Ch 20 - Macroeconomic Objectives: Low and Stable Rate of Inflation
Managing the change in the average price of level and achieving low and stable inflation rate → key objectives of government macroeconomic policy
Inflation: is the sustained increase in general price levels in an economy
Disinflation: fall in the rate of inflation in an economy
Deflation: sustained decrease in the general price levels in an economy
Consumer Price Index (CPI): the price index governments use to measure the rate of inflation
- Weighted on the basis of consumer expenditure
- Annual percentage in the change in the index is the inflation rate
Constructing a weighted price index:
- Price index value = current year price / base year price * 100
- Weighted index = weight * price / 100
- Rate of inflation = percentage change in the weighted index
Limitations of measuring inflation:
- One-off changes in price
- Variation between countries
- Change in quality of goods
- Types of retailer prices vary
- Regional variation
Demand pull inflation: occurs when a rise in aggregate demand in the economy causes pulls in the price level in the economy to increase
- Illustrates a rise in AD, leads to a rise in the average price level
Inflationary gap: periods of demand pull inflation lead to inflationary gap where the short run equilibrium is at a level of real GDP above the full employment level of income
- actual output is above potential output
Cost push inflation: occurs when there is a reduction in the short run AS in the economy and price level is pushed up by rising costs
- Rising costs causes the short run AS to shift which leads to a rise in average price level and a fall in real output
The SRAS curve will shift to the left is the cost of these factors increases:
- Wage push inflation: when wage rises faster than output unit or average costs rise
- Higher prices if firms choose to pass on the increase in unit costs as a higher price
Raw material costs: cost push inflation can be caused by rising commodity prices when increase the cost of manufactured goods
Capital costs: if the prices of machinery and equipment
Effects of inflation:
- Impacts cost of living; price level rises in the economy the cost to households increases
- Inflation has a negative effect on disposable incomes of households where wages cannot keep up with the increase in average price level
- Reduces competitiveness
Deflation: negative rate of inflation where there is sustained fall in the general level of prices in an economy
Demand side deflation: deflation can occur because of a fall in AD and typically occurs in a recession
Supply side deflation: deflation that occurs on the supply side arises when the AD curve shifts to the right and leads to a higher output at lower prices
- It is called “good deflation” as it is associated with higher level of real GDP
Effects of deflation:
- Reduced growth and deflation
- Falling consumer consumption
- Redistribution of goods
- Rise on spending power
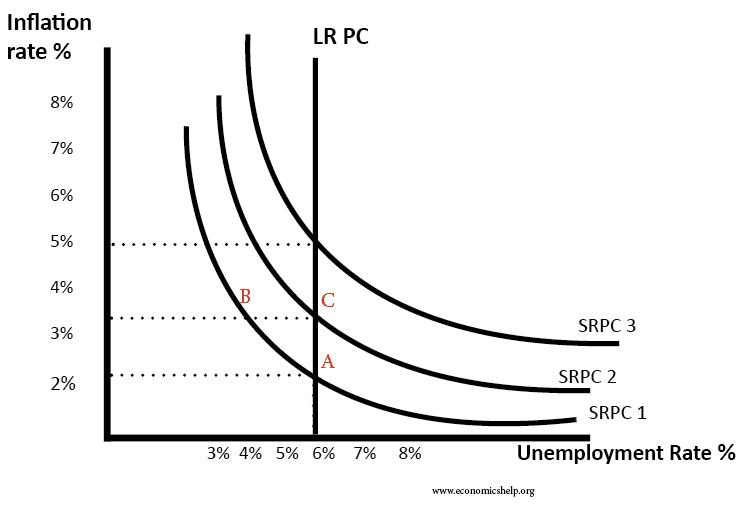
Phillips curve: graph which represents the rate of unemployment and rate of change of money wages. Indicated that wages tend to rise faster when unemployment is low