Organization of the Organism (1.6-1.7)
Cell Structure and Organization
- %%All living organisms are made of cells%%
- %%Cell%%: The basic structural unit of life
- Although cells carry out different functions, animal and plant cells both have common features:
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondria
- Ribosomes
- Golgi Body
- Lysosomes
| %%Plant cell%% | %%Animal cell%% |
|---|---|
| Has a cell wall | No Cell wall |
| Chloroplasts is present | No chloroplasts |
| Vacuoles occupy most space | No vacuole |
| Starch as carbohydrate store | Glycogen as carbohydrate store |
| Autotrophic | Heterotrophic |
| No secretory vesicles | Secretory vesicles present |
| Regular shape | Irregular shape |
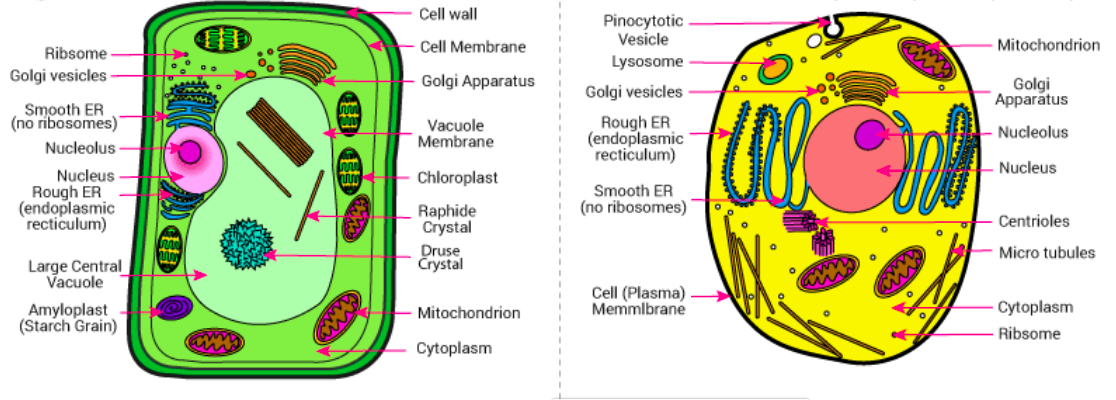
Functions of Cellular structures
Cell wall: makes up the outer most structure in the plant cell, is made of cellulose and is dead
- Fully permeable meaning that the cell wall allows substances in and out of the cell
- Gives the cell its shape and structure
Cell membrane: located in the inner cell wall of a plant cell and in the outermost structure in an animal cell
- Semi-permeable meaning that the cell membrane allows some/specific substances in and out of the cell
Cytoplasm: jelly like fluid inside the cell made of water and dissolves substances eg. glucose & salt
- Site of all metabolic (chemical) reactions
Nucleus: Contains genetic material of the cell in chromosomes which controls cell functions & the center of the cell
- Determines quality and quantity of proteins made by the cell
Chloroplasts: Site of photosynthesis and contains a green pigment (chlorophyll)
- Chlorophyl absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy by photosynthesis
@@6H2O + 6CO2 → C6H12O6 + O6@@
Mitochondria: Made up of a double membrane: inner and outer
- Inner has many folding to increase the surface area for enzyme reactions
- Site of aerobic respiration and release energy
- Nicknamed the “Powerhouse” of the cell
Rough of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Membranous outgrowth of outer nuclear membranes and has ribosomes attached to its surface
- Site of synthesis and transport of protein
Ribosome: The smallest cell of organelles present in the cytoplasm
- Either free or attached to rough ER
- Site of protein synthesis
Vacuole: While large and permanent, it is centrally located in a plant cell but is small and temporary in animal cells.
