Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
Fluid Imbalance
Electrolytes
Substances that produces an electrically conducting solution when dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. The dissolved electrolyte separates into cations and anions, which disperse uniformly through the solvent.
Positively and negatively charged ions that:
• Deliver nutrients • Take away waste
(Groceries in Garbage out)
Solutes: particles dissolved in fluid
• Electrolytes • Albumin
Solvent: fluid
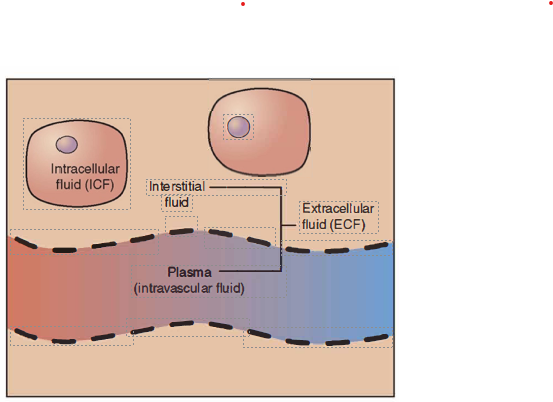
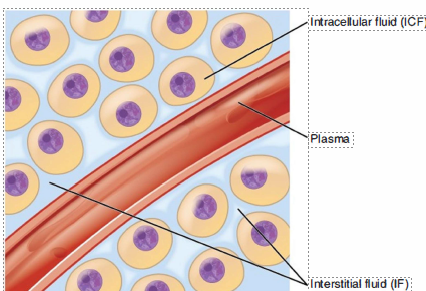
Extracellular fluid (lntravascular)
Intracellular fluid
Interstitial fluid
Fluid Compartments
ICF: Contained in cell. This fluid volume tends to be very stable, because the amount of water in living cells is closely regulated. If the amount of water inside a cell falls to a value that is too low, it becomes too concentrated with solutes to carry on normal cellular activities; if too much water enters a cell, the cell may burst and be destroyed.
ECF: Plasma travels through the body in blood vessels and transports a range of materials, including blood cells, proteins (including clotting factors and antibodies), electrolytes, nutrients, gases, and wastes.
Fluid Compartments
Total Body Water
Human beings are mostly water, ranging from about 75 percent of body mass in infants to about 50-60 percent in adult men and women, to as low as 45 percent in old age. Your brain and kidneys have the highest proportions of water, which composes 80-85 percent of their masses. In contrast, teeth have the lowest proportion of water, at 8-10 percent.
ICF = 40% TBW
ECF = 20% TBW
ISF = (filtrate of blood) Not much water. Some Na+ Except in inflammation (80% of ECF)
IVF = Plasma volume (20% of ECF)
Osmosis
Movement of fluid (solvent) from an area of lesser concentration to an area that is more concentrated. "Dilution to create equilibrium"
Diffusion
Movement of molecules (solutes) from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration
Active, Facilitated and Passive Transport
Central Idea
Transport of molecules across cell membranes
Main Branches
Active Transport
Facilitated Transport
Passive Transport
Active Transport
Definition: Movement of molecules against the concentration gradient, requiring energy
Types:
Primary Active Transport
Secondary Active Transport
Examples:
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Calcium Pump
Facilitated Transport
Definition: Movement of molecules with the concentration gradient, assisted by a carrier protein
Types:
Channel Proteins
Carrier Proteins
Examples:
Aquaporins
Glucose Transporters
Passive Transport
Definition: Movement of molecules with the concentration gradient, not requiring energy
Types:
Simple Diffusion
Osmosis
Facilitated Diffusion
Examples:
Oxygen Diffusion
Water Diffusion
Ion Diffusion
Hydrostatic Pressure
Force against capillary membranes during pumping.
