Chapter 3: Proteins
Proteins:
- Proteins constitute most of the cell’s dry mass.
- Cell’s building blocks and also execute the majority of cell’s functions.
- Heteropolymer of amino acids.
- After water, proteins are the major components of protoplasm.
- Peptide bond is present.
- Most abundant protein on earth: Rubisco
- Most abundant protein in mammals: Collagen
- Proteins embedded in the plasma membrane form channels and pumps that control the passage of small molecules into and out of the cell.
- Proteins from a chemical point of view are very complex and functionally sophisticated molecules.
- The location of each amino acid in the long string of amino acids that forms a protein determines its three-dimensional shape.
Shape and Structure of Proteins:
20 different amino acids.
A protein molecule is a long un-branched chain of these amino acids.
Proteins are called polypeptides.
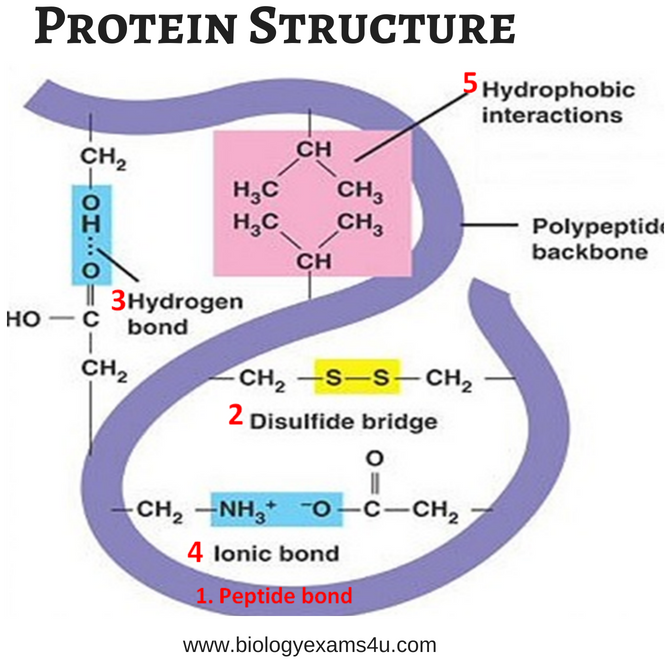
It consists of:
- Peptide bond
- Disulphide bridges
- Hydrogen bond
- Ionic bond
- Hydrophobic interactions
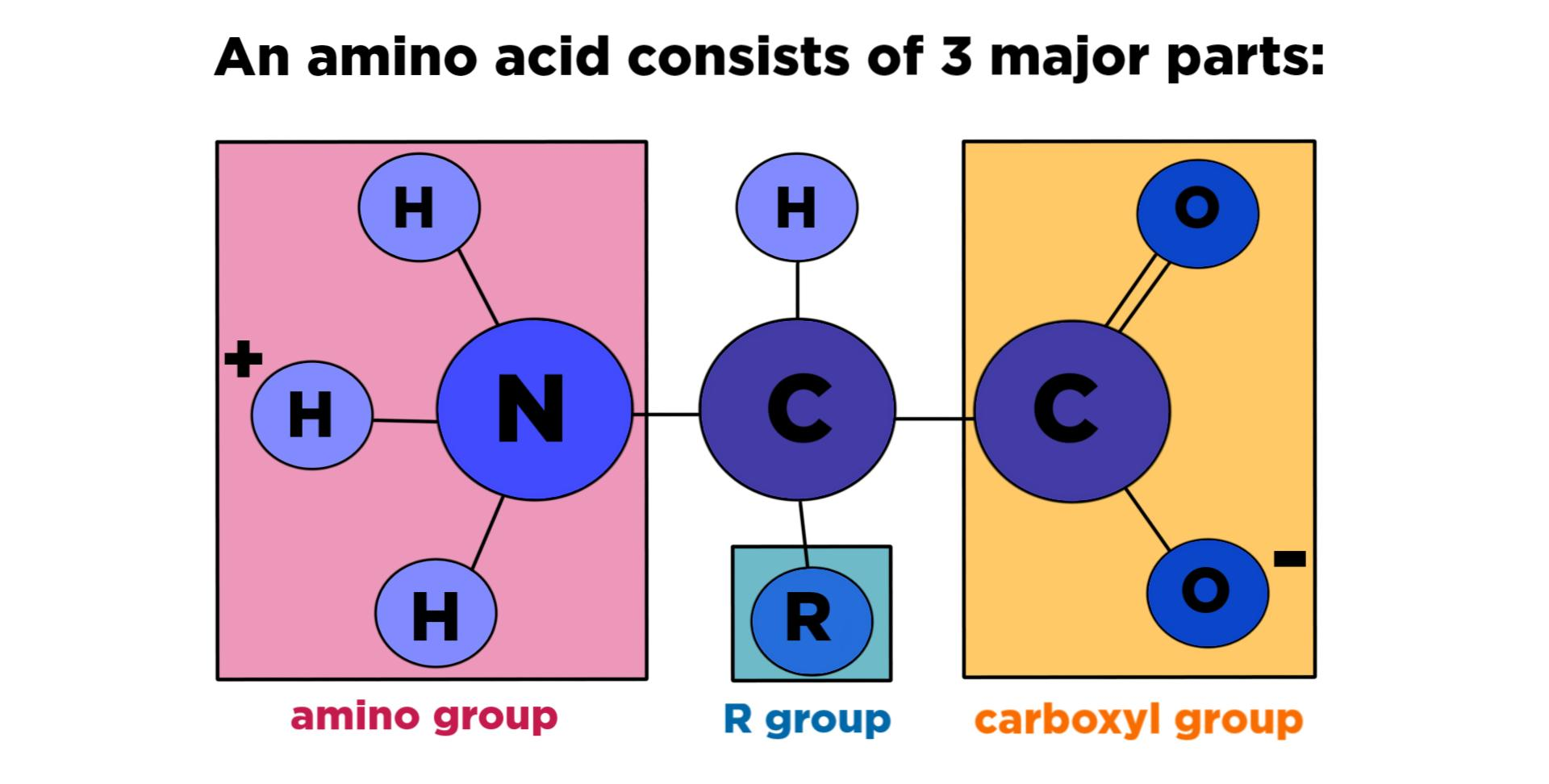
Amino Acids:
Micro molecules/acid soluble pool.
Monomer of protein/building of protein.
Substitute of methane.
Amino acids consist of:
- Amide group: basic group, positively charged.
- R: variable group, decide name, nature, and properties of amino acid.
- COOH: carboxylic acid, acidic group, acidic nature, negatively charged.
- C: chiral carbon or alpha carbon.
Properties of Amino Acids:
- Configuration of protein.
- Amino acids are amphoteric in nature.
- All amino acids are officially active, and they show optical isomerism-except glycine.