- Contains cell sap which is a solution of nutrients and salts
- Provides turgor pressure to the plant cell and helps maintain its shape
Vesicle: Sac like structures containing secretory substances eg. enzymes in the cytoplasm
Specialized Cells
- Large organisms are multicellular
- Different types of cells have particular structures to help them carry out specific functions, and so they become %%specialized%%
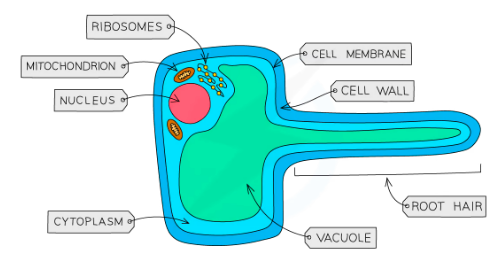
Root Hair Cells
Absorb nutrients from soil by osmosis, absorbs minerals by active uptake/transport, and fixes the plant in the soil
Adaptations:
- Have finger like outgrowth to @@increase the surface area for more absorption@@
- Have extended vacuole and cytoplasm for @@easier absorption@@
- Have more mitochondria to provide energy for @@active uptake/transport@@
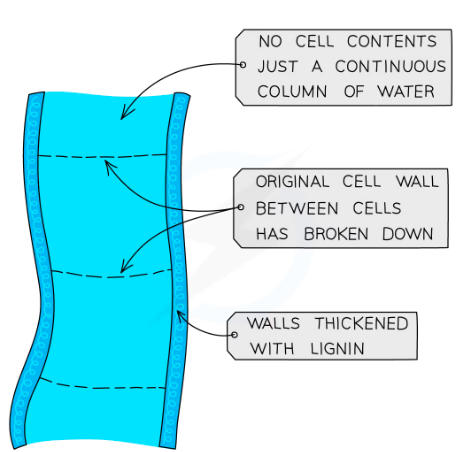
Xylem Vessels
They are found in vascular bundles, transporting water and minerals from the roots to the stem and leaves
Provide mechanical support to the stem and leaves
Adaptations:
Do not have a nucleus or cytoplasm to @@make space for bulk transport of water and minerals@@
Cells are dead and hollow and connected from end to end to @@form a long continuous tube@@
Cell wall is strengthened with lignin (hard substance) which @@gives mechanical support@@
Specialized Animal Cells
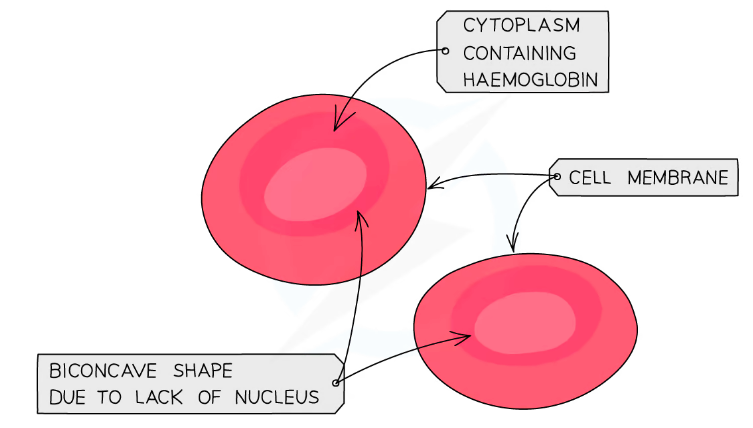
Red Blood Cells
Transport oxygen from lungs to the rest of the body as well as transport CO2 from the body to the lungs
Adaptations:
- Have red pigment (hemoglobin) which @@binds with oxygen to allow transport@@
- Don’t have a nucleus because of its biconcave shape, but their shape enables the cells’ increased surface area to @@carry more oxygen@@
- Are spongy/flexible to squeeze into capillaries
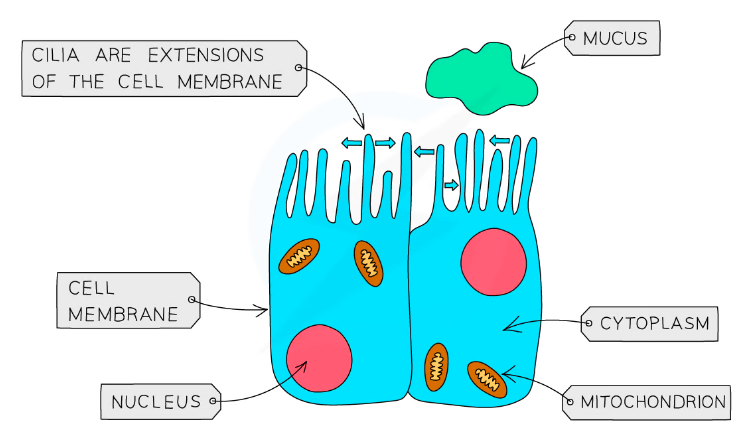
Ciliated Epithelial Cells
Goblet cells secrete mucus which @@trap the dust particles from the inhaled air@@
Cilia of the cells beat and push the trapped dust and air towards the throat (outside)
Muscle Cells
- Contracts and relaxes which brings about movement; structures can be brought closer
- Adaptations:
- Made of myofibrils which have the ability to contract and relax
