Ch 15 Phy Electromagnetic spectrum
Chapter 15: Electromagnetic spectrum
15.1 Electromagnetic Waves
Discovery of Infrared Radiation 🌡
Heating effect strongest for red light, smallest for violet.
Beyond red, thermometer reading increased more → invisible radiation exists → Infrared radiation (IR).
IR = thermal radiation; heat from any hot object.
Radiation & Temperature 🔥
Connection: cool objects → low-frequency radiation; hot objects → high-frequency radiation
Sun: surface ~5500°C → emits UV, mostly absorbed by ozone layer
Ozone depletion → more UV reaches Earth → risk of skin cancer
Electromagnetic Waves Theory 🌊
Prism spectrum → violet refracted most → UV refracted more; IR less.
Light as waves like sound.
Frequency determines colour: red low, violet high.
James Clerk Maxwell: light = oscillations in electric & magnetic fields → electromagnetic waves
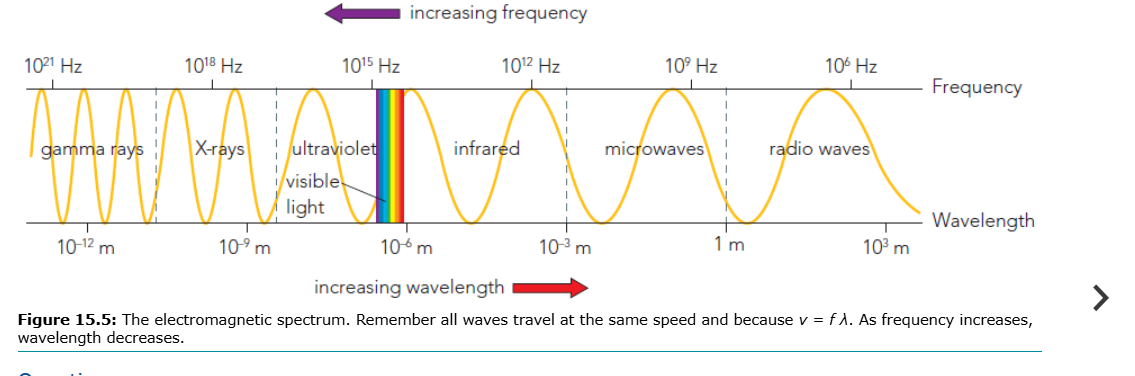
Waves can have any frequency → beyond IR & UV → complete electromagnetic spectrum
Properties of EM Waves ⚡
All transverse waves
Travel at speed of light (~3 × 10⁸ m/s in vacuum)
Can be reflected, refracted, diffracted
Frequency → affects interaction with materials
Wavelength & Frequency 📏
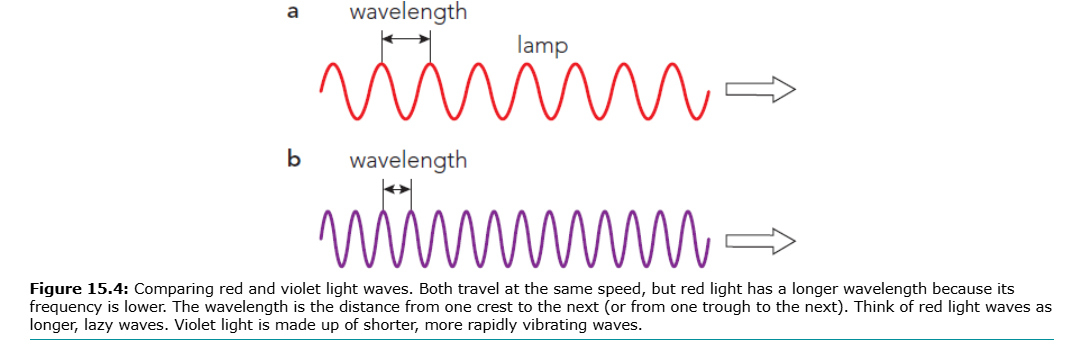
Red light: longer wavelength, lower frequency → "lazy waves"
