In Class Notes 11/12: Understanding Emerging Adulthood Dynamics
Emerging Adulthood 🌟
Emerging adulthood is a stage of life that spans from approximately 18 to 25 years old. This stage is characterized by a transition from adolescence to adulthood, but it is not universally recognized as a distinct stage of development.
What Makes Someone an Adult?
Being an adult is not solely defined by age. While 18 is often considered the age of majority, there are still many things that individuals in this age group cannot do, such as:
Renting a car until the age of 25
Signing certain types of contracts until the age of 21
Drinking or buying tobacco products until the age of 21
Characteristics of Emerging Adulthood
Responsibility: Taking care of oneself, paying bills, and being financially independent
Transitional: A stage of life where individuals are no longer adolescents but not yet fully adults
Not universal: Emerging adulthood is more common in Western, educated, industrialized, rich, and democratic (WEIRD) countries
Physical Health in Emerging Adulthood
Physical Health Aspect | Description |
Organ Reserve | The extra capacity built into our organ systems that allows us to cope with extra demands |
Homeostasis | The body's effort to stay in equilibrium and maintain balance under stress |
Allostasis | The body's longer-term adjustment to stress, involving changes in hormone levels and other physiological processes |
Allostatic Load | The cumulative stress on the body's systems, which can limit functioning and increase vulnerability to disease |
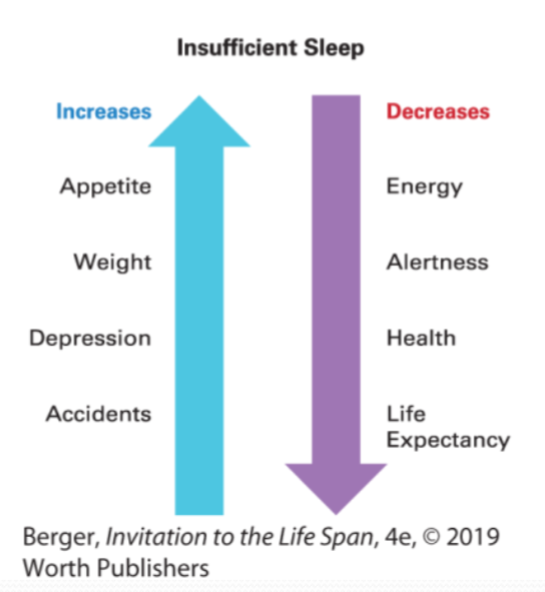
The Importance of Good Health Habits
Exercise: Reduces blood pressure, strengthens the heart and lungs, reduces depression, and reduces the risk of osteoporosis, diabetes, arthritis, dementia, and some cancers
Sleep: 8-9 hours per night is recommended, with some individuals requiring up to 10 hours
Good health habits: Decrease allostatic load by reducing health risks
Sex and Relationships in Emerging Adulthood
Sex drive: Powerful and strong during this stage
Infertility: Rare, but can be caused by untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Birth complications: Rare, but can be caused by untreated STIs
Trends: Later marriages and later parenthood, with most people not getting married until their mid-to-late twenties and not starting to have kids until closer to 30
Risks and Concerns in Emerging Adulthood
Sexually transmitted infections: High rates of STIs, including HIV and AIDS
Sexual assault: A significant concern for individuals in this age group
Sex trafficking: A serious issue that affects individuals in this age group
Birth Rate Trends
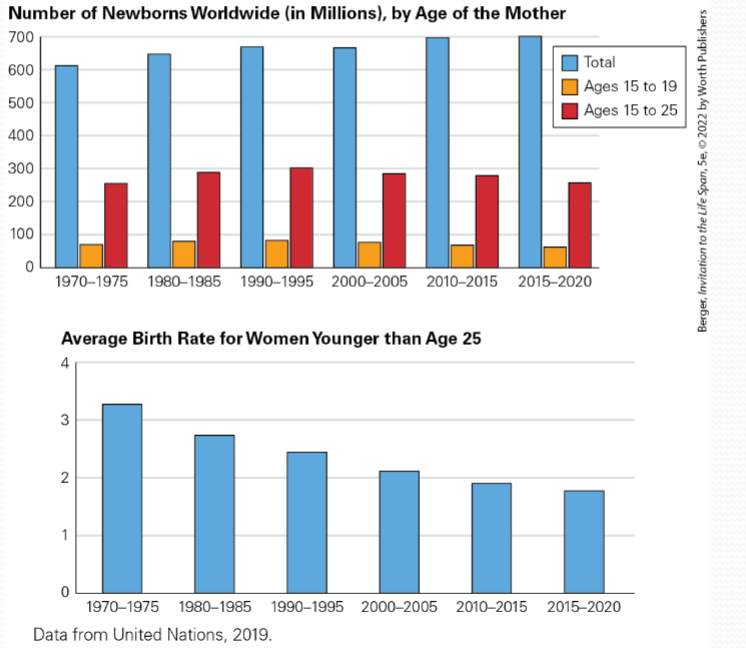
Year | Birth Rate per 1,000 Women under 25 |
1970 | 94.4 |
1990 | 62.1 |
2010 | 47.8 |
2020 | 41.5 |
Note: The birth rate per 1,000 women under 25 has been declining worldwide since 1970.## Risk Taking and Emerging Adulthood 🤔
Risk taking is a common behavior among emerging adults, characterized by a willingness to take chances and engage in potentially hazardous activities. This behavior can be both positive and negative, depending on the situation.
