
Option D.3 Functions of the Liver
Why does it need it?
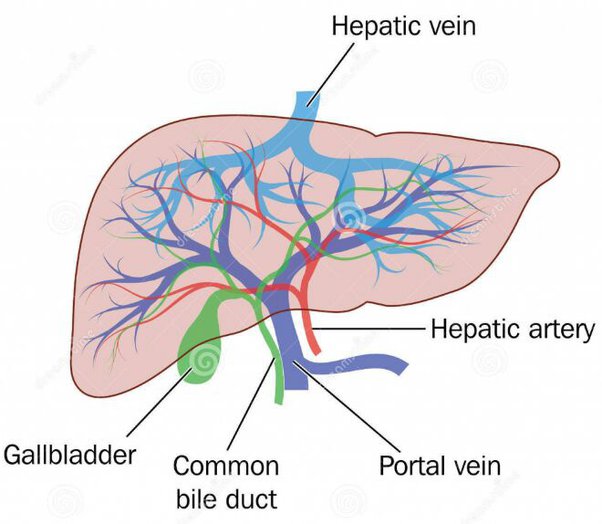
Because the liver removes wastes/toxins from the blood, there needs to be a rich blood supply running to it.
3 types of veins:
2 bring blood to the liver
Hepatic artery- comes form heart, carries oxigen rich blood.
Hepathic Portal Vein - brings nutrients rich blood from stomach/intestines, low in O2 (because it has already gone throgh other organs)
1 leves the liver
Hepathic Vein - return blood back to heart
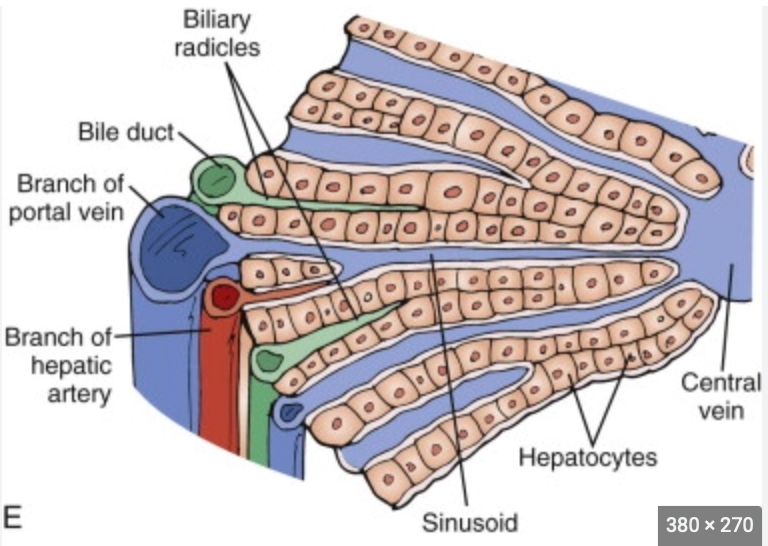
The liver’s tissue is divided into hexagonal structures called lobules.
the lobules have access to all parts of the liver’s blood supply/. To ensure the hepatocytes (liver cells) have enough contact with the blood supply, unique vessles called sinusoids are presents.
Sinusoids: Small blood vessels unique to liver circulation.
Porous blood vessels specialized for exchange of materials.
Contrast sinusoids and capillaries:
Sinusoids have a similar function to that of capillaries. They only differ in structure. Capillaries possess a continuous and complete basal membrane whilst the sinusoids possess only discontinuous incomplete basal membrane.
Pictures
Sugars - insulin tells hepatocutes to uptake glucose. Exess glucose will be stored as glycogen by the liver. If too little glucose enters the liver it will break down the glycogen and release sugar into the bloodstream
Proteins: Can’t be stored so it will be used as energy. Amonia (toxic) is produced as a byproduct of protein metabolism so it converts it into urea to be into urea to be excreted in our urine.
Proteins cannot be stored, so the liver uses them as an energy source and nitrogen waste products are made. (Urea Cycle)
Liver can help to synthesize some non-essential amino acids. (metabolism)
Lipids - it synthesizes phospholipids and cholesterol for storage or for storage or for export to cells to build members, make steroids, and make Vitamin D. Exess cholesterol can made into bile salts used for digestion and excreted with feces.
Regulates the fats circulating in the bloodstream
Synthesizes phospholipids and cholesterol for storage by the liver or exported to cells (cell membranes and building steroids)
Vitamins A and D can be stored by the liver and released into the body when needed.
