SOCIAL CHANGE IN CANADA
“To what extent did social change occur in Canada from 1919 to 1939?”
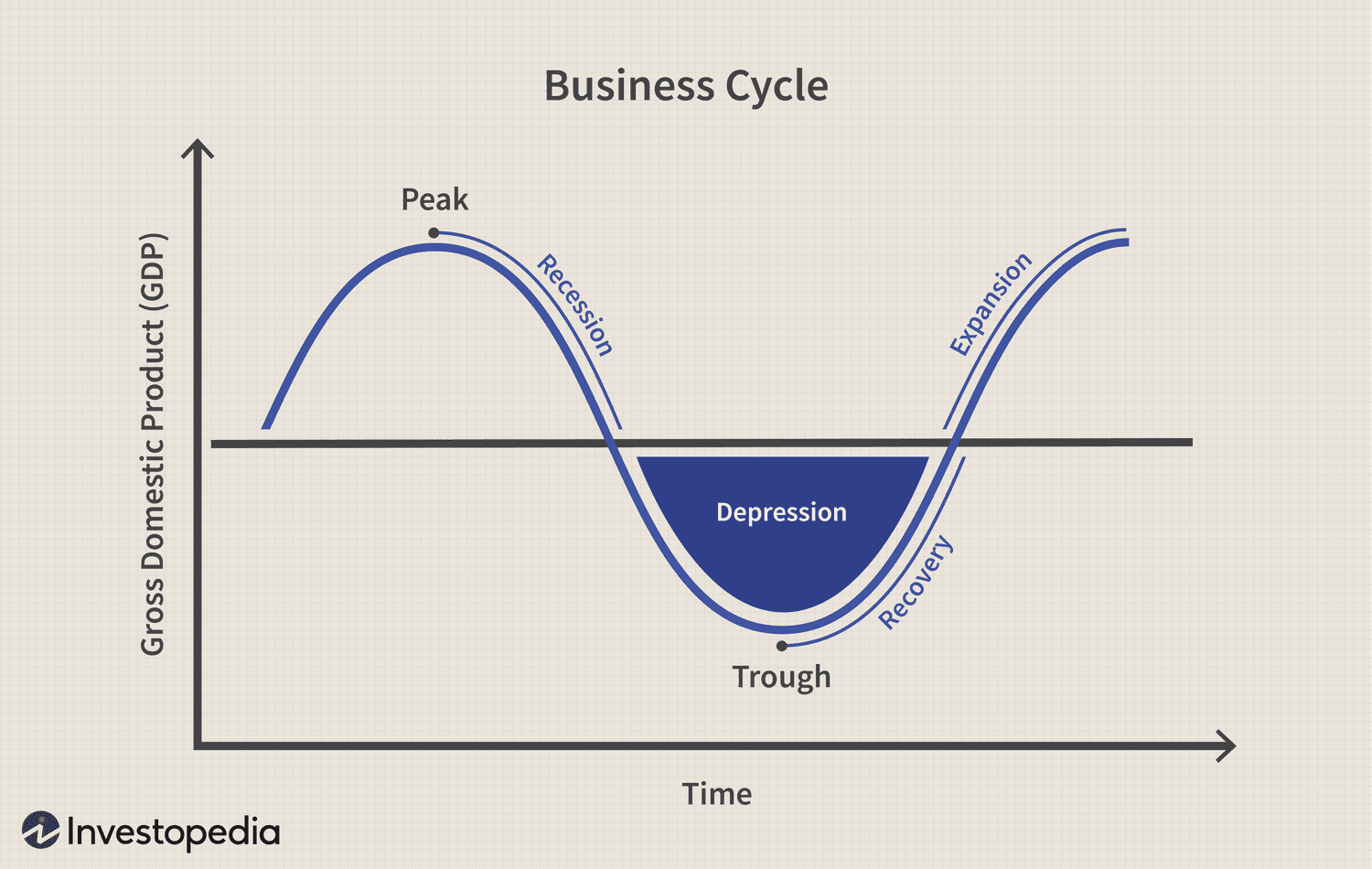
Stock Market Crash
Long Term Causes
- Stock market crash -> catalyst of ww2
- Canada’s stock market and America’s stock market linked
- If one fails the other will too
- Oct 24 black tuesday
- Overproduction and overexpansion
- CND’s dependence on a few primary products (staples)
- CND’s dependence on the USA
- If America stops buying our stocks then we fall
- High Tariffs Choked off International Trade
- Tax that countries put on products they sell
- Decreases trade
- Discourages people from buying goods
- Too Much Credit Buying
- You have to pay back the money you borrowed
- Too Much Credit Buying of Stocks
- If stocks went down there was no way to pay back the bank
Canada’s Primary Products (cannot be manufactured)
- Oil
- Fish
- Wheat
- Timber
Effect on Canada
- Any decline in foreign economy hurt canada’s economy
- Canada’s farmers had an excess of wheat causing prices to go down
- Stock market created for expansion of companies
Some Research Questions;
- What caused the Stock Market Crash?