- Zwitter ions: Dipolar ions
- at low ph (acidic) = positive charge
- at high ph (basic) = negative charge
Classification of L-alpha amino acid:
- Acidic amino acid:
- It contains an extra COOH group.
- Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid.
- Basic amino acid:
- It contain extra NH2 group.
- Histidine, Lysine, Arginine.
- Neutral amino acid:
- It contains one NH2 group and one COOH group.
- Asparagine, serine, tyrosine, etc.
Classification of amino acids on the basis of functional group
Amino acid with aliphatic group: GAVIL
- Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Isoleucine, Leucine
Amino acids containing hydroxyl (-OH) groups: ST
- Serine, Threonine
Sulphur containing amino acids: CM
- Cysteine, Methionine
Acidic amino group: AAGG
- Aspartic acid, Asparagine, Glutamic acid, Glutamine
Basic: LAH
- Leucine, Arginine, Histidine
Aromatic: PTT
- Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Tyrosine
Imino: Proline
Non-polar amino acids: They have no charge on the “R-group”.
Polar amino acids: Have charge on the “R-group”.

Classification of amino acids (on the basis of synthesis in the body)
- Essential amino acid:
- Not synthesized in our bodies.
- Need to be taken in our diets.
- Non-essential amino acids:
- Synthesized in their body cannot be taken in diet.
- Semi-essential amino acids:
- Produced at a very slow rate can be synthesized by the adult body but not in growing children.
Proteins classified on the basis of chemical nature and stability:
- Simple protein:
- Made up of amino acids.
