Amino Acids and Proteins (copy)
Amino Acids
Amino Acid Overview and Types
Overview
Proteins are linear heteropolymers of alpha-amino acids
Amino acids share many features, differing only at the R substituent (group)
the alpha carbon is chiral when the R group is anything other than hydrogen (so anything other than glycine)
all chiral amino acids are optically active
Because of tetrahedral arrangement of bonding orbitals around the alpha-carbon, the four different groups can occupy two unique spatial arrangements and thus have 2 possible stereoisomers: L and D
L and D versions of an amino acids are enantiomers
nonsuperimposable mirror images
only L-amino acids are found in proteins
Amino acids are classified based on their R groups (charge, H-bonding ability, and if they’re acid/basic)
Two main categories: Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic
Hydrophobic amino acids are non-polar (includes AA’s with alkyl/aliphatic and with aromatic R groups)
Hydrophilic amino acids are polar, includes neutral, acidic, and basic R-groups
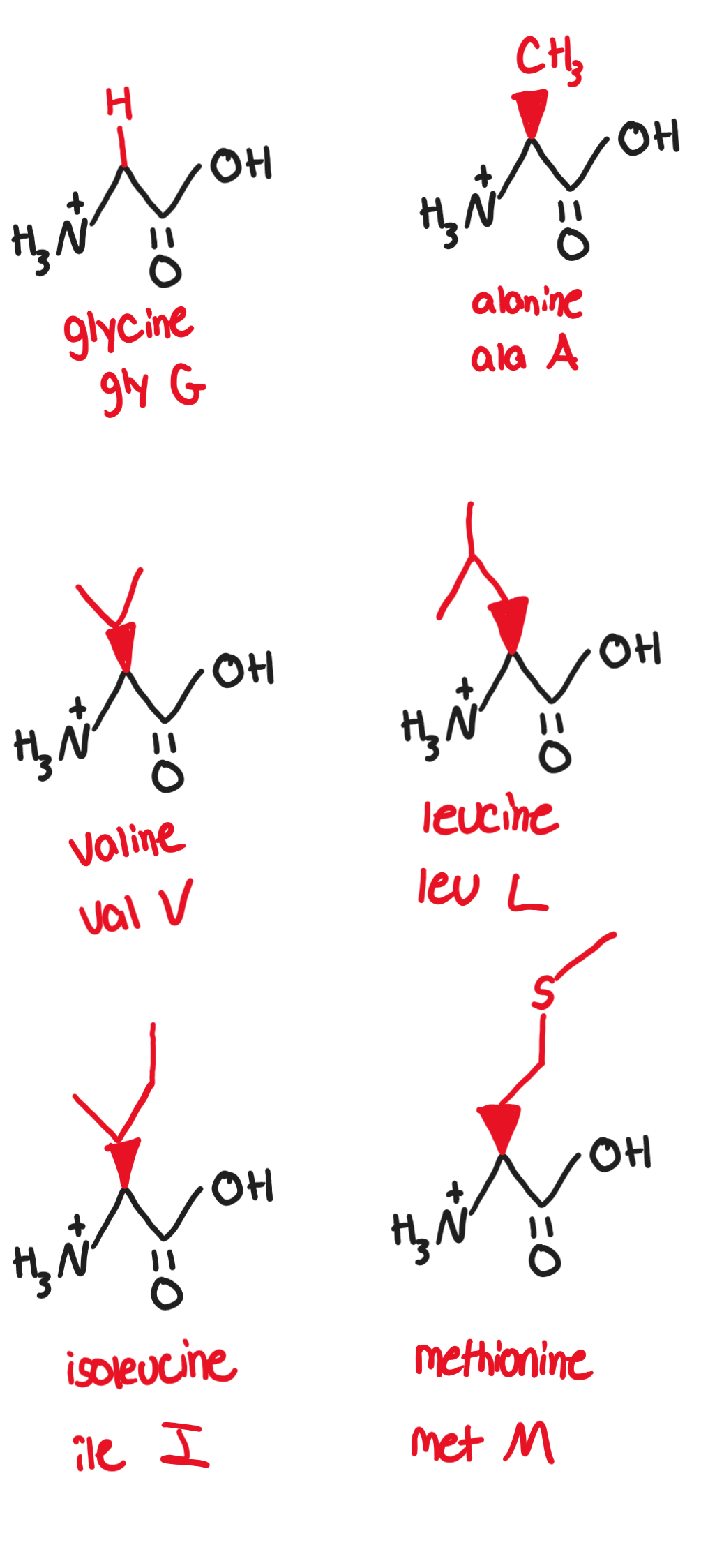
Hydrophobic, nonpolar, aliphatic/alkyl R groups:
Non-polar side chains consist mostly of hydrocarbons
any functional groups are uncharged at biological pH
Glycine, Gly, G (-H)
only achiral amino acid, has a slightly sweet taste
Alanine, Ala, A (-CH3)
canonical example of a simple. small, nonpolar amino acid
Proline, Pro, P (R-group is a ring, bonds with amino group twice)
can break up secondary structures due to the kink proline can cause
can be found within the turns of beta-pleated sheets
Valine, Val, V (-CH(CH3)2)
it substitution for glutamic acid in hemoglobin causes sickle-cell disease
contains isopropyl group
Leucine, Leu, L (-CH2CH(CH3)2)