- More people had a salary to spend
- More people were buying new products and making lots of money
- Since the economy was good, banks gave out lots of loans
- This made companies very rich
- No one knew what do to with this money
- They decided to invest in stocks
- There’s so much money to be made that people took loans to invest even more
- Even the banks decided to borrow customer money to buy stocks
- Stocks were rising so fast that companies were having a hard time keeping up
- Production was slowing down
- People weren’t buying as many things but instead investing in stocks
- What were the consequences of the Stock Market Crash?
- Wages started to fall
- There was increasing debt from loans that most people could not payback
- The stocks were still rising although the situation was bad
- October 24 1929: Black Thursday (the start of the Great Depression)
- When markets open they start to sell A LOT
- Selling so much that price keepers can’t keep up with the volume
- Markets lose 14 billion dollars in one day
- People have lost their life savings
- Others are workless, some shares are worthless
- People who borrowed to invest are drowning in debt
- Companies shut down so people lose their jobs
- Because of the money borrowed by the bank, most were lost in the market
- People were getting paid back 10 cents for every dollar
- Why did many lose their jobs due to the Stock Market Crash?
- When demands for goods fell, many firms went out of business
- Other firms had to cut costs so fewer were hired
- Factory owners were aware of over-production
- They slowed the workflow
- Laid off employees to avoid stockpile
Historical Significance;
- Relief programs for single men
- In 1932 Relief Act
- created 200 federal-funded relief camps for single men
- Relief Camps formed during the Great Depression
- single, unemployed young men were housed and fed in return for some work
- Located in isolated areas in Northern parts of Canada
- Paid 20 cents per day
- Limited medical attention
- Separated from family
- Lack of Heat and Running Water
- Requirements to receive aid from the government
- Prove that you are not able to support yourself and that no relative can help
- Be a man supporting a family
- Have been a resident of the municipality for at least one year before applying
- Turn in your liquor permit
- Turn in your automobile license plates and driver’s license
- Remove telephone from your house
- Register at the unemployment office (to show your willingness to work)
- Work on municipal projects from time to time
- Allow relief office investigators to come to your home to check on these rules
- Fall of wages & Winnipeg general strike
- Canada had to pay $164 million per year to pay off its debt.
- Introduction of income tax.
- Canada's total debt reached $1,665,576,000 because of the war.
- Inflation drove up the costs of food and almost everything else.
- “Bloody Saturday” (21 June, 1919)
- Workers gather downtown to protest and police are sent out to meet them
- Police attacked the protesters - one dies, others wounded
- Finally, strikers return to work
- The unions
- Unions are formed to fight for workers rights
- Unions have left-wing ideas
- communist Russian Revolution
- employers feared communism would spread to North America
- Strike is supposed to be peaceful
- Shut down almost all services in Winnipeg
- Fair pay = 85 cents per hour
- An 8 hour workday
- The right to bargain collectively (as a group) for better working conditions
- wages of 50 cents an hour for unskilled work,
- union wages for skilled,
- at least 120 hours of work a month,
- 36 hour workweek
- the provision of adequate first aid equipment in the camps,
- the extension of the Workmen's Compensation Act to include camp workers,
- recognition of democratically elected workers' committees,
- that workers in camps be granted the right to vote in elections,
- And the camps were removed from the purview of the Department of National Defence.
