3.2 Life History Strategies
^^Life History:^^ series of events from birth through reproduction to death
Life history strategies are…
- shaped by microevolution
- operating through natural selection
- adapted for the specific environment
Life History Strategies Influence Growth Rate of a Population, Including
- age of first reproduction
- number of offspring
- amount of parental care given to offspring
- energy cost of reproduction
2 Patterns of Reproduction
r-Selection
Energy into reproduction not survival
poor competitors
^^Opportunists^^--take advantage of favorable conditions, changes in environment
when favorable conditions are gone, population may crash
populations go through irregular or unstable cycles
characteristics:
- small-bodied
- reproduce when young → many offspring → low survival
- little to no parental care
- Exponential growth
- unpredictable environments
- controlled by density- independent factors
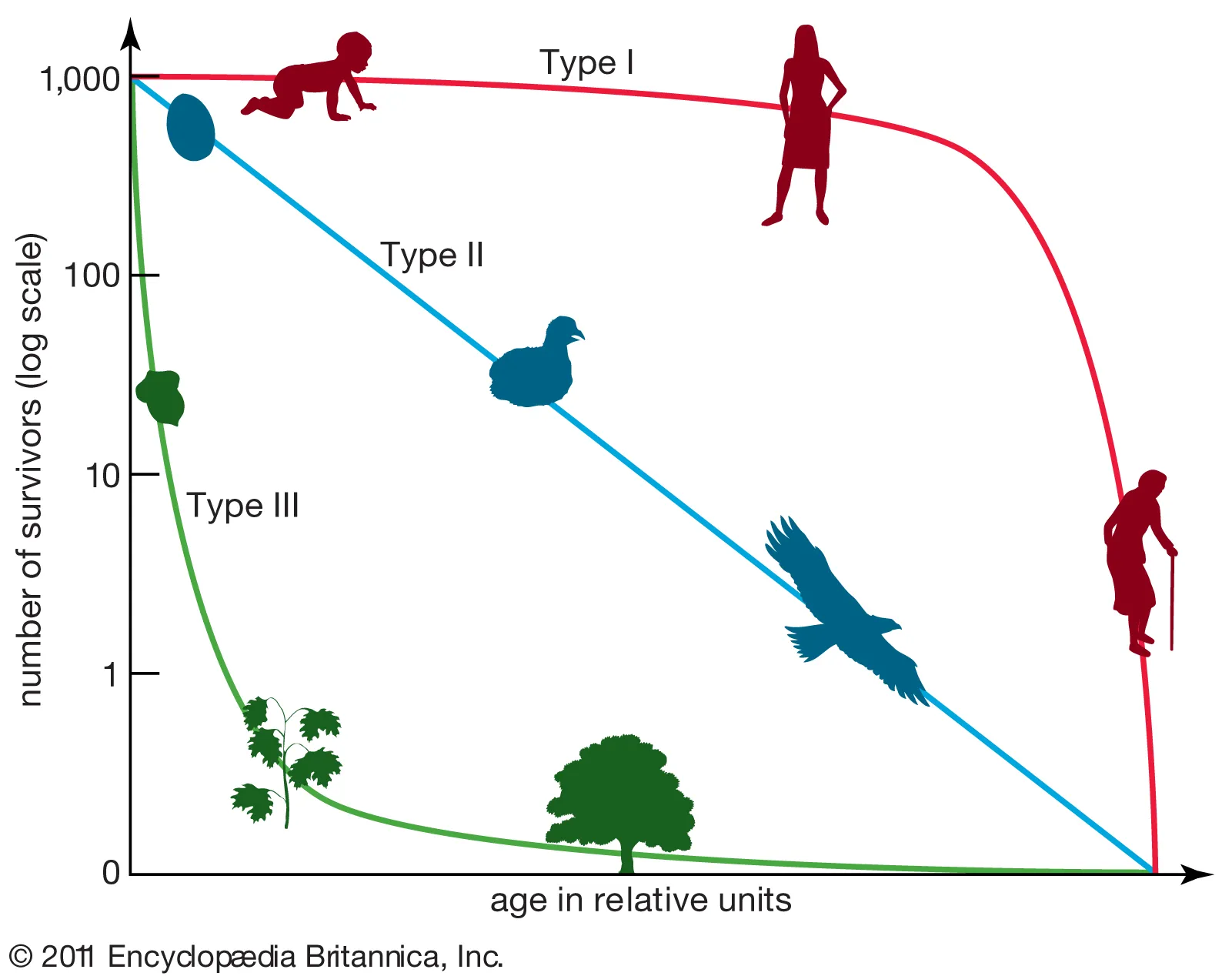
- exhibit type III survivorship curve
examples
- bacteria
- algae
- most annual plants
- dandelions
- most insects
- cockroaches
- rodents
- oysters
K-Selected
energy into long term survival
High parental care
good competitors
thrive best in ecosystems with fairly constant environmental conditions
populations remain close to carrying capacity (K) over long periods of time
characteristics
- larger-bodied
- Late reproduction→fewer offspring→most survive
- high parental care
- live in predictable environments
- controlled by density dependent factors
- exhibit type I survivorship curve
examples
- Humans
- Large trees
- Polar bears
- Elephants
- Most mammals/birds
Survivorship Curve