- Protein part:
- Globular: spherical/oval shaped.
- Fibrous: Collagen, Kinetin, Actin
- Conjugate protein:
- Made up of protein + nonprotein part.
- Derived protein:
- Primary: Due to denaturation of protein.
- Secondary: formed due to digestion.
- Protein are also divided as:
- Complete protein: All 20 essential amino acids present.
- Incomplete protein: One/two essential amino acids lacking.
- Monomeric protein: Made up of one polypeptide chain.
- Oligomeric protein: Made up of two/more polypeptide.
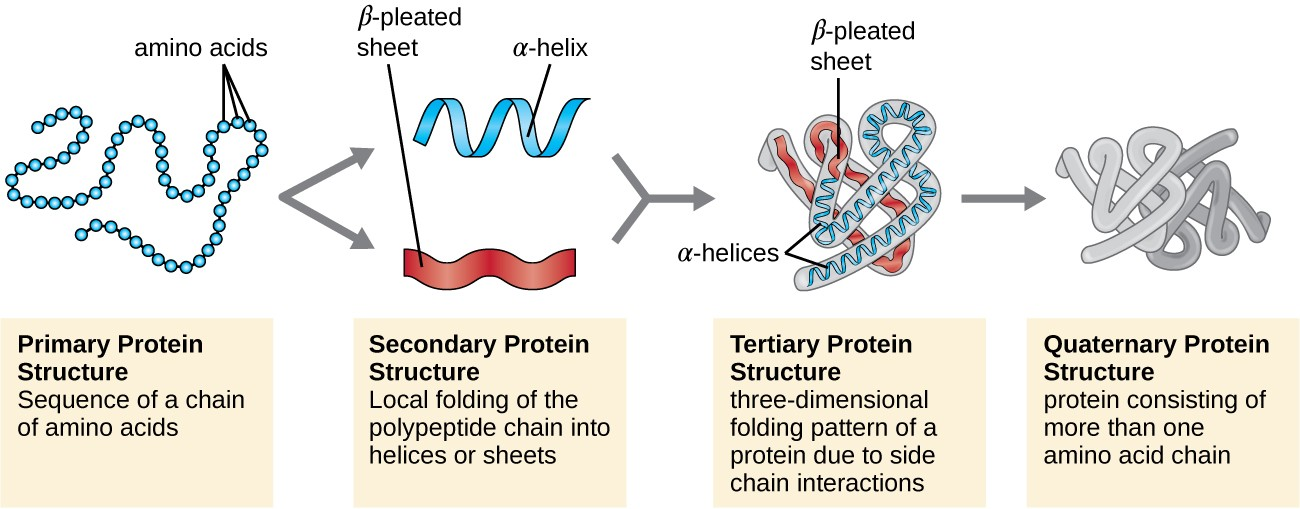
Structure of protein
Primary structure:
- It is a linear chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
- It is a newly formed protein on the ribosome.
- This structure of a protein is highly unstable/not functional but decides the fate of protein.
Secondary structure:
- It comprises of alpha helix and beta plated sheet.
- The folding of linear polypeptide chains in a specific coiled structure is called secondary structure.
- A new bond is formed: Hydrogen bond.
- 2 bonds: hydrogen + peptide
- Alpha helix:
- a most common type of secondary structure and rigid rearrangement of polypeptide chain.
- stable configuration.
- right-handed helix.
- bonds: intramolecular h-bonding, peptide bond.
- Beta-plated sheet:
- made up of 2 or more polypeptide chains are held together by intermolecular-H bonding.
- zig-zag shape.
- protein of secondary structure insoluble in water and fibrous in nature.
Tertiary structure:
- protein of tertiary structure are highly folded and globular in nature.
- soluble in water.
- more folded than secondary.
- bonds:
- peptide bond
- H-bond
- disulfide bond
- hydrophobic interactions
- ionic bond
- most of the proteins and enzymes show tertiary structure in protoplasm.
Quaternary structure:
- it is made up of two or more than two polypeptide chain.
- oligomeric protein in which R-group close to each other.
- all types of bonds like intra, inter-H bonding, ionic bonding, covalent bond, hydrophobic interactions etc, are formed.