PUSHES fluid into ISF/ICF
Osmotic Pressure
Na+ and Plasma protein (solute/particle) pressure
PULLS fluid into IS/ICF
Oncotic Pressure (Colloidal Oncotic Pressure)
The force exerted by albumin
Osmolarity vs. Osmolality
Osmolarity: number of solute particles per 1 L of solvent
Osmolality is the number of solute particles in 1 kg of solvent.
Na+ is the main determining solute
Tonicity
Tonicity is the relative concentration of solutes dissolved in solution which determine the direction and extent of diffusion.
Isotonic
0.9% NSS
Lactated Ringers
Hypotonic
0.45% NSS
Hypertonic
3%Saline
Fluid Homeostasis
Fluid homeostasis is maintained by:
Habit
Thirst
RAAS
Aldosterone
ADH
Natriuretic peptides
Intake ➔ Distribution ➔ Excretion
Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
Edema:
Inflammation
Dependent /Pitting
Increased hydrostatic pressure
Decreased Osmotic pressure
Sequestered fluids:
"3rd Spacing"
Effusions
Fluid Volume Excess:
SIADH
HF
Fluid Volume Deficit:
Burns
Illness
Fever
Blood loss
Electrolyte Imbalances
Intracellular /Extracellular Prevalence
The prevalence of intracellular anions/cations/substances are those that start with "P".
Sodium (Na+) 135-145mEq/L
Hyponatremia
Renal hypovolemia/hyponatremia (condition) = kidney problems
Non-renal hypovolemia/hyponatremia
Diarrhea
Vomiting
Burns
Dilutional Hyponatremia (dilution)
Hypernatremia
Usually due to dehydration (water loss) or renal impairment where there is no reabsorption of water or no ADH secretion
Dilutional Hyponatremia
Also known as water intoxication, it is a potentially life threatening condition which occurs when a person consumes too much water without an adequate intake of electrolytes
Potassium (K+) 3.5 - 5.2mEq/L
Hypokalemia
Causes:
Diuretics
Poor PO intake
ETOH
Bariatric Surgery
Symptoms:
Nausea/vomiting
Cardiac arrhythmias
Weakness/fatigue
Hyperkalemia
Causes:
Usually caused by renal impairment
Symptoms:
Early = numbness/tingling in extremities, muscle cramping, confusion
Late = Bradycardia, irregular HR, arrest
**Peaked T wave
Calcium (Ca+2) 8.7-10 mg/dL
Hypocalcemia
Causes:
Symptoms:
Neuromuscular excitability
Parasthesias
Seizures
Dementia
Death
Trousseau's/Chvostek's
Hypercalcemia
Causes:
Symptoms:
Flaccidity
Constipation
Decreased neuromuscular activity
Phosphorous (P04-) 2.5-4.Smg/dL
Hypophosphatemia
Causes:
Decreased GI absorption
Increased excretion by kidneys
Intracellular shift (acid/base imbalance)
Symptoms:
Tremors
Parasthesia
Weakness
Hyperphosphatemia
Causes:
Renal Failure
Symptoms:
Neuromuscular excitability
Parasthesias
Seizures
Dementia
Death
Trousseau's/Chvostek
Trousseau's Sign
Hand spasm caused by inflating a blood pressure cuff
Sign of hypocalcemia
Can be observed in patients with tetany
Can be a symptom of hypoparathyroidism
Can be used to diagnose latent tetany
Chvostek's Sign
Facial muscle twitching in response to tapping the facial nerve
Sign of hypocalcemia
Can be observed in patients with tetany
Can be a symptom of hypoparathyroidism
Can be used to diagnose latent tetany
Magnesium (Mg+2) 1.5-2.SmEq/dL
Hypomagnesemia
Causes:
Usually in conjunction with hypokalemia
Diarrhea
Laxative abuse
Sepsis/ETOH
Symptoms:
Chvostek's
Tetany
Arrhythmias - Torsades de Pointes
Hypermagnesemia
Causes:
Renal dysfunction/failure
Symptoms:
Weakness
Hypotension
Arrythmias