Lesson 15: Acid-Base Stoichiometry
Neutralization Reactions
A neutralization reaction occurs between a strong acid and a strong base.
The two products are always water (formed by the H+ ion joining with the OH- ion) and an ionic compound. Sometimes the ionic compound is called a salt.
Neutralization Reactions
eg. Ba(OH)2(aq) + HCl(aq) 🡪 H2O(l) + BaCl2(aq)
\n Now, balance the equation:
___ Ba(OH)2(aq) + ___ HCl(aq) 🡪 ___ H2O(l) + ___ BaCl2(aq) \n
Hint: To balance a neutralization reaction, first balance the # of H+ and OH- ions. They always have to be the same # to make water.
Ba(OH)2(aq) + 2HCl(aq) 🡪 2H2O(l) + BaCl2(aq)
Example: A student has spilled 100mL of 0.5 M aqueous potassium hydroxide, KOH. What volume of 2.0 mol/L sulfuric acid, H2SO4(aq) is required to neutralize the spill?
H2SO4(aq) + 2KOH(aq) 🡪 2H2O(l) + K2SO4(aq)
0.0125 L 0.100L
2.0 mol/L 0.50 mol/L
0.025 mol 0.05 mol
1 2
0.025 0.025
Titration problems
A 10 mL sample of NaOH of an unknown concentration is titrated with 0.245 M sulfuric acid. The results are summarized below. Fill in the chart below and use the reaction below to calculate the concentration of NaOH.
2NaOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) 🡪 Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
\n
| trial 1 | trial 2 | trial 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Final reading | 15.7 mL | 30.6 | 45.7 |
| Initial reading | 0.2 mL | 15.7 | 30.6 |
| vol of H2SO4 added | 15.5 mL | 14.9 | 15.1 |
Find the average of the 3 trials
(15.5 + 14.9 + 15.1)/3 = 15.17
Now do the neutralization stoichiometry
2NaOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) 🡪 Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
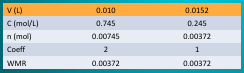 \n
\n
When 0.352M barium hydroxide was titrated with an unknown concentration of hydrochloric acid, it was found that it required an average of 14.5mL of barium hydroxide to neutralize 50 mL of the hydrochloric acid. What is the concentration of the hydrochloric acid?
Ba(OH)2(aq) + 2HCl(aq) 🡪 2H2O(l) + BaCl2(aq)
| V (L) | 0.0145 | 0.050 |
|---|---|---|
| C (mol/L) | 0.352 | 0.204 |
| n (mol) | 0.0051 | 0.0102 |
| coeff | 1 | 2 |
| WMR | 0.0051 | 0.0051 |
A 0.32g solid sample of magnesium hydroxide was titrated with 0.643M HCl. The sample was dissolved in water in an Erlenmeyer flask and titrated with HCl. It was found that it (on average) took 17.1mL of the HCl to neutralize the magnesium hydroxide. Use this data calculate the molar mass of magnesium hydroxide.
\n
Mg(OH)2(s) + 2HCl(aq) 🡪 2H2O(l) + MgCl2(aq)
| m (g) | 0.32 | 0.0171 | V (L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M (g/mol) | 58.18 | 0.643 | C (mol/L) |
| n (mol) | 0.00550 | 0.0110 | n (mol) |
| coeff | 1 | 2 | coeff |
| WMR | 0.0055 | 0.0055 | WMR |