essential amino acid (animals and humans cannot synthesize it ourselves so it must be obtained from diet)
Isoleucine, Ile, I (-CH(CH3)CH2CH3)
essential amino acid
Methionine, Met, M (-CH2CH2SCH3)
C-S bond makes molecule nonpolar, involved in DNA methylation and angiogenesis
essential amino acid found especially in eggs
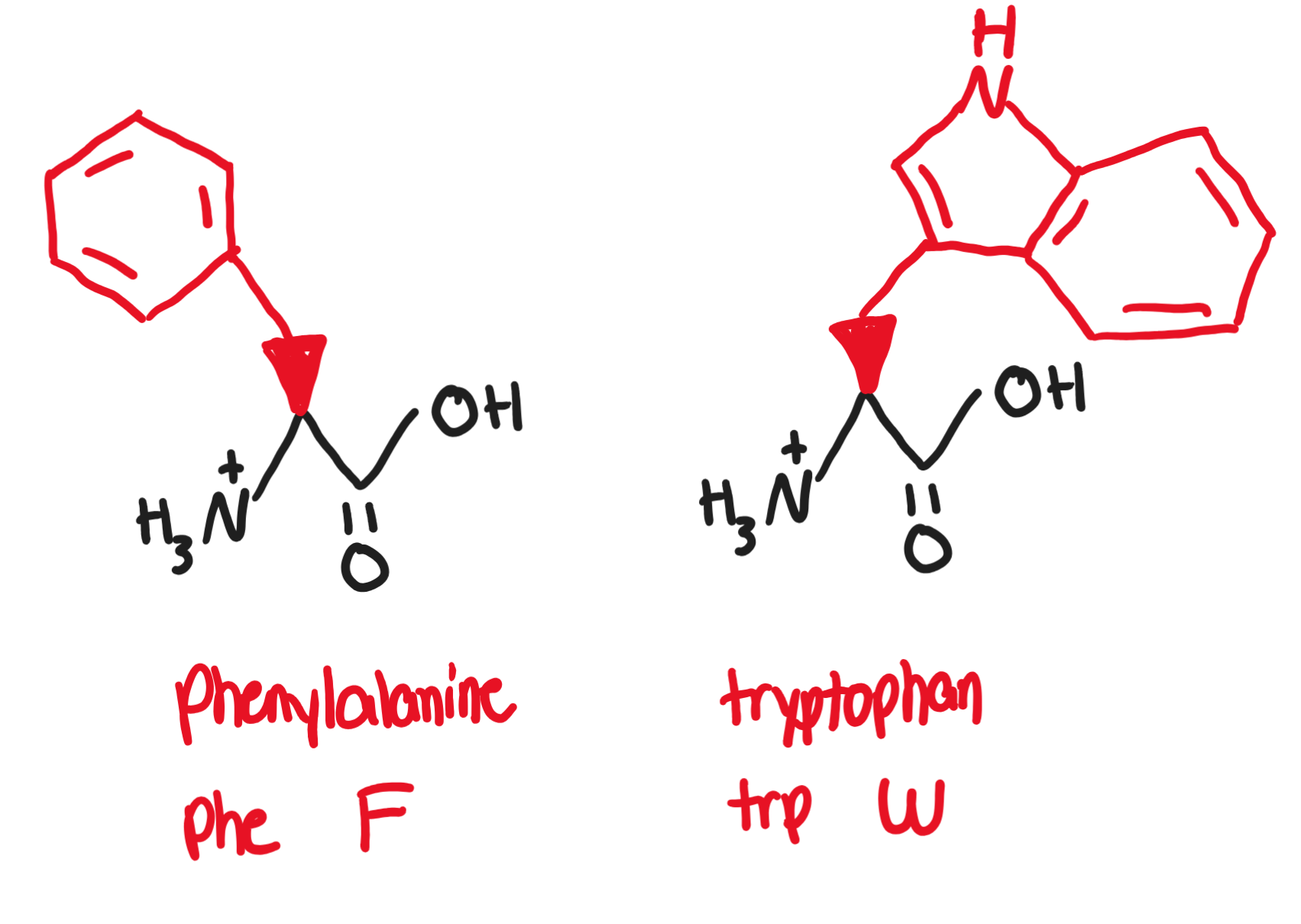
Hydrophobic, non-polar, aromatic R groups
Aromatic R-groups can absorb UV light
the higher the concentration of protein in a substance, the more UV light is absorbed
Phenylalanine, Phe, F (-CH2-benzene)
present in artificial sweetener aspartame
Tryptophan, Trp, W (two rings)
precursor of serotonin and melatonin
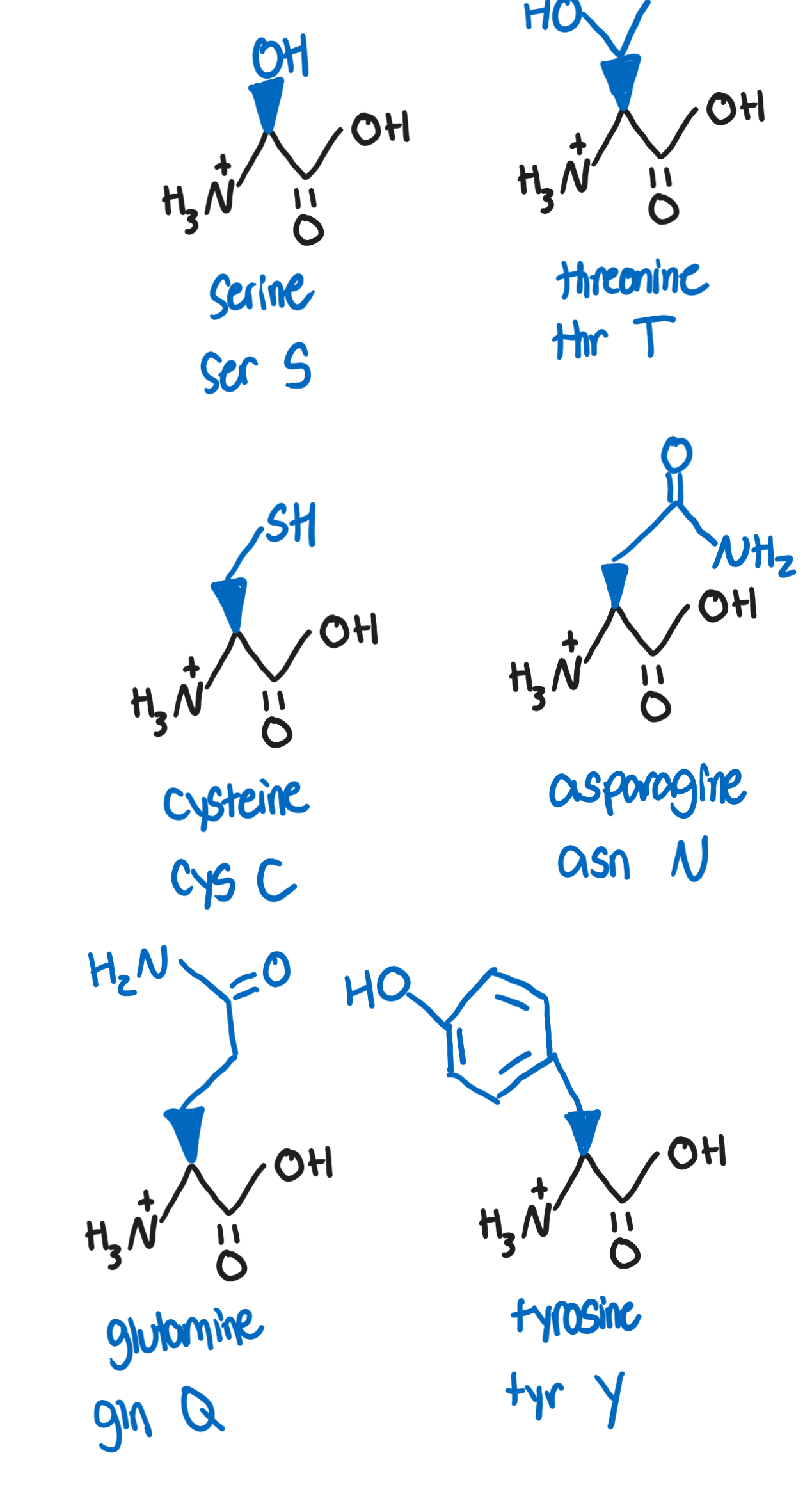
Hydrophilic, polar, neutral R groups
side chains are hydrophilic, thus on surface of proteins and are subjected to chemical modifications
