ess 4.3
==4.3.1==
food products from aquatic ecosystems
algae consumption
- green algae
- brown algae
- red algae
fish - most popular aquatic food
- the global fish consumption/production rate continues to increase
- used for human consumption
- animal/pet feed
- fertelizers
- gelatin
- why is fish demand so high?
- human pop. growth
- health benefits
- growth in income, people can afford fish
shellfish:
- molluuscs:
- invertebret
- ex:
- gastropods
- sea snails
- bivalves
- clams
- oyster
- scallops
- Cephalopods
- octopus
- squid
other animals:
- Crustacean: have exoskeleton:
- ex:
- lobsters
- shrimp
- Echinoderms
- invertebret w/ symmetry
- ex: strafish
- reptiles
- Amphibians
- aquatic mammals
seal hunting
- used by natives
- used for meat, clothes, fur
- threatened habitats
- Canada has attempted to regulate seal hunting:
- setting limits to number of hunted seals
4.3.2
capture fisheries
- fishery growth driven by:
- human pop & increased demand for fish
- technological developments
nets:
- oftentimes nets will capture animals that are not meant to be in
- trawler nets: used to catch fish by dragging a net along a seabed
- purse siene nets: used to catch schools of a species, the fish are surrounded by the net, which is then closed like a draw string purse to trap the fish.
- drift nets: hung vertically in the water, used to get sardines, swordfish, tuna
fish yeild
- fish stocks are only renewable if removal rate doesnt exceed growth rate
overfishing - why its common
- property rights - no one owns fish
- zero sum gain
4.3.3
reduction in fishing
- reducing boat size
- restricting gear
- reducing number of boats
- restricting fishing times
- marine protected areas
cod fisheries- case studies
- newfoundland
- technology allows for more fishing
- they overfished, resulting in tons of job loss
- iceland
- gov’t took action to prevent overfishing
- protecting territorial waters
- restrictions
- exclusion zones
4.3.3
- aquaculture: farming of aquatic organisms
- Open based systems:
- farm organisms in thier natural ecosystem
- semi closed systems:
- take water from ecosystem and bring them into tanks on land
- enviornment impacts:
- habitat loss
- increase in organic sediments
- increase in avaliable nutrients
- use of medicine/hormones
- disease
- managing env. impact of fish farms:
- removal of dead fish
- reducing waste of uneaten feed
- aerate water
sustainable yield
natural income
can measure in biomass or number of individuals
SY= (births + immigration) - (deaths & emigration)
yield: total growth from year to year
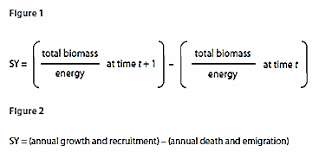
bycatch: marine creatures lost/killed due to fishing practices
- dolphins
- turtles
- sharks
whaling
- innuit culture:
- part of thier culture
- northern canada
- a hunting culture
- not for profit
- used every part of the whale
- “connection w/ enviornment”
- acceptance by canadian people'
- japan culture:
- commerical
- cultural - traditional
- not using whole animal
- meat sold illegally
- left IWC