- these protein play important/significant role in the regulation of metabolism and cellular function.
ENZYMES
- Enzymes enhance the rate of biological chemical reaction by lowering down activation energy.
- It is a biological catalyst.
- Enzymes are biological middlemen.
- All enzymes are proteinaceous except ribozyme and ribonuclease.
- Enzymes show tertiary and quarternary structure and very specific for biological activity.
- Maximum enzymes are found in mitochondria.
- Small enzyme: Peroxidase.
- Largest enzyme: Catalase
Characteristics features of enzymes:
- Enzymes do not disturb reaction equilibrium.
- Turn over (The number of substrate molecules transformed per min/per sec by one enzyme molecules)
- Turn over no. depends on:
- number of active sites of an enzyme.
- fastest reaction
- separation of product.
- Active site catalytic is directly proportional to turn over number.
- Maximum turn-over number: Carbonic anhydrase.
- Minimum turn-over: lysozyme
- Reversibility in nature:
- Substrate + Enzyme → ES complex
- Very specific in nature:
- temperature specific:
- high temperature: denaturation
- low temperature: inactivation
- ph specific
- Molecular weight is high.
- Amphoteric in nature.
Nomenclature and Classification of Enzymes
- Nomenclature: suffix= ase
- Source of extraction: from where it is extracted.
- 6 classes of enzymes:
- OTHLiL
- Oxidoreductase:
- enzymes involved in oxidation-reduction reaction.
- alcohol dehydrogenase, cytochrome oxidase.
- Transferase:
- Enzyme that catalyze reactions the transfer of functional group.