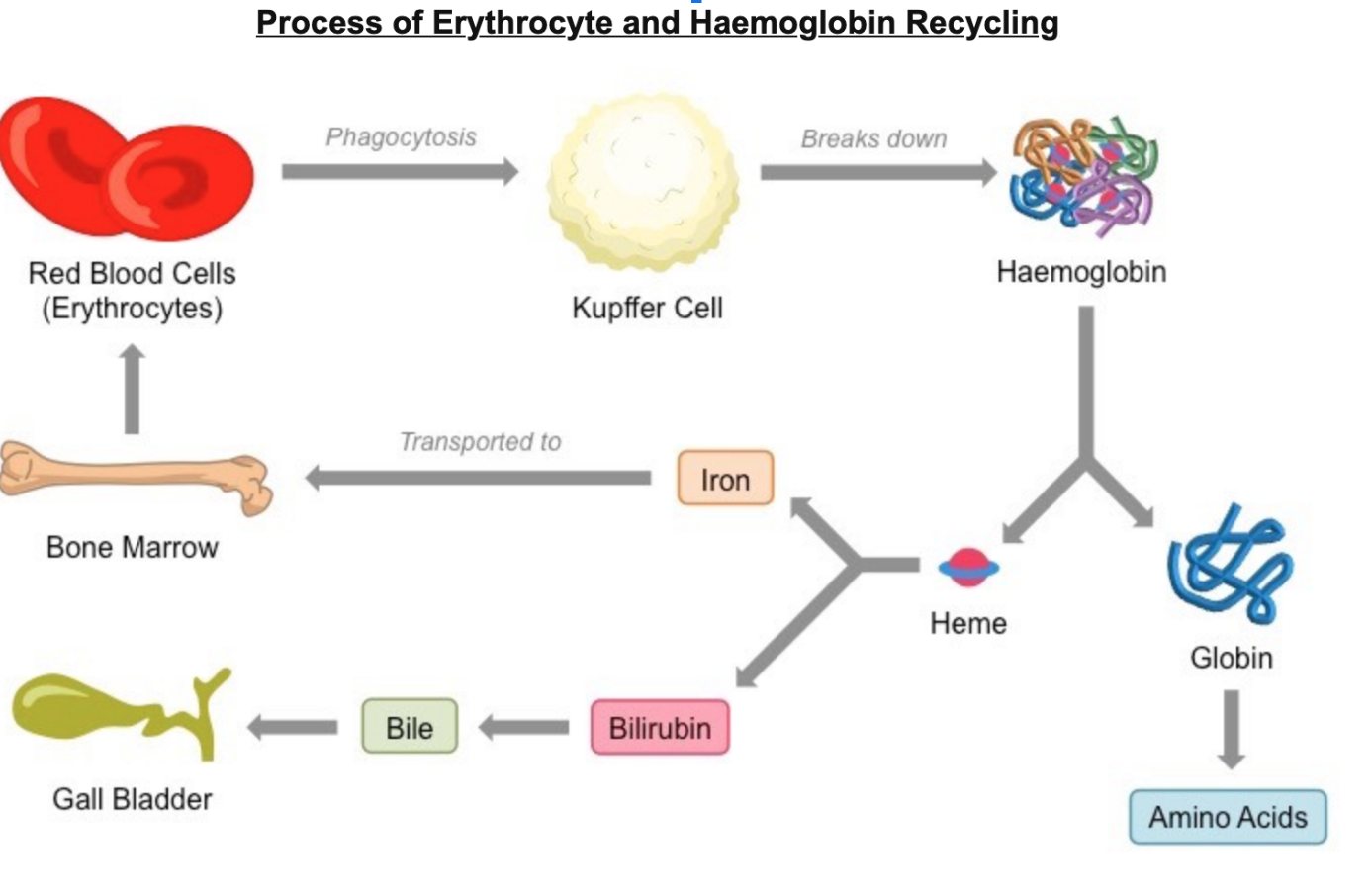
Liver and Spleen RECYCLE old red blood cells
Kupffer Cells - cells that recognizeRed blood cells as damaged after they become swollen and engulf them via phagocytosis and destroy them.
What happens to the iron form the Hymoglobin during RBC recycling process?
Hemoglobin is broken down into amino acids (globin), and heme. The heme group is broken down into iron and bilirubin then the iron will be transferred to bone marrow for new red blood cell production.
Bilirubin - a product of RBC breakdown that becomes part of the bile & excreted out of the body
If the liver isn’t functioning properly, high levels of bilirubin can build up in the blood causing jaundice due to its yellowish pigment.
Higher than usual levels of bilirubin may indicate different types of liver or bile duct problems. Sometimes, higher bilirubin levels may be caused by an increased rate of destruction of red blood cells.
