Common Blood Chemistry Test
What are blood chemistry tests?
- Tests performed on blood sample to measure the amount of certain analytes in our body
- involve electrolytes, proteins, enzymes, hormones, vitamins, minerals, lipids and glucose
- provide important information on the function of kidneys, liver, heart, and other organs
- used for screening and diagnosis of various human diseases, as well as treatment monitoring
Lipids (fats)
- organic, nonpolar compounds
- mainly composed of carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds (hydrocarbon chains)
- rich source of energy & storage for excess calories
- integral part of cell membrane
- protection & insulation
- <<precursors for steroid hormones, prostaglandins, leukotrienes & lipoxins<<
Fatty acids
occur in esterified form (^^as building blocks for lipids^^), and free fatty acid form
linear hydrocarbon chains with terminal carboxyl group (-COOH)
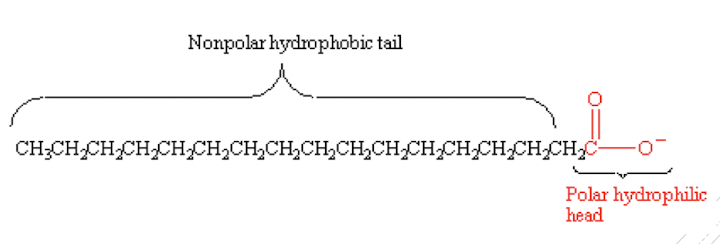
amphipathic/amphiphilic molecule
categorisation based on the length of hydrocarbon chain:
- short-chain FA: ≤6 carbons
- medium-chain FA: 8-12 carbons
- long-chain FA: 14-18 carbons
- very-long chain FA: ≥20 carbons
most commonly found: palmitic acid (16C) & stearic acid (18C)
categorisation based on the degree of saturation in the hydrocarbon chain:
- saturated FA
- unsaturated FA
Triglycerides (triacylglycerols)
- consists of ^^1 molecule of glycerol^^ esterified with ==3 fatty acids molecules==
- present in dietary fat; synthesised in the liver & adipose tissue
Cholesterol
- ==unsaturated== ==steroid alcohol==; amphipathic lipid (both hydrophilic and hydrophobic)
- almost exclusively synthesised by animals
- present in dietary fat; synthesised in liver
- precursor of steroid hormones & bile acids; does not serve as a source of energy fuel
Lipoproteins
consists of a non-polar core triglycerides & cholesteryl esters
surrounded by a polar surface layer of phospholipids, cholesterol, & apolipoproteins
classification based on different density fractions after ultracentrifugation
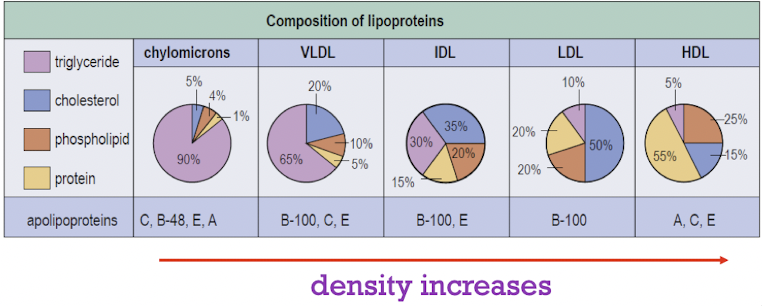
LDL - associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease
Lipids/Lipoproteins Analyses
Dyslipidemias
diseases associated with abnormal lipid concentrations
cause:
- genetic abnormalities
- environmental/lifestyle imbalances
- secondary to other diseases
defined by clinical characteristics & laboratory test results
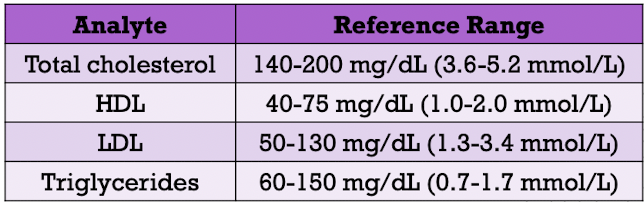
laboratory analyses:
- total cholesterol
- HDL
- LDL
- triglycerides
clinical reference ranges for lipids
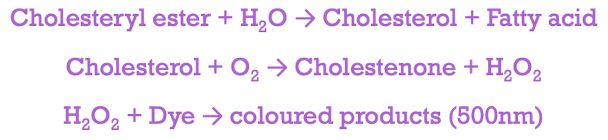
Cholesterol measurement
serum/plasma specimens are collected after fasting for at least 12 hours
serum/plasma specimens can be refrigerated at 4C for several days