- the end of the blacklisting and of military control
- the establishment of a non-contributory unemployment insurance
- the repeal of Section 98 of the Criminal Code
- On to Ottawa trek
- early April 1935
- during the Great Depression
- strike and protest by Unemployment Relief Camp workers
- organized by the Workers' Unity League (WUL)
- led by WUL officer Arthur "Slim" Evans
- The League was affiliated with the international Communist movement
- The protest was motivated by concern for;
- improved conditions and benefits in the camps
- apparent reluctance of the federal government to provide work and wages programs
- Bennett offered NO assistance
- plan to travel to Ottawa to protest;
- the horrible work conditions
- the failure of the government to offer good jobs
- Regina riot
- workers are confronted by rcmp before they reach ottawa
- 120 Trekkers and citizens had been arrested.
- Charles Millar, a plainclothes policeman, died
- Nick Schaack, a Trekker, would later die in the hospital from injuries sustained in the riot
- All charges under Section 98 were dropped due to lack of evidence
- only eight were charged in relation to the riot
- strike ended with the trekkers returning to their homes or to their work camps
- no resolution to their grievances
- After the Trek, the Saskatchewan government provided free transportation as a peace sign back to the west
- Social Change
- Several demands of the Trekkers were eventually met
- Trek set the tone for the social and the public support
- behind welfare provisions of the postwar era
- Universal Health Care
- Unemployment Insurance
- A minimum wage
- A ban on child labour
SAMPLE ESSAY/ANALYSIS;
The Dirty Thirties were a time of significant change in Canada. The 1929 Stock Market Crash paved the path for the communist movement and the fair treatment of workers and citizens alike. To what extent did social change occur in Canada from 1919 to 1939? This short essay will look at the social change caused by the stock market crash due to increasing debt, falling wages, and the fight for workers’ rights. This directly relates to the historical concept of causation referenced in this essay. The loss of jobs due to the Stock Market Crash changed the social stability of Canada. \n
The economic instability in Canada caused many citizens to lose their jobs, resulting in the favouritism of married men over single men. The post-war was a time of economic prosperity for Canada. Many citizens had leftover money from their increasing salaries and so most decided to invest in stocks. However, production was slowing down, companies could not keep up with the rapidly rising stocks and many workers were laid off to avoid stockpiling. Inflation drove up the costs of food and almost everything else so many could no longer support themselves. Canada then fell into the Great Depression on October 24 of 1929. Requirements were to be met if you were to receive aid from the government such as being a man who has a family to support. For single, unemployed and young men, 200 federal-funded relief camps were created through the 1932 Relief Act. They were housed and fed in return for heavy work, but the living conditions were not ideal and eventually, a communist group named the Unions were formed to fight for workers rights. The Unions had left-wing ideas that were widely supported by the mass. However, due to the communist Russian revolution, employers feared communism would spread to North America and therefore refused to hire anyone a part of the Unions. Several protests took place as a sign of the fight for governmental and societal reform. On June 21 1919, “Bloody Saturday '', workers and members of the Union gathered downtown to protest for the right to bargain collectively as a group for better working conditions. In early April 1935, during the Great Depression, a protest and strike was organized by the WUL, led by Arthur “Slim” Evans. There was a concern for improved conditions and benefits in the camps and the reluctance of the government to provide work and wage programs to those in need. The workers are confronted by RCMP before they reach Ottawa and a blood bath ensued. The strike ended and the Trekkers went back home with no resolution to their grievances. \n
Social change occurred in Canada from 1919 to 1939 when citizens started protesting for their rights and safety under the law. The communist idea motivated workers to fight for fair treatment in the workforce post-war. Due to the mass amount of protesting, several demands were eventually met, such as universal health care, unemployment insurance, a minimum wage and a ban on child labour. The On-To Ottawa trek set the tone for the social and public support that was the motivation behind welfare provisions in the postwar era. Therefore, significant change occurred in the Dirty Thirties due to the loss of jobs and lack of insurance for workers’ rights caused by the 1929 stock market crash.
