Kevin Kaleraj - STUDY GUIDE Honors - Semester 2 Final 24
Second Semester Biology Final Study Guide
Unit 7:Horticultural 2.0
What is the function of DNA?
Name and identify the three parts of the DNA nucleotide. (click on image to edit)

Explain how each of the four bases differ.
Fill out the boxes below and summarize the process of protein synthesis/gene expression in 3 words (often called the “central dogma”)
⇢ | ⇢ |
|---|
Fill out the Venn diagram for DNA/RNA that includes: components, where found, and how used. (click to edit image)
![]()
Write a 2-3 sentence summary of transcription that includes these terms: DNA, RNA polymerase, RNA, nucleus.
Write a 2-3 sentence summary of translation that includes these terms: cytoplasm, codon, ribosome, mRNA, tRNA, amino acid, and protein.
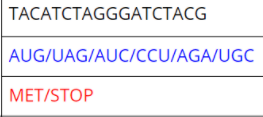
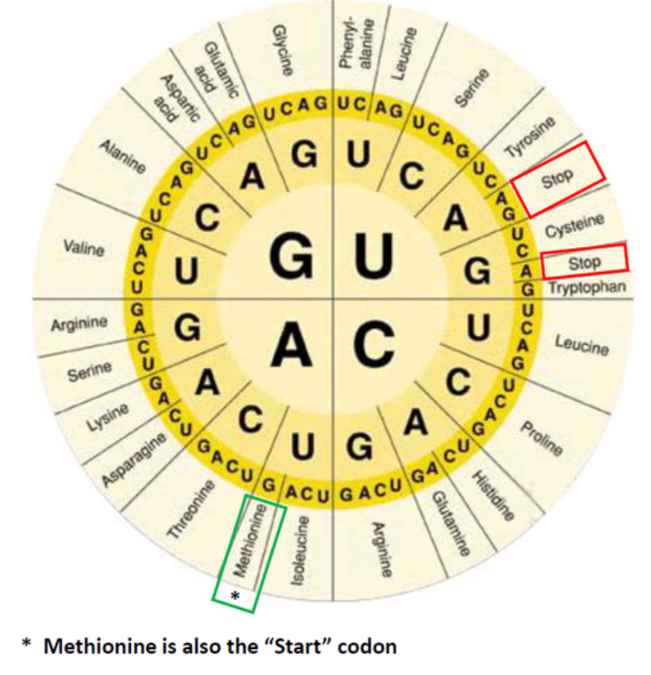
Transcribe a DNA template strand into mRNA and Translate mRNA into a sequence of Amino Acids using the Amino Acid Codon Chart
GATTACTTGTATGCCTTAATT
Unit 8: When Good Cells Go Bad
Describe what is happening to the DNA in various stages of the cell cycle.
Stage | Definition | What happens during this phase? |
|---|---|---|
Interphase | G1 S G2 | |
Prophase | ||
Metaphase | ||
Anaphase | ||
Telophase | ||
Cytokinesis |
Label each phase of cell cycle. (click on image to edit)
![]()
Give 3-4 reasons why cells divide.
What and when is the Go phase?
Define mutation.
Type of Mutation | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
Missense Substitution |
| |
Nonsense Substitution |
| |
Silent Substitution |
| |
Deletion Frameshift |
| |
Insertion Frameshift |
|
Explain how checkpoints are used in preventing cancerous behaviors in cells.
Unit 9: Stem Cells and Other tech
Not included on the final exam but that’s okay because you learned a lot.
Unit 10: Who Am I?
Be able to interpret a karyotype.
What is the relationship between homologous pairs of chromosomes and ploidy (haploid/diploid)?
How do the gametes formed during meiosis differ from body cells?
Give three elements of meiosis that increase genetic diversity.
Know the definition of the following terms:
Vocab Term | Definition | Visual/example |
|---|---|---|
Allele | ||
Trait | ||
Gene | ||
Genotype | ||
Phenotype | ||
Dominant | ||
Recessive | ||
Homozygous | ||
Heterozygous |
In pea plants, tall is dominant over short. Cross two heterozygous tall pea plants. T=tall t=short
Parental Cross: ________ x _________
What % of the offspring will be tall?
What % of the offspring will be short?
7. Dihybrid: Dobby the House Elf falls head over heels for Elf-ette name Dabbin. THey marry and decide to raise a family of little house elves. Dobby’s pointed ears are dominant(E), and knows that he is heterozygous for ear shape. Dabbin’s ears are round. Dobby’s long nose is a recessive trait (n), and Dabbin is homozygous dominant for her stubby nose.
What is the genotype of Dobby?
What are Dobby’s gametes?
What is the genotype of Dabbin?
What are Dabbin’s gametes?
What are the chances they will have a child with a stubby nose and pointed ears?
8. Unibrows are caused by a recessive allele. In order to have a unibrow a person must have the homozygous recessive genotype. The individuals shaded in the pedigree below have unibrow. Unshaded individuals may be homozygous normal or carriers. B= two eyebrows b=unibrow Based on this information, what are the genotypes of all of the individuals? (click on the image to edit)
![]()
Unit 11: CSI
CSI Example | Type of inheritance |
|---|---|
Hair texture | |
Blood Type | |
Colorblind | |
Cystic Fibrosis |
Snapdragons are an example of incomplete dominance. Cross a red snapdragon with a heterozygous snapdragon. R=red W=white RW=pink
Parental Cross: ________ x _________
What percent will be pink?
What percent will be white?
What percent will be red?
A husband and wife have the blood genotypes AB and O.
Parental Cross: ________ x _________
What percent of their offspring will have type A blood?
What percent of their offspring will have type B blood?
What are the two inheritance types for the ABo gene?
Eye color is sex-linked (X-linked) in fruit flies. Red eye (XR)color is dominant over white eye (Xr) color. Cross a white-eyed male (XY) with a heterozygous red-eyed female (XX) fruit fly.
Parental Cross: ________ x _________
What percent of females will have white eyes?
What percent of males will have white eyes?
Unit 12: Just a Theory
How is natural selection a mechanism for evolution?
What are the differences between homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures?
Compare and contrast divergent and convergent evolution.
Compare these three types of selection: directional, disruptive, stabilizing
How is each of the following used as evidence for evolution?
-fossil record
-biochemistry
-comparative anatomy
-
Be prepared to write in the VIDA table format: Variation, Inheritance, Differential Survival and Reproduction, Adaptation