HDL measurement
- two-step procedure with manual pretreatment
- precipitation reagent aggregates non-HDLs which are sedimented via centrifugation
- HDL is then quantified by enzymatic assays
LDL measurement
- via Friedewald calculation
- total cholesterol, triglycerides and HDL are quantified
- VLDL is estimated as [triglyceride level/5] in mg/dL unit
- LDL = total cholesterol - HDL - VLDL
Triglyceride measurement
- perform in conjunction with total cholesterol
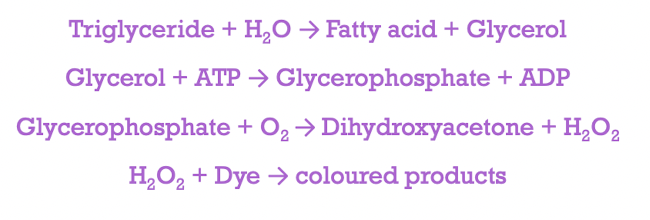
Lipid Disorders
[[Arteriosclerosis[[
deposition of lipids (esterified cholesterol) in artery walls
results in fatty streaks → plaques (smooth muscle cells, extracellular lipid, calcification & fibrous tissue) → partial or complete occulsion of blood flow
LDL → initiate & promote plaque formation
→ every 1% decrease in LDL concentration leads to 2% decrease in arteriosclerosis risk
Hypercholesterolemia
- associated with genetic abnormalities [i.e., familial hypercholesterolemia (FH)]
- homozygotes
- total cholesterol ~800-1000mg/dL (20-26 mmol/L)
- first heart attack in teenage years
- heterozygotes
- ~300-600 mg/dL (8-15 mmol/L)
- symptomatic for heart disease in 20s-50s
Hypertriglyceridemia
- due to genetic abnormalities (e.g., FH)
- consequence of secondary causes (e.g., hormonal abnormalities, diabetes mellitus or nephrosis)
- imbalance between synthesis & clearance of VLDL
- many coronary heart disease patients have moderately elevated triglycerides & decreased HLDL level
Summary (Part 1)
- [ ] Different types of lipids
- [ ] Laboratory analyses for lipids/lipoproteins
- [ ] Development of arteriosclerosis
Carbohydrates
Large macromolecules containing C, H & O atoms
Generic formula:
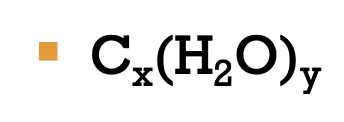
Contain C=O and -OH functional groups
Grouping based on the number of carbon:
- trioses (3C)
- tetroses (4C)
- pentoses (5C)
- hexoses (6C)
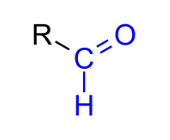
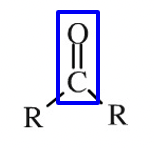
Grouping based on the location of the C=O functional group
aldehyde group (O=CH-)
ketone group (O=C)
Saccharide - basic unit structure
Classification:
- monosaccharide (e.g., glucose, fructose, galactose)
- disaccharide (e.g., lactose, maltose, sucrose)
- oligosaccharide (e.g., oligofructose, maltotriose)
- polysaccharide (e.g., amylose, glycogen)
Glucose
- Major energy supply
- primarily stored as glycogen in liver & muscle
- disease states:
- hyperglycaemia
- hypoglycaemia
Hyperglycaemia
- hyper (high) + glykys (sweet/sugar) + haima (blood)
- an increase in blood glucose level
- defined as blood glucose level (>125mg/dL during fasting)
- Causes:
- reduced insulin secretion
- decreased glucose utilisation
- increased glucose production
- Laboratory findings (blood specimen)