"Risk taking is a bad thing if it's something that's going to cause you to get hurt. But it can also be a good thing because at this age, you're more willing to take a chance on something, like starting a business or trying out a career that you may or may not love."
Factors Influencing Risk Taking
Maturation: Emerging adults' brains are still developing, particularly the prefrontal cortex, which affects decision-making and impulse control.
Freedom: Emerging adults often have more freedom to make choices and take risks, as they are less likely to have significant responsibilities.
Impulsivity: Emerging adults are more likely to act on impulse, which can lead to risky behaviors.
Accidental Injury Rates by Age 📊
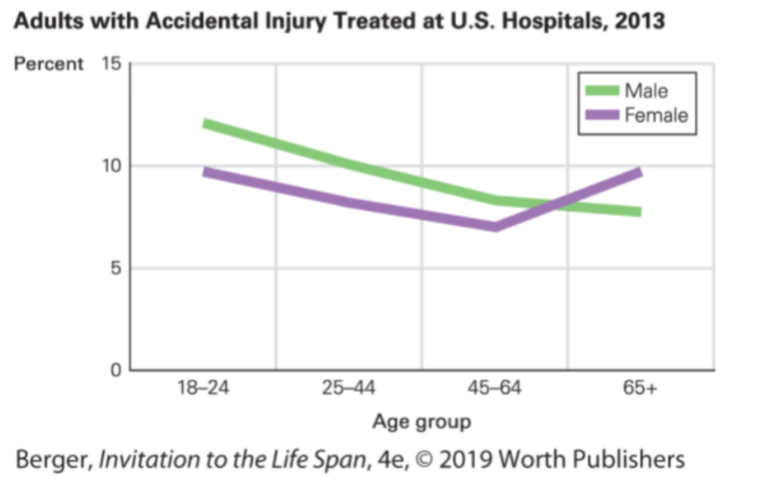
Age Group | Accidental Injury Rate |
18-24 | High |
25-34 | Moderate |
35-44 | Low |
45-54 | Low |
55-64 | Low |
65+ | High (especially among women) |
Risky Behaviors
Alcohol abuse: Emerging adults are more likely to engage in binge drinking and drunk driving.
Drug abuse: Emerging adults are more likely to use illegal drugs, with peak usage around age 20.
Driving without a seatbelt: Young adult males are more likely to drive without a seatbelt, which can lead to fatal accidents.
Substance Use by Age 📊
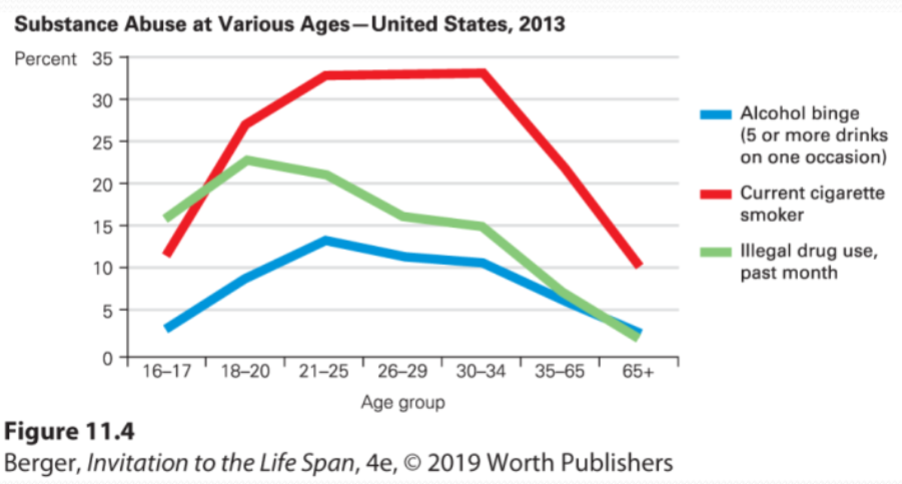
Age Group | Alcohol Binge Drinking | Illegal Drug Use | Cigarette Smoking |
16-17 | Low | Low | Low |
18-20 | Moderate | High | Moderate |
21-24 | High | High | High |
25-34 | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
35-44 | Low | Low | Low |
45-54 | Low | Low | Low |
55-64 | Low | Low | Low |
65+ | Low | Low | Low |
Post-Formal Thought 🤓
Post-formal thought is a stage of cognitive development proposed by Jean Piaget, characterized by:
"Being more practical, more flexible, and less impulsive, less reactive. Post-formal thinkers are able to use formal analysis, develop arguments, and solve big world problems. They find problems and see them as an opportunity to change something."
