uses reverse transcriptase to convert its genetic material from RNA to DNA
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (ADIS): Syndrome which occurs when patients have advanced and severe forms of
HIVYou can have HIV without having aids.
Antiretroviral drugs
difficult to tolerate due to side effects and drug interactions
Can be combined in a “cocktail” that attacks viral replication in multiple stages
must be taken chronically
some cocktails available as a single tablet
NRIs and NtRTIs
They inhibit reverse transcriptase, which prevents the formation of a DNA copy of viral RNA
Class Side Effects are nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain which improves in the first few weeks. More permanent effects are lactic acidosis with hepatic steatosis
NRITs and NtRTIs
NNRTIs
Protease Inhibitors
work by decreasing the formation of the protease enzyme, which cleaves specific HIV protein precursors necessary for the construction of new infectious virions
Typically combined with other HIV drugs; metabolized through cytochrome P-450 resulting in many drug interactions which are sometimes severe; not to be used with statins;
Side effects include redistribution of body fat, facial atrophy, breast enlargement, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, the possibility of increased bleeding episodes in patients with hemophilia.
Protease Inhibitors
Fusion Inhibitors
Chemokine Coreceptor Antagonist
medication is maraviroc (Celestin)
It works by preventing HIV from attaching and entering immune cells.
special characteristic is that it has to be given with other antiretroviral drugs
Side effects of Chemokine Coreceptor Antagonists include cough, abdominal pain, dizziness, fever.
risk for hepatotoxicity with allergic features monitor closely for infection
Integrase Inhibitors
Responding to Exposure to HIV
Healthcare worker risks
exposure to blood and other bodily fluids
needlestick injuries
Postexposure Prophylaxis
can be decreased the risk of infection by 80% should start treatment with 2 hours
Combining antiretroviral medications
advantage
improve adherence
disadvantage
fixed doses unsuitable for unstable patients
examples
Lamivudine-zidovudine (Combivir)
Elvitegravir-cobicistat-emtricitabine-tenofovir (Stribild)
Emtricitabine-tenofovir (Truvada)
Immunization
Immunity is resistance to an infectious disease.
Immunization: the process whereby a person acquires immunity or resistance to an infectious disease
Methods of acquiring immunity:
Passive Immunity: antibodies transferred to an individual
occurs naturally during pregnancy
happens artificially during administration of immunoglobulin
Active Immunity: individual makes their own antibodies
naturally through exposure to pathogens
artificially through vaccines
Purpose is to prevent viral infections by providing immunity
exposes a patient to a component of a virus or altered viral strain
development of antibodies specific to the virus
patient’s defenses primes for subsequent exposure
viral mutations
patient’s defenses do not recognize mutated virus since they were primed against the original virus
example is influenza which is redone yearly
A vaccine induces the body to make antibodies which recognize the virus antigen and fight infection
Live Attenuated Vaccines: use live but weakened pathogens to induce an immune response
Inactivated Vaccines: use pathogens that have been killed
Immunization Schedule
Schedule source: adult and childhood vaccination schedules are published by the CDC
vaccines for children: most lead to a lifetime immunity
boosters given for continued protection
vaccines for healthcare workers: hepatitis B vaccination and annual influenza vaccine often required by employers
CDC recommended immunizations
Common Vaccines
Travel Vaccines
Recommended when traveling from areas of low infection rates to areas of high infection rates
Given two or more weeks before travel to give the immune system time to mount sufficient response
Travel clinics may be located in clinics or pharmacies and provide immunizations and advice about what vaccines are necessary
Dosage Forms and Administration
Most require storage in refrigerator or freezer, storage temperatures strictly followed
If warmed to room temperature must be used right away
Not to be refrigerated again if warmed to room temperature
Must be used within minutes to hours once reconstituted
Advance mixing of vaccines not recommended
Vaccines not to be mixed in same syringe with other medications
Cautions and considerations
Patients to receive vaccine information sheet (VIS) and sign a consent form as required by law.
Healthcare personnel trained in vaccine administration must be trained in CPR
Complementary and Alternative Therapy
Andrographis
May reduce symptom severity and duration of influenza if started within 36 to 48 hours
Side effects include chest discomfort, headache, nausea, rash.
May interact with anticoagulants, blood pressure medications, and immunosuppressants
Colloidal silver
Used topically and orally for infection
Side effects include argyria, neurologic deficits, kidney damage.
Elderberry
May be used for influenza when initiated within 48 hours of symptoms
Oscillococcinum
 Knowt
Knowt