Chapter 31: Excretion
Excretion
Removal of waste products of metabolism made in the body
Homeostasis
Maintenance of a constant internal environment.
The temperature of the human body must be kept at a constant temperature, fluid balance and chemical balance.
Excretion is important to keep body at optimal temperature (37o)
Temperature Regulation in Animals
Body temperature is controlled by the rate of chemical reaction within our cells. Chemical reactions are enzyme controlled.
High temperatures damage enzymes, low temperatures slow down reactions.
Ectotherms gain or lose heat from their external environment e.g. frogs, reptiles, snakes
Usually characterised by laying shelled eggs
Endotherms generate their own heat from metabolic reactions e.g. birds, dogs, humans (mammals)
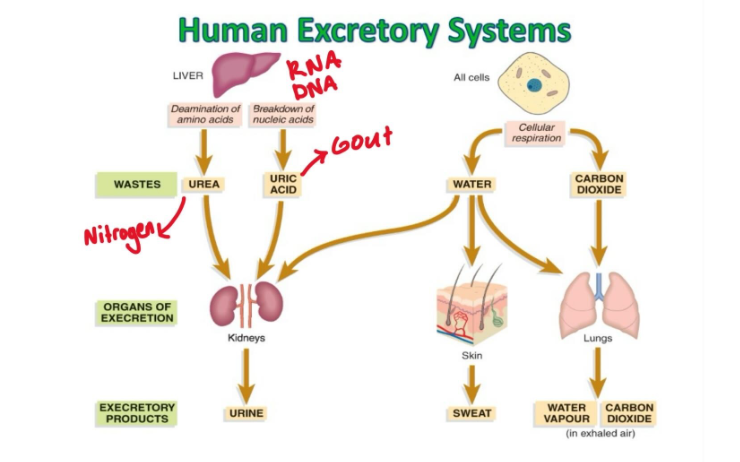
Organs of Excretion in Humans
Skin
Lungs
Kidneys
The Skin
Consists of two layers: outer epidermis and inner dermis.
Epidermis consists of three layers: cornified layer, granular layer and malpighian layer.
The malpighian layer (also called basal layer) is the site of active cell division. It contain most of the melanin responsible for dark skin.
As new basal cells are constantly dividing by mitosis, the new cells formed push older cells formed push older cells to the surface.
The cells enter the granular layer where they mature to form cells containing a protein called keratin. Here the cells become larger, flatter, dehydrated, fuse together and die.
They then move into the cornified layer, where the cells are durable and constantly being worn away. We have between 10 and 30 thin layers of dead cells here.
Melanocytes in the malpighian layer produce melanin. This is the pigment which gives skin, hair, and the iris its colour.
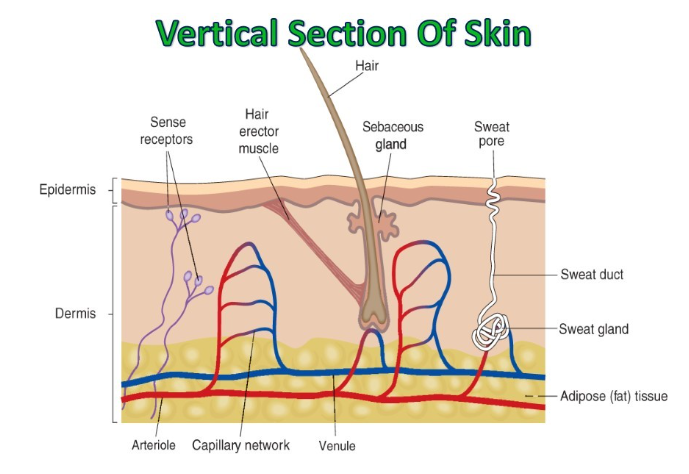
Dermis lies between the epidermis and adipose tissue and consists of a connective tissue containing the protein collagen. Dermis contains sweat glands, hair follicles and sebaceous glands, blood vessels and nerve receptors.
Functions of Skin
Epidermis protects body from damage and water loss.
Dermis protects internal damage to organs.
Melanin protects skin from UV light.
Sebum is produced by sebaceous glands which maintains hair moisture and flexibility, and prevents skin from drying up and cracking.
Vitamin D made in skin in response to sunlight. Necessary to absorb vitamin C.
Food storage - fat in adipose tissue
Sense organ - receptor detect sensation of touch and temperature
Excretion - sweat glands act as organs of excretion. Wastes removed from body through sweat.
Temperature Regulation - Cold Conditions
The skin may be used to retain heat if the body temperature falls. The body fat under the skin is a good insulator.
In cold conditions the skin retains heat by:
Erector muscles contract. This causes hairs to stand up and is called piloerection. This traps a layer of air to reduce heat loss.
Blood vessels near the skin contract ti reduce heat loss. This is called vasoconstriction.
Vertical Section of Skin
Temperature Regulation - Warm Conditions
Humans use their skin to get rid of excess heat when necessary.
In warm conditions the skin reduces our temperature by:
Blood vessels near skin dilate allowing warm blood to flow near skin surface (visodilation)
Sweat glands release water for evaporation. This evaporation removes excess heat.
Erector muscles relax and hairs remain flat against skin so no air is trapped.
Sweating causes lack of water in blood if the body overheats. Essential salts are also lost, such as potassium. This is why ‘sports’ drinks have added salts to replace those that are lost.
The Urinary System

The urinary system consists of two kidneys - the main excretory organs of the body. The kidneys are located in the lower abdominal cavity.
Kidneys are brown, bean shaped organs the size of a small fist.
Each kidney has a large artery (renal artery) carring blood to it from the aorta. The aorta contains blood containing waste products collected from all over the body.
Each kidney has a large vein (renal vein) which carries away deoxygenated blood.
Each kidney also has a third tube attached to it. This is called the ureter and carries away urine away from the kidney