- e.g.: hexokinase, trans-aminase.
- Hydrolase:
- Enzyme catalyzing hydrolysis of ester, ether, peptides etc.
- These enzyme breaks large molecules into smaller molecules by the introduction/presence of H2O molecules.
- Lyases:
- They break specific covalent bonds and remove a group without hydrolysis, oxidation etc.
- e.g. Aldolase, fumarase.
- Isomerase:
- Rearrangement of molecular structure to form isomers.
- Ligases:
- Enzyme catalysing the synthetic reaction where two molecules are joined together.
Types of Enzymes:
- Simple enzyme: consist of only proteins and catalyze their substrate specific reactions.
- Conjugate enzyme/Holo enzyme: Made up of protein and non-protein parts.
- Protein part: Apoenzyme
- Non-protein part: Co-factor
- Organic:
- Coenzyme: A coenzyme is a loosely bound/organic co-factor. It can be easily removed.
- Prosthetic group: A prosthetic group is tightly bound organic co-factor.
- Inorganic: They form coordination bond with side-chain at the active site and the same time for one/more coordination bond with substrate.
Mode of enzyme action
Mostly enzymes are protein in nature.
The hypothesis regarding the mode of enzyme action
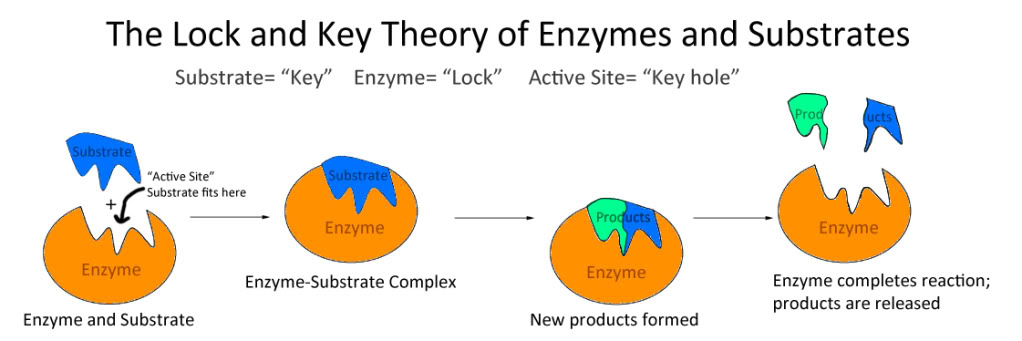
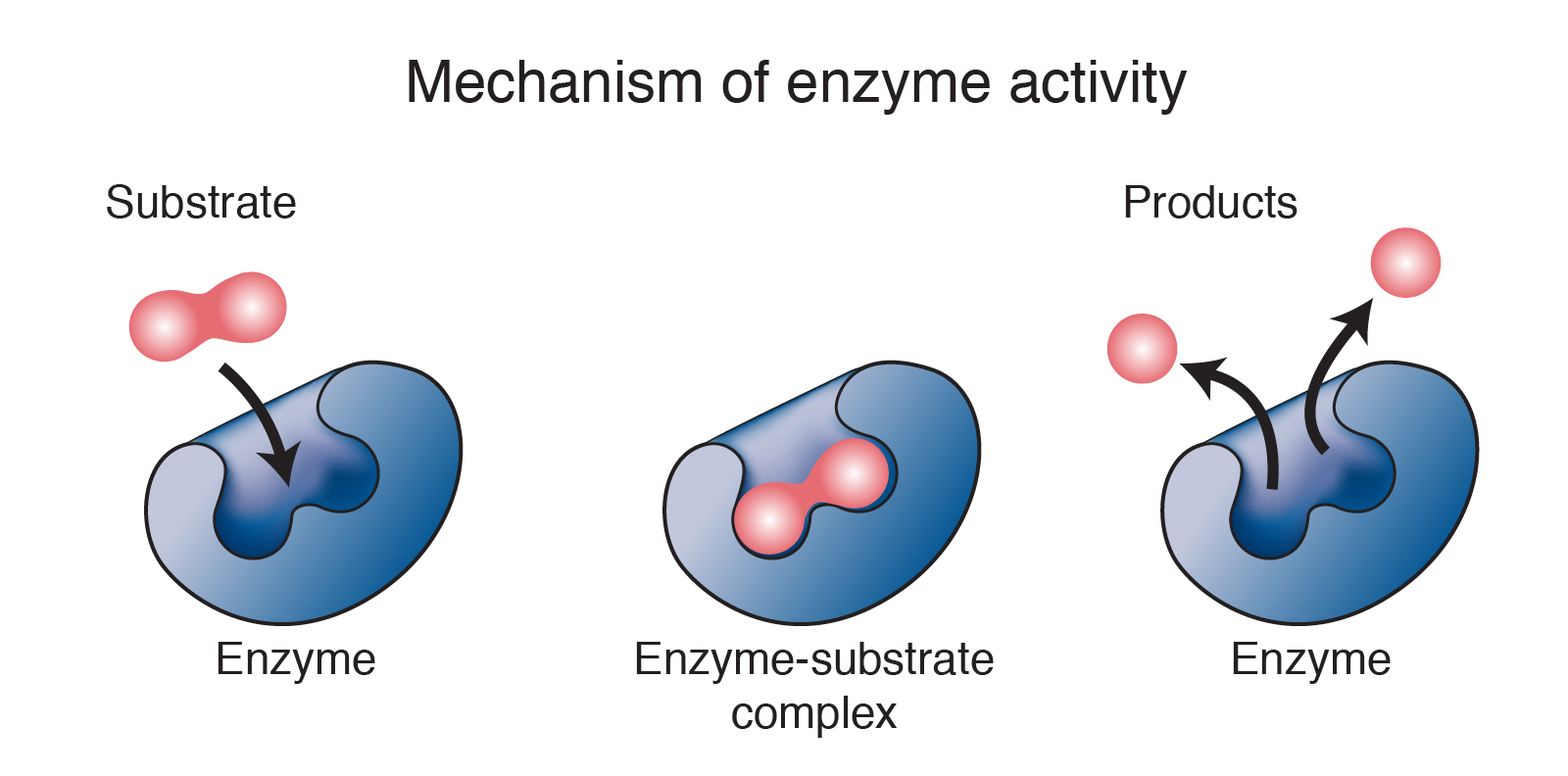
Lock and Key Hypothesis:
- According to this theory:
- Enzymes are rigid and pre-shaped.
- Substrate fit to the active site just as a key fit into a proper lock.
Induced fit hypothesis/ theory:
- Proposed by Kosh land.The monomer
- Most accepted hypothesis on the basis of enzyme action.
- Enzymes are not rigid and pre-shaped.