Violet light: shorter wavelength, higher frequency → "fast waves"
Visible light: 400 nm (violet) → 700 nm (red), frequency ~10¹⁴ Hz
EM waves obey v = f λ → higher frequency = shorter wavelength
Uses of EM Waves 📡
Type | Uses |
|---|---|
Radio waves | Radio/TV broadcasting, radio astronomy, RFID chips for data storage |
Microwaves | Satellite TV, mobile phones, microwave ovens |
Infrared (IR) | Remote controls, grills, toasters, optical fibres, medical imaging & therapy |
Visible light | Vision, cameras, microscopes, photosynthesis |
Ultraviolet (UV) | Forensics (body fluids), banknote security, water sterilisation |
X-rays | Airport security scanners, medical imaging |
Gamma rays | Cancer treatment, sterilisation, cancer detection |
15.2 Electromagnetic Hazards ⚠
All EM radiation can be hazardous
IR → burns
UV → skin/eye damage, skin cancer
Sunbeds → risk of skin damage
High frequency waves (X-rays & gamma rays) → cell mutations, cancer
Protection: distance, shielding (metal cases), warning labels
Microwaves → heating effect; caution for workers near masts & ovens
Mobile phones → only slight heating; prolonged use → potentially higher risk, especially in children
15.3 Communicating Using Electromagnetic Waves 🌐
Satellites 🛰
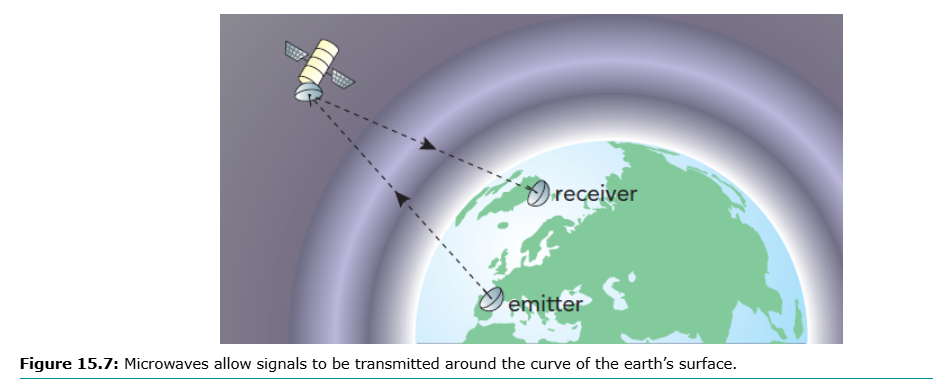
Orbit Earth → transmit information using microwaves