- increased glucose level in plasma
- increased serum osmolality
- ketones in serum (ketonemia)
- decreased blood pH (acidosis)
- electrolyte imbalance
Diabetes Mellitus
metabolic disorder characterised by chronic hyperglycemia
arise from defects in the secretion, or action of insulin, or both
clinically defined as high plasma glucose concentrations at which there is an increased risk of retinopathy, nephropathy & neuropathy
type 1 diabetes mellitus
- pancreatic islet B-cell destruction
- tendency to ketoacidosis
type 2 diabetes mellitus
- insulin resistance
- insulin secretory defect
gestational diabetes mellitus
- glucose intolerance
- metabolic & hormonal changes during pregnancy
Laboratory diagnosis
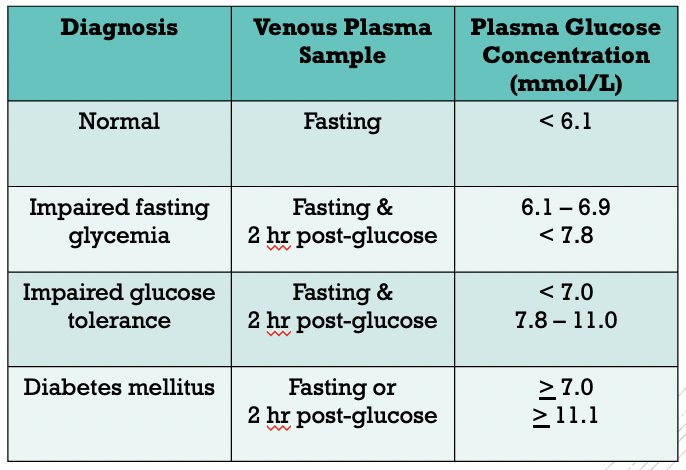
measurement of glycated haemoglobin
‘time-weighted’ average plasma glucose concentration over the past 2-3 months
in vivo glycation of haemoglobin is proportional to plasma glucose concetration
average plasma glucose concentration during the last 30 days accounts for 50% of the HBAlc concentration (glycated haemoglobin)
expressed as a proportion of total haemoglobin (in percentage)
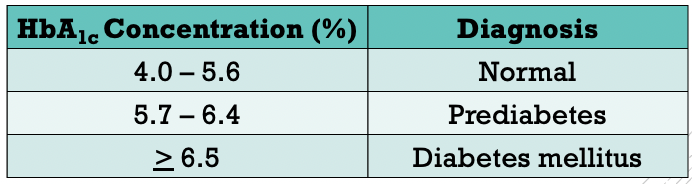
Prediabetes
- higher than normal blood glucose level, but insufficiently high to be considered as diabetes
- increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus, heart disease & stroke
- <<reversible<<
- criteria:
- 126mg/dL > fasting glucose level ≥ 100 mg/dL
- 200mg/dL > 2hr OGTT level ≥ 140 mg/dL
- HBAlc concentration of 5.7-6.4%
Glucose Assay
- serum/plasma sample
- enzymatic approach - glucose oxidase, hexokinase, glucose dehydrogenase
- generate measurable coloured product proportional to glucose concentration
Glucometer
- medical device for point-of-care measurement of blood glucose concentration
- rapid & easy home-based blood glucose monitoring, particularly among individuals with Type 1, 2 & gestational diabetes mellitus
- requires only a small amount of blood sample (from fingertip)
Hypoglycaemia
- Blood glucose level is lower than the standard range
- fasting blood sugar ≤ 70 mg/dL or 3.9 mmol/L
- common among
- particularly in type 1 diabetic patients
- type 2 diabetic patients who are on insulin/medication
- rare in individuals with normal glucose metabolism
- diagnosis should be made only if the individual demonstrates:
- hypoglycaemic symptoms
- low plasma glucose concentration <50 mg/dL
- symptoms are relieved by administering glucose/glucagon
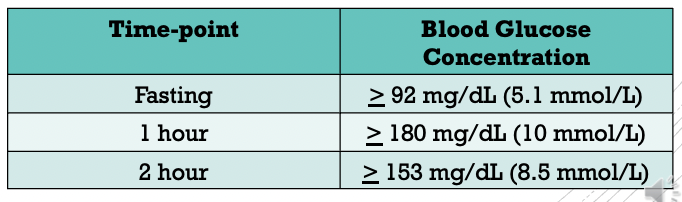
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Recommendation: all nondiabetic pregnant women should be screened at 24-28 weeks of gestation
one-step approach: 2-hr oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) by using 75g glucose load