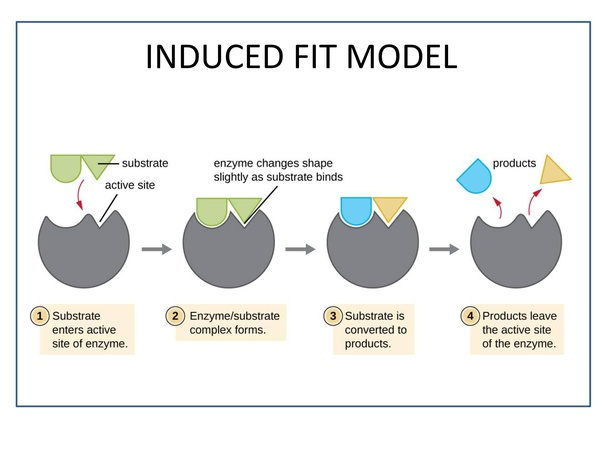
Mechanism of enzyme action:
Substrate → Product
Lowering down of activation energy.
Do not alter the equilibrium.
Enzymes are biocatalyst.
Factors affecting enzyme action:
- Temperature:
- at high temperature: denaturation
- at low temperature: inactivation
- optimum temperature: 25-40 degrees Celsius for enzymatic activity.
- pH:
- optimum pH = enzyme activity very high.
- enzymes:
- endoenzyme (inside cell)
- exoenzyme (enzymes are synthesized inside in the cell but secreted from the cell to work externally).
- Substrate concentration:
- Enzyme is larger in size and bears several active sites with the increase in substrate concentration the velocity of the reaction rises in first and the reaction reaches a maximum velocity. (Vmax)
- The velocity is not exceeded by any further rise in the concentration of substrate.
- Michalis Menten Constant (Km):
- It is a mathematical derivation/constant which indicate concentration of substrate at which reaction velocity reaches half of Vmax.
- Km indicate affinity of the enzyme for its substrate.
- A high Km indicate low affinity of enzyme and low Km indicate high affinity.
- Km is inversely proportional to turn over number.
- Allosteric enzymes do not obey Km.
Inhibitors:
It is chemical molecules inhibit enzyme activity.
Inhibitors are of two types:
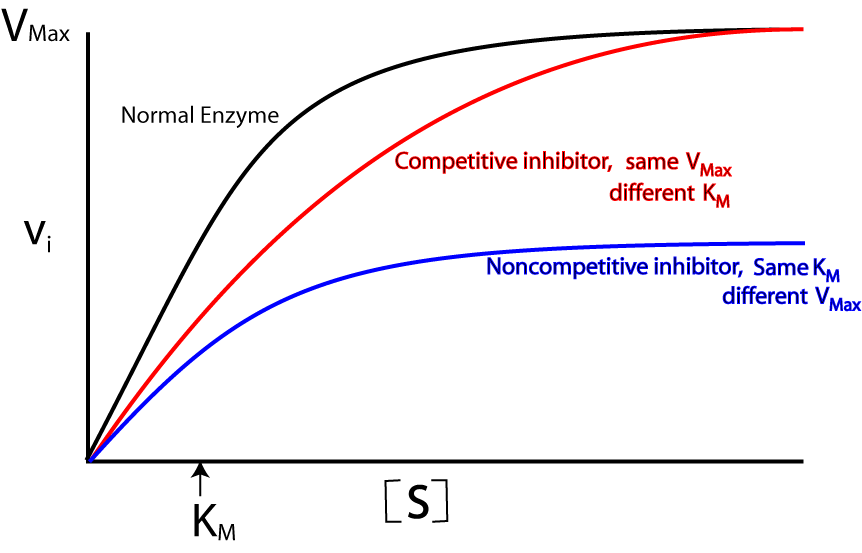
- Competitive inhibitors:
- Inhibitors are structure similar to substrate.
- They favor lock and key hypothesis.
- Reversible in nature.
- Km increase but Vmax remain constant.
Non-competitive inhibitors:
- Some inhibitors do not compete for active site of enzyme but destroy the structure of enzyme, the physical structure of enzyme is altered as a result and do not form enzyme-substrate complex.
- They favor induced-fit theory.
- Irreversible in nature.
- Km remain constant but Vmax change.
\
\
\
\
\