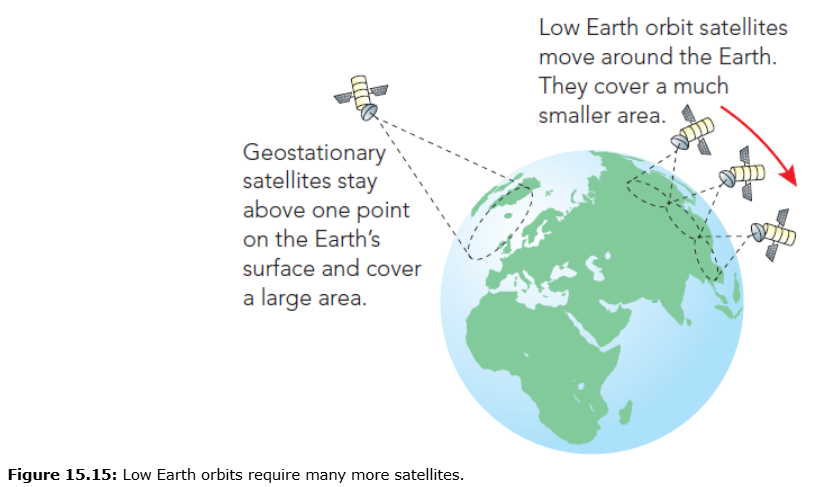
Geostationary satellites: ~35,000 km, stay above fixed point, suitable for TV & satellite phones, slight delay
Low Earth Orbit (LEO): 2000 km, orbit ~2 hours, fast communication, need many satellites, less data per satellite
Right Wave for the Job 📶
Mobile phones / Wi-Fi → microwaves (pass walls, small aerial)
Bluetooth → radio waves, short range, weakened by walls
Optical fibres → IR & visible light, high frequency → carry more data, faster internet
Analogue vs Digital Signals 💻
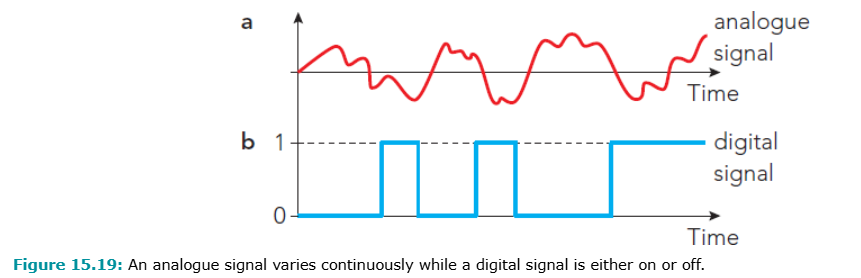
Analogue: continuous signal, varies like sound wave, can distort → noise
Digital: pulses (on/off), clearer, faster, compatible with computers
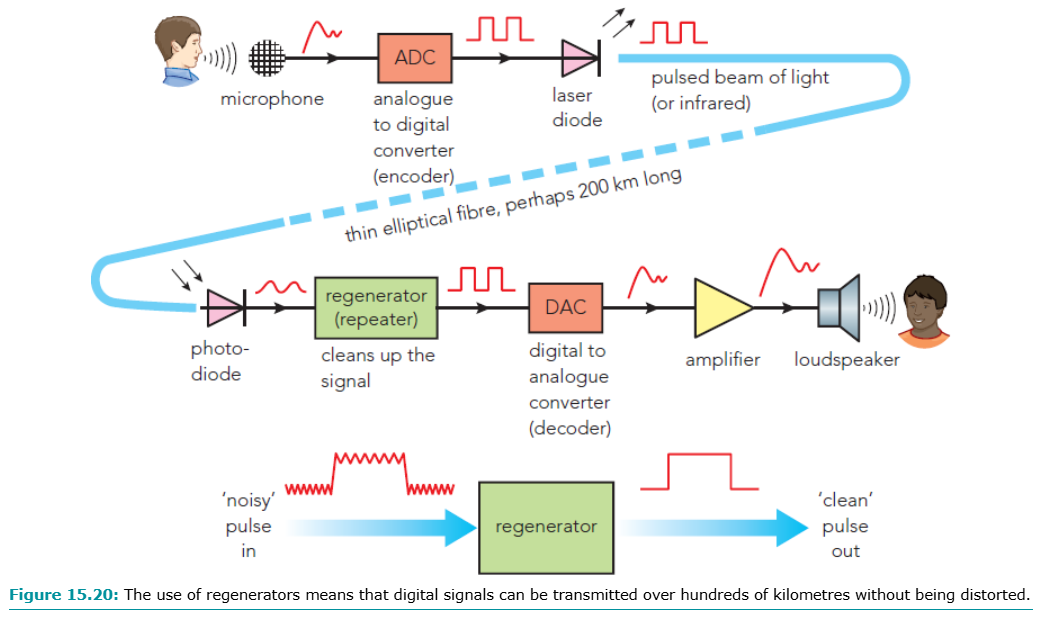
Digital call process:
Sound → analogue → converter → digital pulses
Travel via optical fibres
Regenerators clean & boost signal
Second converter → digital → analogue → sound
Digital signals → high speed, accurate, long distance transmission without distortion
✅ Key Formulas & Concepts
v = f λ (speed = frequency × wavelength)
Higher frequency → shorter wavelength
Hotter object → emits higher frequency radiation
EM spectrum: radio → microwaves → IR → visible → UV → X-rays → gamma
Random monkeys invade villagers using x-ray guns.