OpenCV Module 8: Image Features and Image Alignment
Image Alignment:
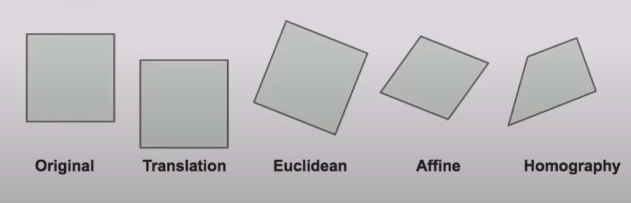
A Homography transforms a square to arbitrary quad.
Theory:
Images of two planes are related by a Homography
We need 4 corresponding points to estimate Homography

Step 1: Read Template and Scanned Image
#Read reference image
refFilename = "form.jpg"
print("Reading reference image: ", refFilename)
im1 = cv2.imread(refFilename, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
im1 = cv2.cvtColor(im1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
#Read image to be aligned
imFilename = "scanned-form.jpg"
print("Reading image to align: ", imFilename)
im2 = cv2.imread(imFilename, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
im2 = cv2.cvtColor(im2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)» Reading reference image: form.jpg
» Reading image to align: scanned-form.jpg
#Display images
plt.figure(figsize=[20,10])
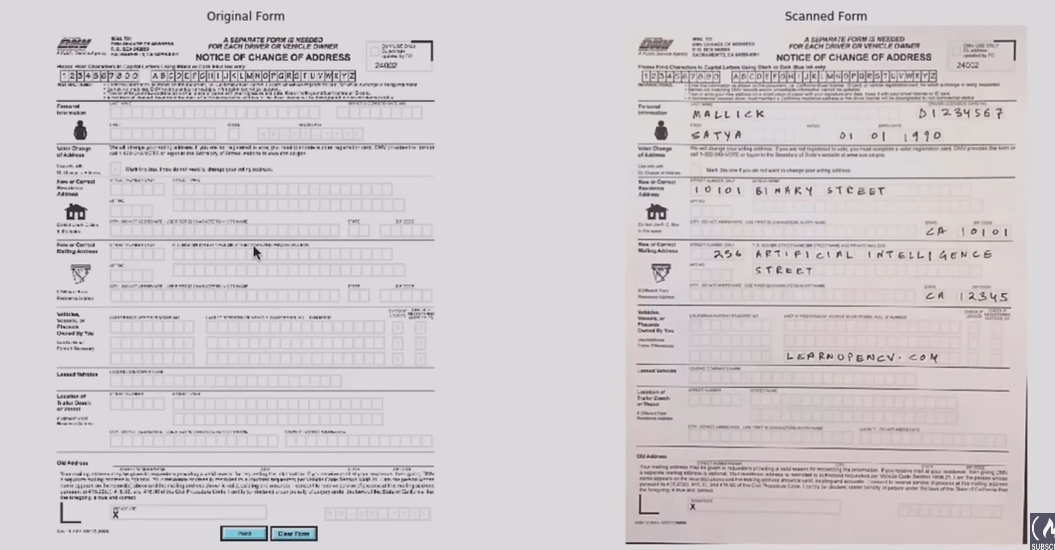
plt.subplot(121);plt.axis('off');plt.imshow(im1); plt.title("Original Form")
plt.subplot(122);plt.axis('off');plt.imshow(im2); plt.title("Scanned Form")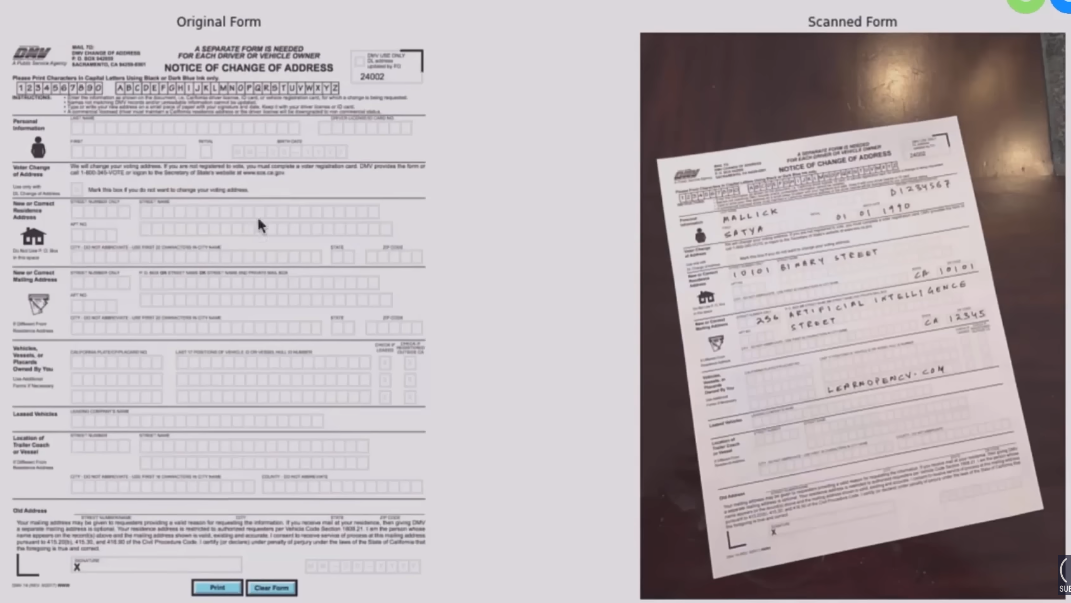
Step 2: Find keypoints in both images
#Convert images to grayscale
im1_gray = cv2.cvtColor(im1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
im2_gray = cv2.cvtColor(im2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#Detect ORB features and compute descriptors.
