Science 9- Unit 3
Nutrients needed by humans
Humans need about 24 elements to survive
About 99% of those elements is made up of oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium, and phosphorus. The other 1% is made up of potassium, sulfur, sodium, chorine, and magnesium. The rest is made up of things we eat called micronutrients.
Nutrient- a chemical substance in every living thing on earth
Macro mineral- any mineral required in a diet
Trace element- an amount of a mineral left behind
Enzyme- A biological catalyst that is almost always a protein
Carbohydrates, Lipids, and proteins
Carbohydrates are our immediate source to energy. In plants, they are a component of the cell wall. They are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. (Sucrose)
Lipids are fatty compounds that provide many functions, such as regulate hormones, cushion organs, and store energy (triglyceride)
Proteins are found in meats and dairy, and they are made by connecting amino acids. Proteins provide many functions such as making skin and nails and speeding up chemical reactions.
Vitamins
Vitamins are a group of substances that are needed for cell fiction, growth, and development.
Humans need 13 different vitamins, 9 of which are soluble in water ( to be dissolved) and 4 are fat soluble
Uptake of nutrients by humans
The digestive system breaks down all the food we eat into nutrients such as sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids.
The liver, gallbladder, and pancreas, all supply enzymes that help the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, breakdown food
Food is physically broke down when our stomach churns. Food is also broke down by saliva, and by enzymes in the small intestine and stomach
After the food is broken down, the nutrients are spread around the body through your bloodstream
Uptake in nutrients by plants
Plants absorb elements in the soil and distribute them throughout themselves. They then use these elements to create the nutrients that they need!
Diffusion- the movement of a chemical from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Osmosis- the movement of water from a low nutrient concentration to a high nutrient concentration
Plants do photosynthesis to survive ( Co2+ Water + Sunlight= Glucose + o2)
Pesticides
Pesticides are a chemical used to control pests
Pests are killed by insecticides (chemical used to control insects), fungicides (a chemical used to control molds and fungi), and herbicides (a chemical used to control weeds)
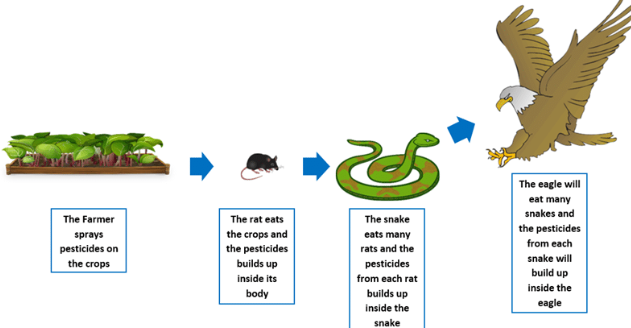
Biomagnification is a process where chemicals accumulate in the tissues of an organism along a food chain
Biological magnification- Increase in the contaminated substance
DDT was an insecticide that was not at all noticeable.
Acids and Bases
Acids are chemicals that produce an acidic substance having a ph value less than 7. These chemicals are acidic
Bases are chemicals that produce a basic having a ph value of more than 7. These chemicals are basic
PH strips are pieces of paper that change color and indicate an approximate ph
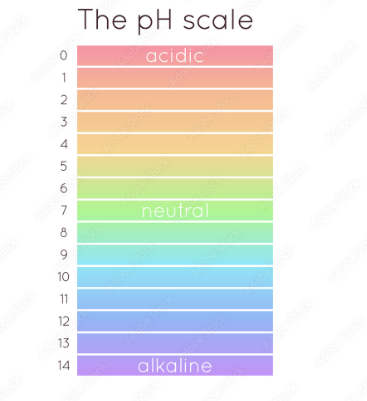
PH indicators are chemicals that change from one color to another when the ph changes
Acids usually taste sour ( because they react with carbonates and metals) and Bases usually taste bitter and are slippery
Acids and Basics react in a neutralization reaction. This produces a salt and water
Acid precipitation- rain or snow containing acid compounds from the air
Litmus- mixture of plant compounds used as a chemical indicator
Oxidation- a chemical reaction in which oxygen combines with other elements to form new substances
Leach- Dissolves in the water and the water seeps downwards
Liming- Process of adding calcium carbonate to the environment
Biological measures + Chemical measures
Biological measures are drawn from bodily activities of humans or from biological systems in nature.
Dissolved oxygen is needed by aquatic animals just as it is needed by humans
Heavy metals are a metal at a high density
Catalyst- a substance that speeds up chemical reaction
Catalytive converter- a device that encourages complete oxidation during combustion
Scrubber- a device that uses a sorbent to reduce oxide emission
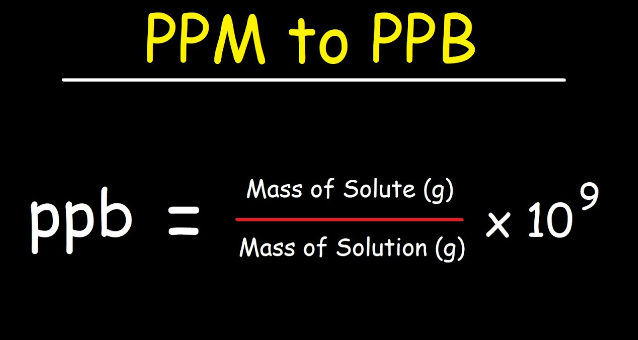
if its ppt them x by 10 to the power of 12. if its ppm them x 10 to the power of 6