Higher Education and Emerging Adulthood 📚
Massification: The expansion of higher education after World War II, with the goal of making college accessible to all.
Benefits of college: College graduates tend to have better health, smoke less, eat better, exercise more, and have longer life expectancies.
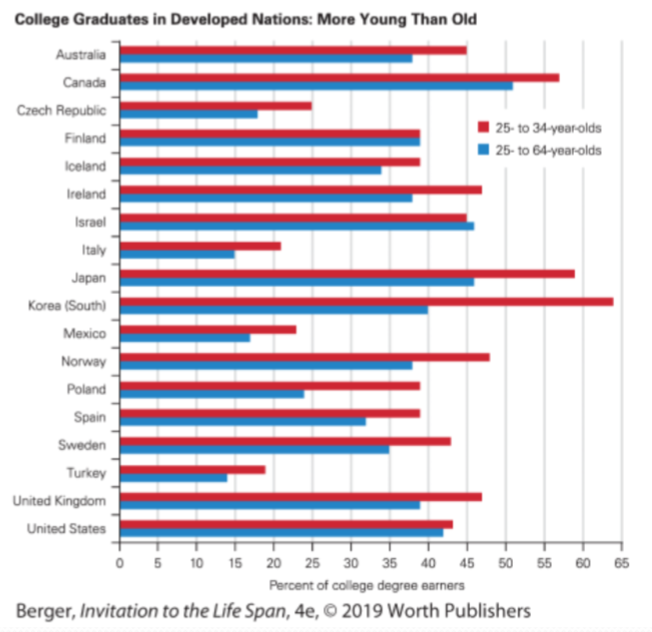
College graduates by country: Countries with the highest percentage of college graduates include Korea, Japan, Canada, Australia, and Norway.
The Cost of College 💸
Funding: The way college is funded has changed over time, with the federal government providing less funding and students taking on more debt.
Student loans: Students often take on significant debt to finance their education, which can be a burden if they do not consider realistic expected salaries.## 📊 Financial Considerations for College Students
Many students who attend college do not graduate, and one of the biggest reasons for this is financial difficulties.
Even if a student stops attending college, they are still required to pay back their student loans. Payments typically begin 6 months after the student stops attending.
📝 Planning for Graduation
Poor planning, bad advising, and having to retake classes can all lead to delayed graduation.
It is essential for students to understand the requirements for their degree and to stay on top of their coursework to avoid these issues.
Reason for Delayed Graduation | Description |
Poor planning | Students may not have a clear plan for completing their degree, leading to delays. |
Bad advising | Students may receive incorrect or inadequate advice from their advisors, leading to delays. |
Retaking classes | Students may need to retake classes, which can add to the overall time it takes to complete their degree. |
🏫 College Size and Graduation Rates
Colleges with the lowest graduation rates are often the most popular among students.
This may be due to factors such as the college's reputation, campus life, and sports teams.
However, larger colleges can also make it difficult for students to get the classes they need, which can lead to delayed graduation.
🤔 Critical Thinking and Post-Formal Thought
College used to focus on providing a well-rounded education, but now it is more focused on preparing students for a specific career.
As a result, students are not developing their critical thinking skills as much as they used to.
A study found that students' growth in critical thinking and communication over 4 years of college is only about half as much as it was 20 years ago.
"Post-formal thought" refers to the ability to think critically and abstractly, and to consider multiple perspectives.
📚 Motives for Attending College
Some students attend college for reasons other than to get an education, such as to play sports or to please their parents.
These motives can affect a student's learning and overall college experience.
🌎 The Effects of Diversity
Being around people from different backgrounds and cultures can challenge a person's thinking and help them develop intellectually.
Individuals who have diverse friend groups are more likely to advance to the stage of post-formal thought.
📊 Identity Development in Emerging Adulthood
Emerging adulthood is a time of identity exploration and development.