Critical Analysis:
Social change occurred in Canada from 1919 to 1939 when citizens started protesting for their rights and safety under the law. The communist idea motivated workers to fight for fair treatment in the workforce post-war. Due to the mass amount of protesting, several demands were eventually met, such as universal health care, unemployment insurance, a minimum wage and a ban on child labour. The On-To Ottawa trek set the tone for the social and public support that was the motivation behind welfare provisions in the postwar era. Therefore, significant change occurred in the Dirty Thirties due to the loss of jobs and lack of insurance for workers’ rights caused by the 1929 stock market crash.
TOTAL WAR SAMPLE ESSAY OUTLINE:
Hook: Propaganda succeeded in WWII by evoking emotion and demanding action.
Research Question: To what extent did propaganda aid in Canada’s WW2 effort? \n
Scope: Disney films/cartoons and propaganda posters.
Arguments:
A = Propaganda raised awareness for Canada’s war effort which persuaded the public to support total war. \n
B = The Canadian public was motivated into action through propaganda in support of Canada’s effort. \n
Historical Concept: Perspective because propaganda was used to villainize the enemy and provide a certain view to motivate, anger or upset the public into action.
Thesis: Propaganda greatly aided the WW2 effort in Canada. \n
Historical Context:
- By 1942, Canada was committed to a policy of “Total War”.
- All industries, materials and people were put to work for the war effort.
- Canada became an industrial power, new factories were built, and old ones adapted for war purposes.
- Factories churned out thousands of guns, ships, fighter planes and military vehicles.
- Fuhrer's face;
- film portrays events in Nazi Germany
- release came while the United States also was on total war footing
- Coffee, meat and food oils were rationed
- civilians were heavily employed in military production
- propaganda in support of the war effort (such as the film itself) was pervasive
- The film's criticism therefore emphasizes violence and terror under the Nazi government, as compared with the dull grind that all the warring nations faced
Facts:
Disney’s Propoganda
- Raise Public Moral
- Total War --Even Cartoons Characters Serve in Uniform
- Confront difficult topics
- Escape from Problems and Burdens of War
- Vilify Fascist Leaders
- Demonstrate Nazi Danger
- Fight for a common goal (victory)
Why did Disney make propaganda films?
- To raise public moral
- Total War -- even cartoon characters serve in uniform
- To confront difficult topics
- To escape from the problems and burdens of war
Goals of Der Fuehrer’s Face (a Disney Film);
- To vilify facist leaders
- To demonstrate the Nazi danger
- To fight for a common goal (victory)
Historical Context of Der Fuehrer's Face;
- released while the U.S was on total war
- coffee, meat & food oils rationed
- civilians heavily employed in military production
- propaganda in support of the war was persuasive
- film emphazised violence and terror under the Nazi government
- compares to dull grind of the allies
Total War Propaganda;
- Instill ideas of honour & duty
- Importance of training and victory
- Common wartime goals
- Humour
- Danger of the Nazi way of life
- Vilification of Enemy Nations
- Blatant racism
- Appeals to all audiences
- Message: hard work = victory
- Buy victory bonds
- Pay taxes on time
- Informs public of government goals
- Entertain public during a difficult time of struggle
Out of the Frying Pan into the Fire;
- In ww2, government urged americans on save excess fat
- fat rendered from cooking donated to the army
- made explosives (glycerin)
- idea was to engage women in the war effort
- could support the war from their kitchen
- handing over cooking fat to the government meant fulfilling your patriotic duty
- Disney's propaganda
The New Spirit 1942;
- almost every industry was tasked with supporting the war effort
- this was to stop axis powers from dominating
- cartoons went from entertaining children to educating adults
- produced to inspire income tax filings
- 60 million people (canadians & americans) saw the donald duck cartoon
- before 1943, only 8-16 million US people filed their income tax
- after release, 35 million people filed
- 80% increase by the end of the war
Stop That Tank;
- disney also created training videos
- hitler as the protagonist
- resourcefulness of the allies
- good vs evil
- defeatable enemy
- common goals of the allies
- hitler gained power through fear
- we must guard fear by using reason
- created to boost;
- patriotism
- moral
- public opinion
- propaganda used to talk about difficult topics
- danger of nazi actions
- nazi ideology
- humor
- cruelty of children
- cautionary tale
- realism vs fantasy