Jaundice is a condition where the %%skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow due to high amounts of bilirubin. %%
This coloration is an indication of serious disease related to the liver in adults:
Hepatitis
Liver Cancer
Liver failure, etc.
Some babies initially have Jaundice and need to lay under a special UV light/ blanket that helps to break down the bilirubin.
Neonatal jaundice is caused by the liver being not fully developed and able to process the large amounts of bilirubin.
If jaundice is left untreated, neurologic damage can result in newborns.
Detoxification - the liver removes toxins form blood & processes them into non-toxic or less-toxic substances that your body excretes.
Examples of those toxins:
amonia (nitrogenous waste)
products of metabolism
breakdown of pathogens
medications
alcohol
What structural elements of a liver cell help it do its specialized function?
extensive rough ER
The liver makes many plasma (blood) proteins. Name 2 common examples.
Albumin (carries vitamins, hormones etc..)
Fibrogen (for blood clotting)
Why does it need it?
Because the liver removes wastes/toxins from the blood, there needs to be a rich blood supply running to it.
3 types of veins:
2 bring blood to the liver
Hepatic artery- comes form heart, carries oxigen rich blood.
Hepathic Portal Vein - brings nutrients rich blood from stomach/intestines, low in O2 (because it has already gone throgh other organs)
1 leves the liver
Hepathic Vein - return blood back to heart
The liver’s tissue is divided into hexagonal structures called lobules.
the lobules have access to all parts of the liver’s blood supply/. To ensure the hepatocytes (liver cells) have enough contact with the blood supply, unique vessles called sinusoids are presents.
Sinusoids: Small blood vessels unique to liver circulation.
Porous blood vessels specialized for exchange of materials.
Contrast sinusoids and capillaries:
Sinusoids have a similar function to that of capillaries. They only differ in structure. Capillaries possess a continuous and complete basal membrane whilst the sinusoids possess only discontinuous incomplete basal membrane.
Pictures


Sugars - insulin tells hepatocutes to uptake glucose. Exess glucose will be stored as glycogen by the liver. If too little glucose enters the liver it will break down the glycogen and release sugar into the bloodstream
Proteins: Can’t be stored so it will be used as energy. Amonia (toxic) is produced as a byproduct of protein metabolism so it converts it into urea to be into urea to be excreted in our urine.
Proteins cannot be stored, so the liver uses them as an energy source and nitrogen waste products are made. (Urea Cycle)
Liver can help to synthesize some non-essential amino acids. (metabolism)
Lipids - it synthesizes phospholipids and cholesterol for storage or for storage or for export to cells to build members, make steroids, and make Vitamin D. Exess cholesterol can made into bile salts used for digestion and excreted with feces.
Regulates the fats circulating in the bloodstream
Synthesizes phospholipids and cholesterol for storage by the liver or exported to cells (cell membranes and building steroids)
Vitamins A and D can be stored by the liver and released into the body when needed.
Liver and Spleen RECYCLE old red blood cells
Kupffer Cells - cells that recognizeRed blood cells as damaged after they become swollen and engulf them via phagocytosis and destroy them.
What happens to the iron form the Hymoglobin during RBC recycling process?
Hemoglobin is broken down into amino acids (globin), and heme. The heme group is broken down into iron and bilirubin then the iron will be transferred to bone marrow for new red blood cell production.
Bilirubin - a product of RBC breakdown that becomes part of the bile & excreted out of the body
If the liver isn’t functioning properly, high levels of bilirubin can build up in the blood causing jaundice due to its yellowish pigment.
Higher than usual levels of bilirubin may indicate different types of liver or bile duct problems. Sometimes, higher bilirubin levels may be caused by an increased rate of destruction of red blood cells.
Jaundice is a condition where the %%skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow due to high amounts of bilirubin. %%
This coloration is an indication of serious disease related to the liver in adults:
Hepatitis
Liver Cancer
Liver failure, etc.
Some babies initially have Jaundice and need to lay under a special UV light/ blanket that helps to break down the bilirubin.
Neonatal jaundice is caused by the liver being not fully developed and able to process the large amounts of bilirubin.
If jaundice is left untreated, neurologic damage can result in newborns.

Detoxification - the liver removes toxins form blood & processes them into non-toxic or less-toxic substances that your body excretes.
Examples of those toxins:
amonia (nitrogenous waste)
products of metabolism
breakdown of pathogens
medications
alcohol
What structural elements of a liver cell help it do its specialized function?
extensive rough ER
The liver makes many plasma (blood) proteins. Name 2 common examples.
Albumin (carries vitamins, hormones etc..)
Fibrogen (for blood clotting)