6.5 Rate Law
Rate Law Equation
Reactant concentrations determine how quickly a reaction proceeds (reaction rate)
Reaction rate can be expressed mathematically in a rate law equation:
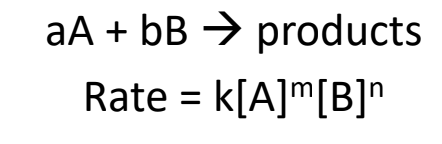
Where:
k = rate constant (unique for every reaction, must be determined experimentally)
m and n (maybe p) = order of reaction (describes relationship between rate and concentration of reactant)
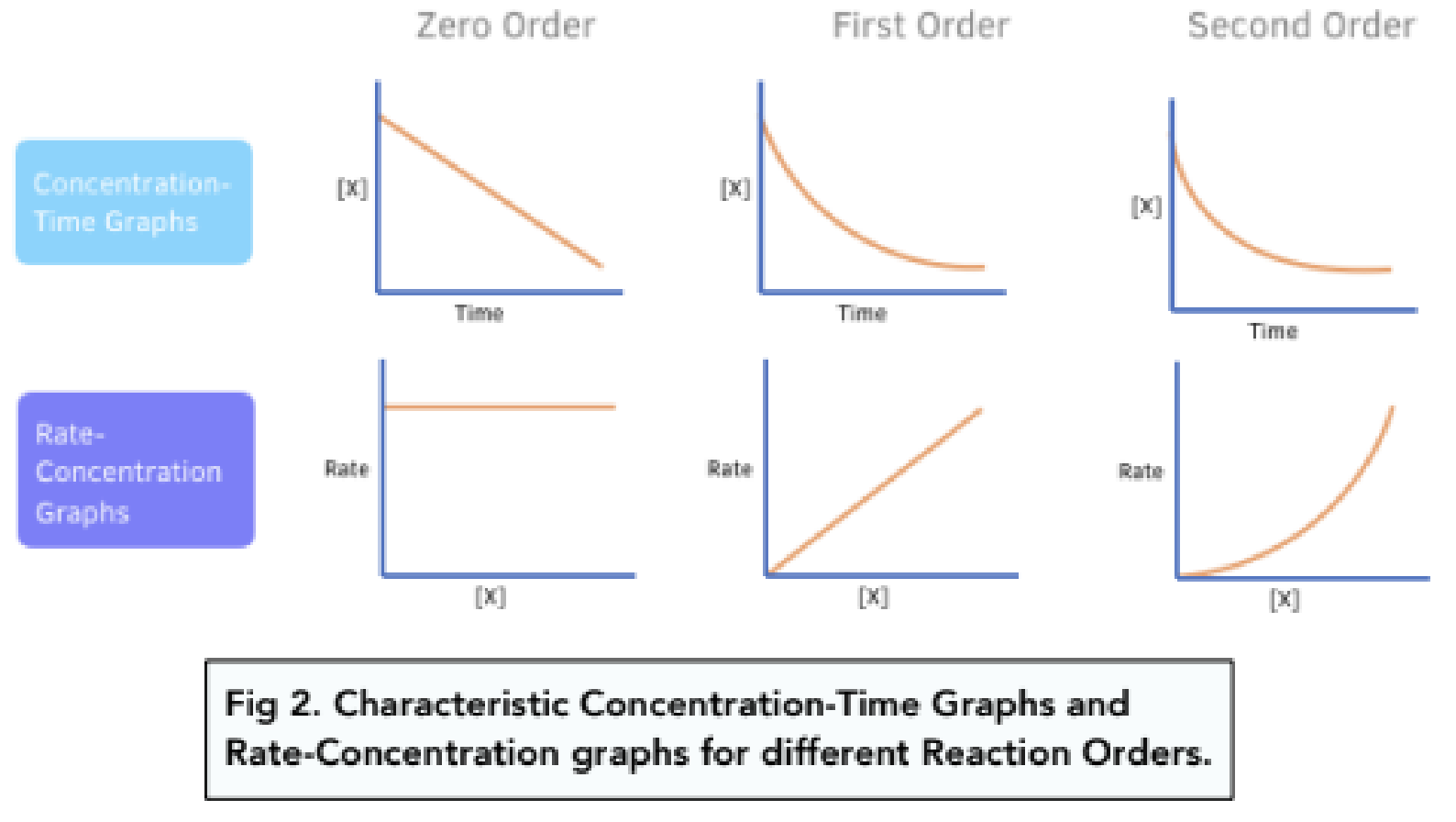
Order of Reaction
1st order (1)
Rate is directly proportional
2nd order (2)
Rate is exponentially proportional
0 order (0)
Rate is NOT related (changing concentration does NOT affect rate)
Determining order of reaction
Using experimental data for instantaneous reaction rate just after t=0 (when products are insignificant), compare rates where ONE reactant is changed and others are kept constant
IF rate does NOT change when reactant is doubled, order is 0
Rate = [A]0
IF rate doubles when reactant is doubled, order is 1
Rate = [A]1
IF rate quadruples when reactant is doubled, order is 2
Rate = [A]2
TOTAL ORDER OF REACTION IS EQUAL TO THE SUM OF ALL EXPONENTS IN RATE LAW EQUATION.