MAX_NUM_FEATURES = 500
orb = cv2.ORB_create(MAX_NUM_FEATURES)
keypoints1, descriptors1 = orb.detectAndCompute(im1_gray, None)
keypoints2, descriptors2 = orb.detectAndCompute(im2_gray, None)
#Display
im1_display = cv2.drawKeypoints(im1, keypoints1, outImage=np.array([]), color=(255,0,0), flags=cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DEFAULT)
im2_display = cv2.drawKeypoints(im2, keypoints2, outImage=np.array([]), color=(255,0,0), flags=cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DEFAULT)
plt.figure(figsize=[20,10])
plt.subplot(121);plt.axis('off');plt.imshow(im1_display); plt.title("Original Form")
plt.subplot(122);plt.axis('off');plt.imshow(im2_display); plt.title("Scanned Form")
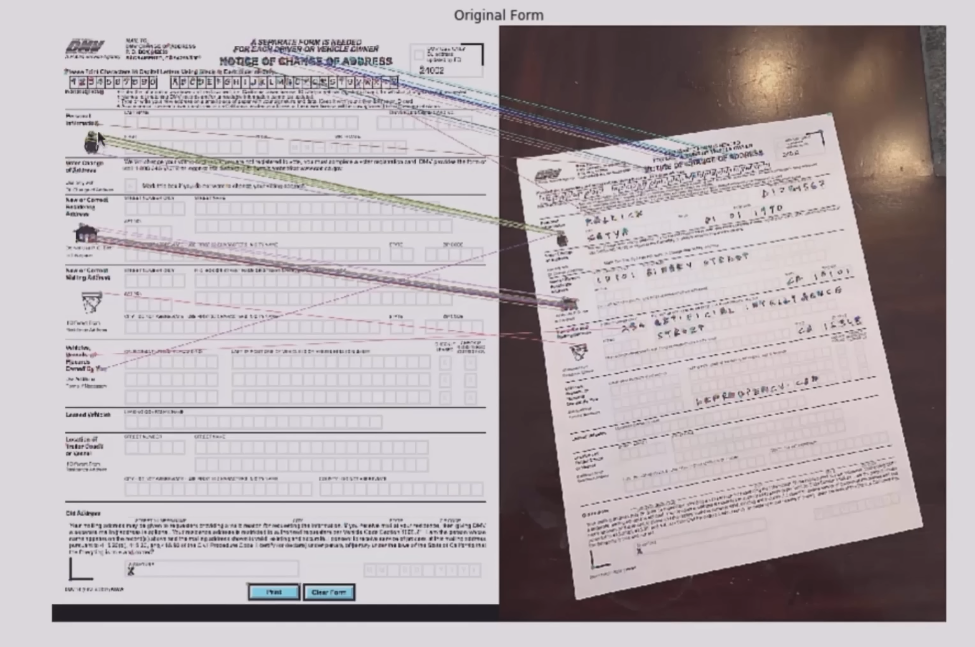
Step 3: Match keypoints in the two images
#Match features
matcher = cv2.DescriptorMatcher_create(cv2.DESCRIPTOR_MATCHER_BRUTEFORCE_HAMMING)
matches = matcher.match(descriptors1, descriptors2, None)
#Sort matches by score
matches.sort(key=lambda x: x.distance, reverse=False)
#Remove not so good matches
numGoodMatches = int(len(matches) * 0.1)
matches = matches[:numGoodMatches]
#Draw top matches
im_matches = cv2.drawMatches(im1, keypoints, im2, keypoints2, matches, None)
plt.figure(figsize=[40,10])
plt.imshow(im_matches);plt.axis('off');plt.title("Original form");
Step 4: Find Homography
#Extract location of good matches
points1 = np.zeros((len(matches), 2), dtype=np.float32)
points2 = np.zeros((len(matches), 2), dtype=np.float32)
for i, match in enumerate(matches):
points1[i,:] = keypoints[match.queryIdx].pt
points2[i,:] = keypoints[match.queryIdx].pt
#Find Homography
h, mask = cv2.findHomography(points2, points1, cv2.RANSAC)Step 5: Warp Image
#Use homography to warp images
height, width, channels, im1.shape
im2_reg = cv2.warpPerspective(im2, h, (width, height))
#Display results
plt.figure(figsize=[20,10]);
plt.subplot(121);plt.imshow(im1);plt.axis('off');plt.title("Original Form");
plt.subplot(122);plt.imshow(im2_reg);plt.axis('off');plt.title("Scanned Form");