requires overnight fasting of at least 8hr
==Complete Blood Count==
- to evaluate overall health
- to screen, diagnose & monitor certain health disorders, e.g., anaemia, infection & leukemia
- Measurement and/or counting of:
- red blood cells
- white blood cells
- haemoglobin
- haematocrit
- platelets
- mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
Red Blood Cells
- measure the number of red blood cells, which carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of our body
- normal count (male):
- 4.35-5.65 million cells/ul
- normal count (female):
- 3.92-5.13 million cells/ul
- increased level may indicate:
- polycythemia
- respiratory distress
- high altitude
- decreased level may be a sign of:
- iron anemia
- vitamin B12, vitamin B6 and/or folic acid anaemia
- haemorrhage
- liver & renal dysfunction
White Blood Cells
measure the total number of WBCs (without differential)
measure the number of each of the 5 basic white blood cell types (differential)
- neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes & monocytes
- expressed as percentage or absolute value
elevated white blood cells count may indicate inflammation or infection
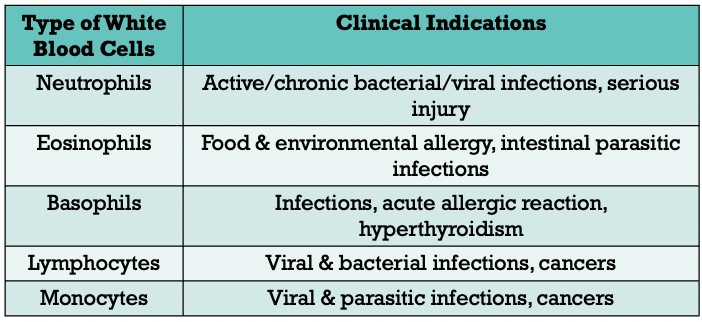
low cells count may indicate autoimmune diseases, bone marrow disorders or cancers
normal: 3.49-9.6 billion cell/litre
Haemoglobin
- protein that carries oxygen in the red blood cells
- normal (male): 132-166 g/L
- normal (female): 116-150 g/L
- increased level may indicate dehydration, emphysema, asthma, polycythemia
- decreased level may indicate iron deficiency anaemia, microscopic internal bleeding, digestive inflammation
Hematocrit
- known as packed cell volume
- percentage of the total occupied by packed red blood cells when a given volume of whole blood is centrifuged
- normal (male): 38.3% - 48.6%
- normal (female): 35.5% - 44.9%
- abnormal value indicates the similar clinical conditions as haemoglobin
Platelets
- responsible for blood coagulation and vascular integrity
- reference (male): 135-317 billion/L
- reference (female): 157-361 billion/L
- increased level: atherosclerosis, rheumatoid/inflammatory arthiritis, certain cancers
- decreased level: idiopathic thrombocytopenia, blood loss
Means Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
- the volume in cubic microns occupied by an average single red blood cell
- ↑ level (macrocytic RBCs): vitamin B12/folic acid anaemia, dehydration
- ↓ level (microcytic RBCs): iron anaemia, microscopic internal bleeding
- other RBCs-related markers:
- MCH (mean corpuscular haemoglobin)
- MCHC (mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration)
Summary (Part 2)
- [ ] Hyperglycaemia and hypoglycaemia
- [ ] complete blood count & its clinical indications