The four identity statuses are:
Achievement
Moratorium
Foreclosure
Diffusion
Identity Status | Description |
Achievement | A person has explored different identities and has committed to one. |
Moratorium | A person is in the process of exploring different identities. |
Foreclosure | A person has committed to an identity without fully exploring other options. |
Diffusion | A person has not yet committed to an identity. |
💼 Career Development in Emerging Adulthood
Emerging adulthood is a critical stage for acquiring resources and skills and developing work values.
Many young adults will change their identity status to achievement by age 25, and almost all will have changed their status by age 29.
Emerging adults are likely to change jobs at least once a year between the ages of 18 and 25.
📊 Personality Development in Emerging Adulthood
Research has found both genetic continuity and developmental improvements in personality among 17- to 24-year-olds.
Most emerging adults are still open to new experiences and have rising self-esteem.
There is a positive trend of more happiness in this age group, which may be due to the fact that they like being able to make their own choices.## Intimacy vs Isolation 🤝
Erickson's 6th developmental crisis, Intimacy vs Isolation, centers on the fact that humans are social creatures, seeking relationships of various types. This stage progresses from attraction to close connection to an ongoing commitment.
Romantic Intimacy
Romantic intimacy at this stage is characterized by:
Attraction
Close connection
Ongoing commitment
Relationships tend to last longer once individuals reach this stage. Marriage and parenthood are traditional ways to achieve intimacy and adulthood, but they are not the only options.
Family Influences
Parents are still critical influences at this age, and all members of the family have linked lives. However, fewer emerging adults (18-21 years old) are completely financially independent due to the increasing time it takes to establish a career.
The Impact of Parental Support
Sometimes, too much parental support can be a negative factor in adulting. This is because:
"If you don't have any adversity in your life growing up, then you don't become resilient. If you don't become resilient, you don't have the skills to handle adult stuff."
Cultural Expectations
Cultural expectations play a significant role in determining happiness when living with parents during this stage. For example:
Culture | Expectations |
US | Most young adults prefer to live on their own if the economy is good and they are employed. |
Japan and Italy | Almost all young adults stay at home until they get married. |
US (economy downturn) | Multigenerational living becomes more common. |
Romantic Relationships
In the US, romantic relationships often prioritize:
Trust
Emotional closeness
Honesty
Faithfulness
In other cultures, factors like financial stability and family approval may be more important.
Postponing Marriage and Children
Many emerging adults are postponing marriage and children to focus on career and education. This is partly due to the increasing time it takes to establish a career.
Cohabitation
Cohabitation, or living with a romantic partner without being married, is becoming more common. In the US and Europe, the majority of young adults will live together rather than get married before age 25.
Culture | Attitude towards Cohabitation |
US and Europe | Cohabitation is common and accepted. |
Japan, Ireland, and Italy | There is a cultural taboo against living together. |
The Impact of Cohabitation on Marriage
Living together before marriage does not seem to prevent marital problems. In fact, cohabitation is linked to higher divorce rates when couples do get married. This may be due to the prevalence of churning relationships, where couples repeatedly break up and get back together.
Trends in Cohabitation
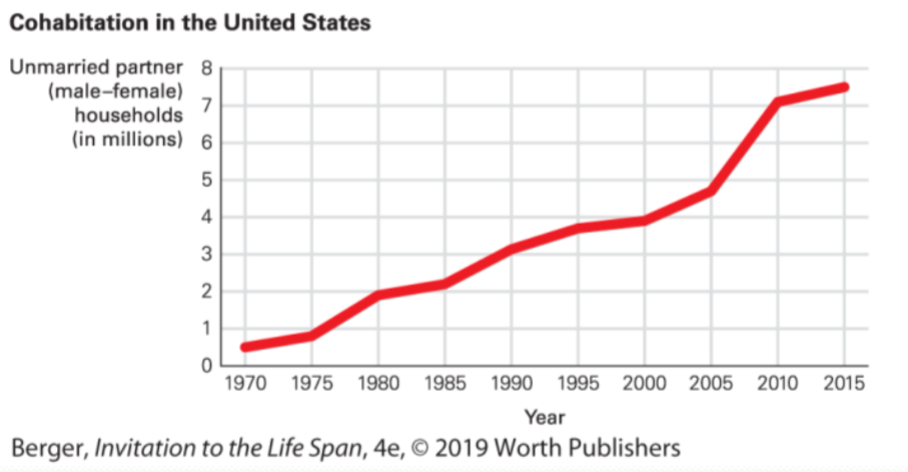
The rate of cohabitation in the US has increased significantly over the years:
Year | Rate of Cohabitation |
1970 | Low |
2015 | Much higher |
This shift in cultural attitude is likely tied to the fact that people are waiting longer to get married due to establishing new careers and other factors.