- Have protein fiber which can @@shorten the cell when energy is present@@
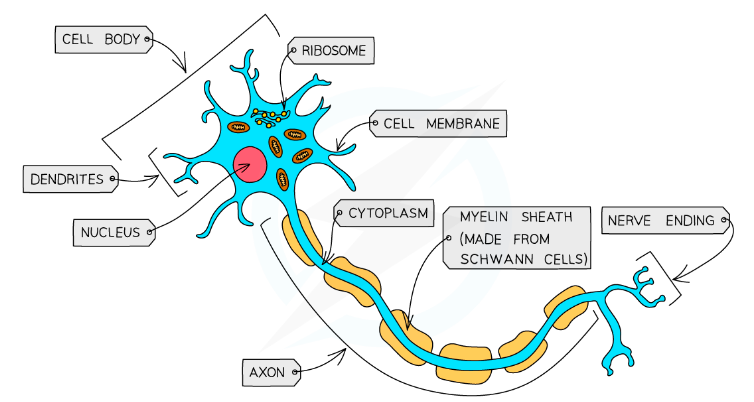
Nerve Cells
Sensory Nerve Cell: conducts message from sense organ to the central nervous system
Motor Nerve Cell: carries message from central nervous system to the effector
Adaptations
- Have extensions and branches so that it @@communicates with other nerve cells and glands@@
- The Axon (extension of the cytoplasm away from cell body to carry impulse long distances) is covered with fatty sheath which @@insulates the cell and speeds up the nerve impulse@@
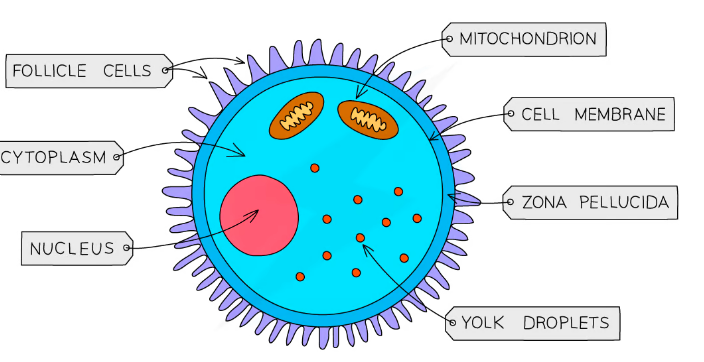
Egg Cells
Female Gamete: responsible for reproduction in females
Adaptations:
- A lot of cytoplasm that contains a lot of nutrients for the @@growth of the early embryo@@
- Haploid nucleus contains @@genetic material for fertilizations@@
- Cell membrane @@modifies after fertilization so that only one sperm cell can penetrate@@
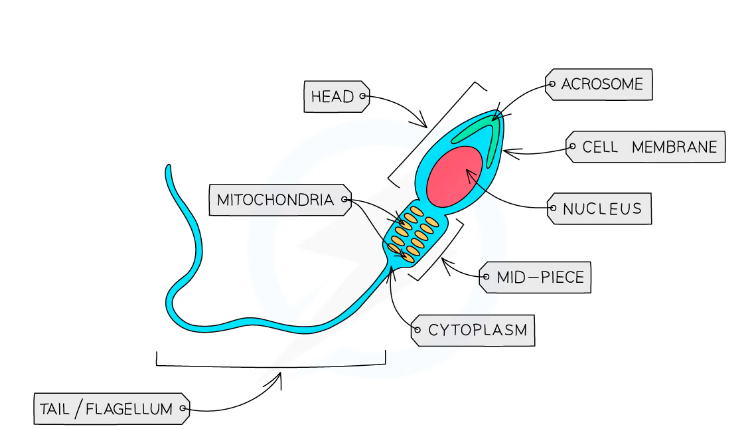
Sperm Cells
Male Gamete: responsible for reproduction in males
Adaptations:
- Head contains haploid nucleus
- @@Acrosome in head contains digestive enzymes to breakdown jelly coat around egg cell so sperm can penetrate egg cell@@
- Many mitochondria to provide energy so sperm can ==travel long distances==
- Flagellum allows sperm to travel
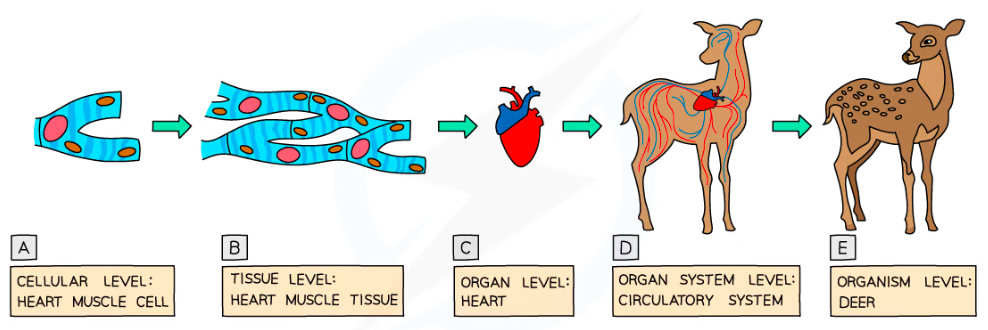
Levels of Organization
Cell: Basic structural and functional unit of life
Tissue: A group of identical cells which work together to perform a specific function
Organ: Many tissues which work together to perform a specific function
Organism: A group of organ systems which coordinate with each other to create an effective functioning of the body
%%Cell → Tissue→ Organ → Organ System → Organism%%
Size of Specimens
Size of a structure or an organism
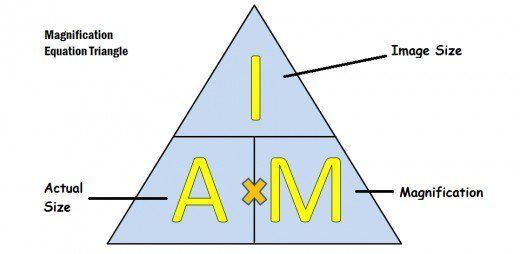
Magnification = Measured length / Actual length
- Magnification has no units so is represented as eg. x100
- The image size is usually given in centimeters (cm) or millimeters (mm) so make sure to @@convert both the actual size and image size units to be the same to get the correct magnification@@
- 1cm = 10mm
- 1mm = 1000μm (micrometer)