7.4 Le Chatelier's Principle
When a chemical system at equilibrium is disturbed by a change in a property (such as concentration, temperature or pressure), the system in a way that opposes the change.
- Any change in a system that results in a change in reactant and product concentration is known as an equilibrium shift.
Nature of Change
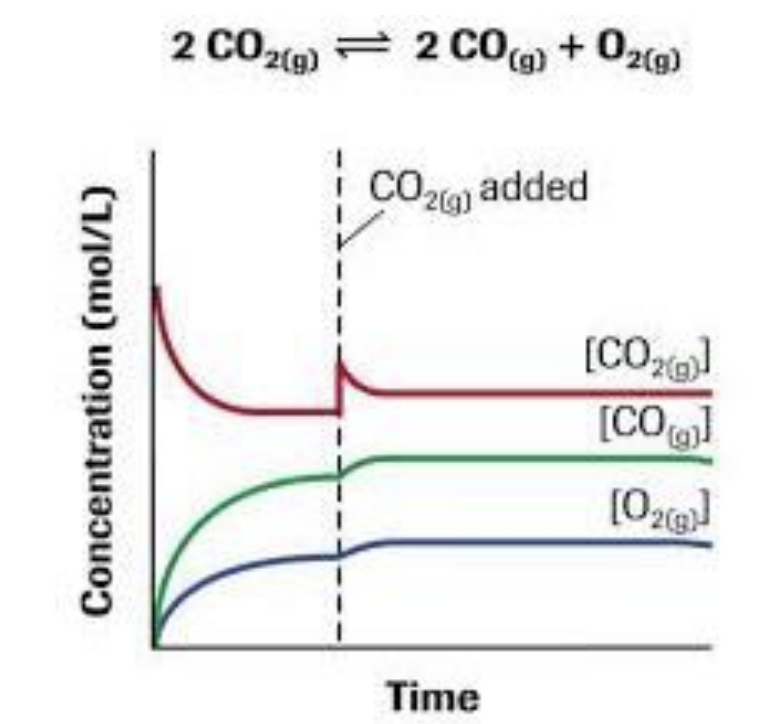
- Adding or removing [R]
- Adding or removing [P]
- Increasing or decreasing pressure by increasing or decreasing volume
- Adding or removing heat energy
- Adding a catalyst or inert gas does not change equilibrium concentrations (catalysts make the system reach equilibrium faster, but result is the same)
Concentration
Add [R]
- increase frequency of collisions between Reactants
- increase in [P]
- increase forward Rx
Remove [P]
- decrease frequency of collisions between products
- increase in [P]
- increase forward Rx
Add [P]
- increase frequency of collisions between products
- increase in [R]
- increase reverse Rx
Remove [R]
- decrease frequency of collisions between reactants
- increase in [R]
- increase reverse Rx
Note: addition/removal of a substance in solid or liquid state does not change equilibrium
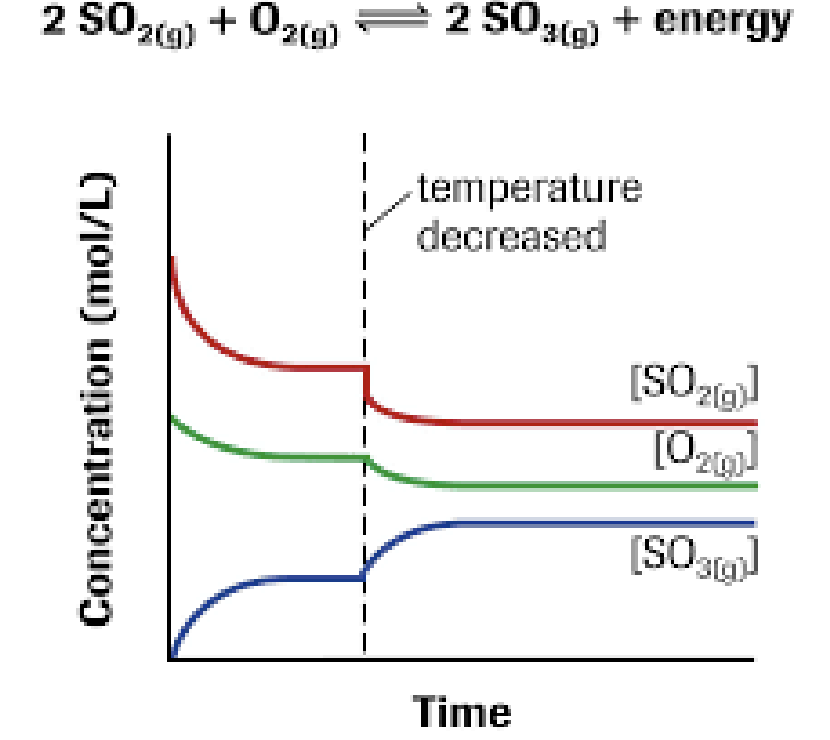
Temperature
Exothermic reaction:
- Reactants ↔ Products + HEAT
- Adding heat → drives reverse reaction (adding product)
Endothermic reaction:
- Reactants + HEAT ↔ Products
- Adding heat → drives forward reaction (adding reactant)
Pressure & Volume

By increasing the pressure, we drive the reaction to the side where there are fewer total particles, or smaller concentration (forward in this case)
By decreasing the pressure, we drive the reaction to the side where there are more total particles or larger concentration (reverse in this case)
Note: Pressure only affects gases as you cannot change volume of a liquid (does not affect aqueous states).

Remember that P and V are related inversely
When volume is decreased (pressure increased), reaction shifts in favour of the side with fewer moles
In this case, reaction shifts right, favours forward reaction, products increase, reactants decrease