can be oxidized or reduced, affecting conformation of protein
Serine, Ser, S (-CH2OH)
target for phosphorylation and other processes involved in post-translational modifications and signaling (due to OH group)
Threonine, Thr, T (-CH(OH)CH3)
target for phosphorylation due to OH groups
essential amino acid
Cysteine, Cys, C (-CH2SH)
can form covalent disulfide bridges (important in tertiary structures)
Asparagine, Asn, N (-CH2(CO)NH2)
reacts to reducing sugars (glucose and fructose) in baked and fried foods to form acrylamide, a potentially carcinogenic compound
Glutamine, Gln, Q (-CH2CH2(CO)NH2)
most common as a free-amino acid in human blood and is involved in a wide range of metabolic reactions
Tyrosine, Tyr, Y (CH2-benzene-OH)
can undergo post translational modifications and phosphorylation
aromatic
Hydrophilic, polar, basic R groups
Lysine, Lys, K (-(CH2)4NH3+)
the primary amine at the end of the chain is fairly reactive and is the target for many covalent modifications (methylation and acetylations)
Arginine, Arg, R (-NHC(NH2+)NH2)
plays a role in regulating blood pressure and other biomolecule synthesis
guanidino group can be protonated and can be resonance-stabilized (makes arginine the most basic of all amino acids)
Histidine, His, H (CH2-aromatic with N and NH2)
is deprotonated at physiological pH
can serve as a buffer in pHs slightly more acidic than physiological
![]()
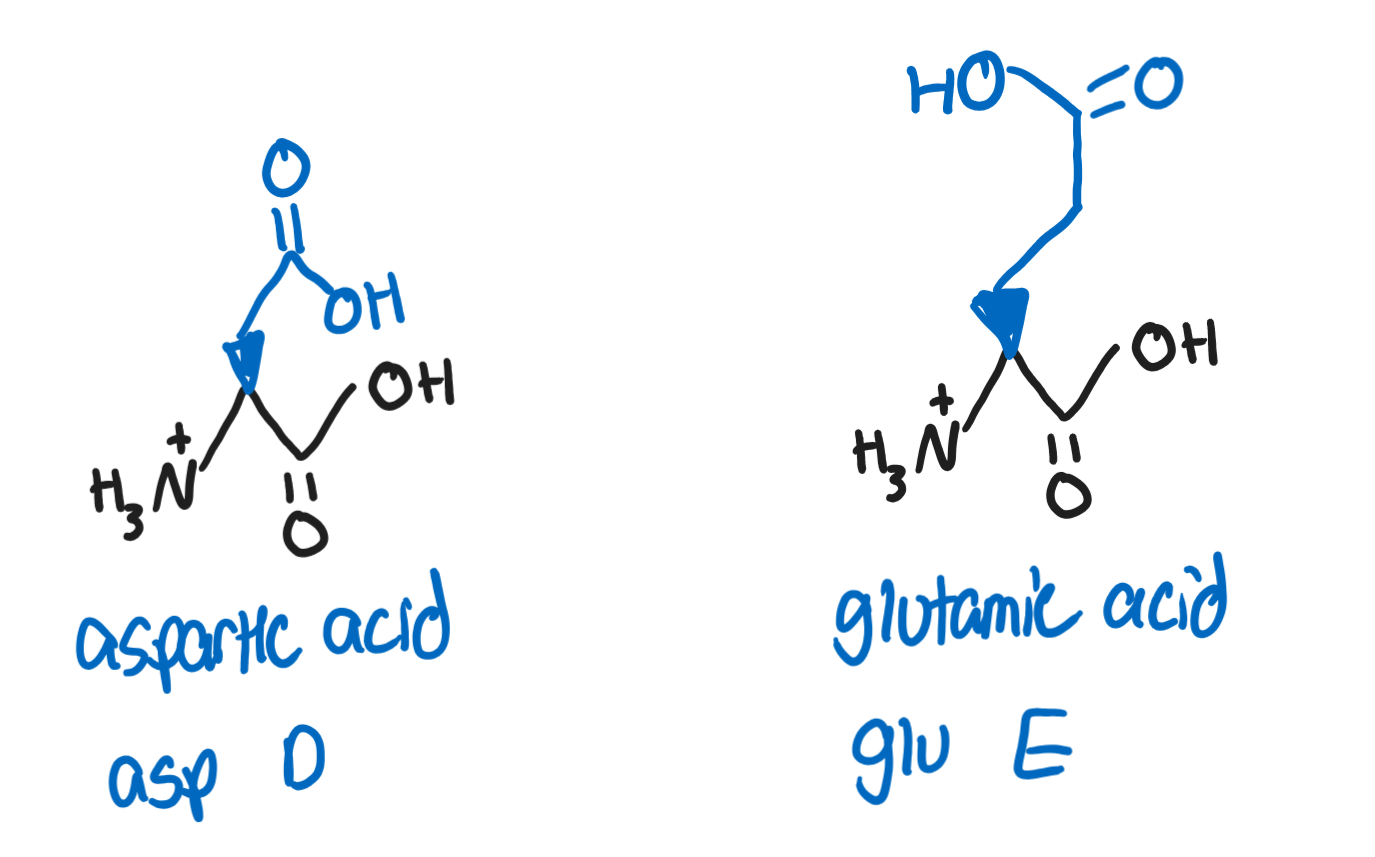
Hydrophilic, polar, acidic R groups
Aspartic Acid, Asp, D (-CH2COOH)
deprotonated form is called aspartate
a component of artificer sweetener aspartame
Glutamic Acid, Glu, E (-CH2CH2COOH)
deprotonated form is called glutamate
important as a structural amino acid in proteins and important in neurotransmitters