Lecture 9: Earth Formation, Hadean, and the Archean
Formation of Our Solar System
Big Bang Theory
Big Bang Theory: leading explanation of universe formation caused by a cataclysmic explosion; ~13.8 Ga
Before explosion, all matter and energy was packed into one point, then released (exploded).
Our Galaxy and Solar System
Billions of galaxies
Our galaxy: Milky Way
~300 billion stars
Sun is our star
Stars, Asteroids, and Comets
Star: immense ball of incandescent gas in which nuclear reactions produce heat and light.
Multiple stars = galaxy
Asteroids: Chunks of rock and/or metal which range in size that orbit sun.
Comets: Chunks of ice, dust, and other frozen gases.
When a asteroid or meteor comes into our atmosphere, it usually burns up, does not pass.
Meteors get in our atmosphere but burn up and do not pass through.
Meteorites pass through atmosphere and lands on the planet.
Nebula
Nebula: Slowly rotating and collapsing cloud of dust and light gases.
Nebular formation
Nebula contracts under gravity in a disk
Contraction accelerates rotation of disk
Matter concentrates in center, forming a proto-sun
Proto-sun becomes dense and hot; fusion ignites (coming together)
Early Solar System
How our planets form
Littered with debris
Accretion of matter (clumping of particles)
As planets grew, gained more gravitational energy attracting more matter
Planetesimals → protoplanets → planets
Smallest to biggest
The Sun, Planets, and Everything Else
Sun comprises of 99.8% of mass of entire solar system
Rest is Earth, 7 planets, and everything else
All material and space debris is removed from a planet’s orbit
There is still debris in Pluto’s orbit, so its not a planet.
The Hadean Eon
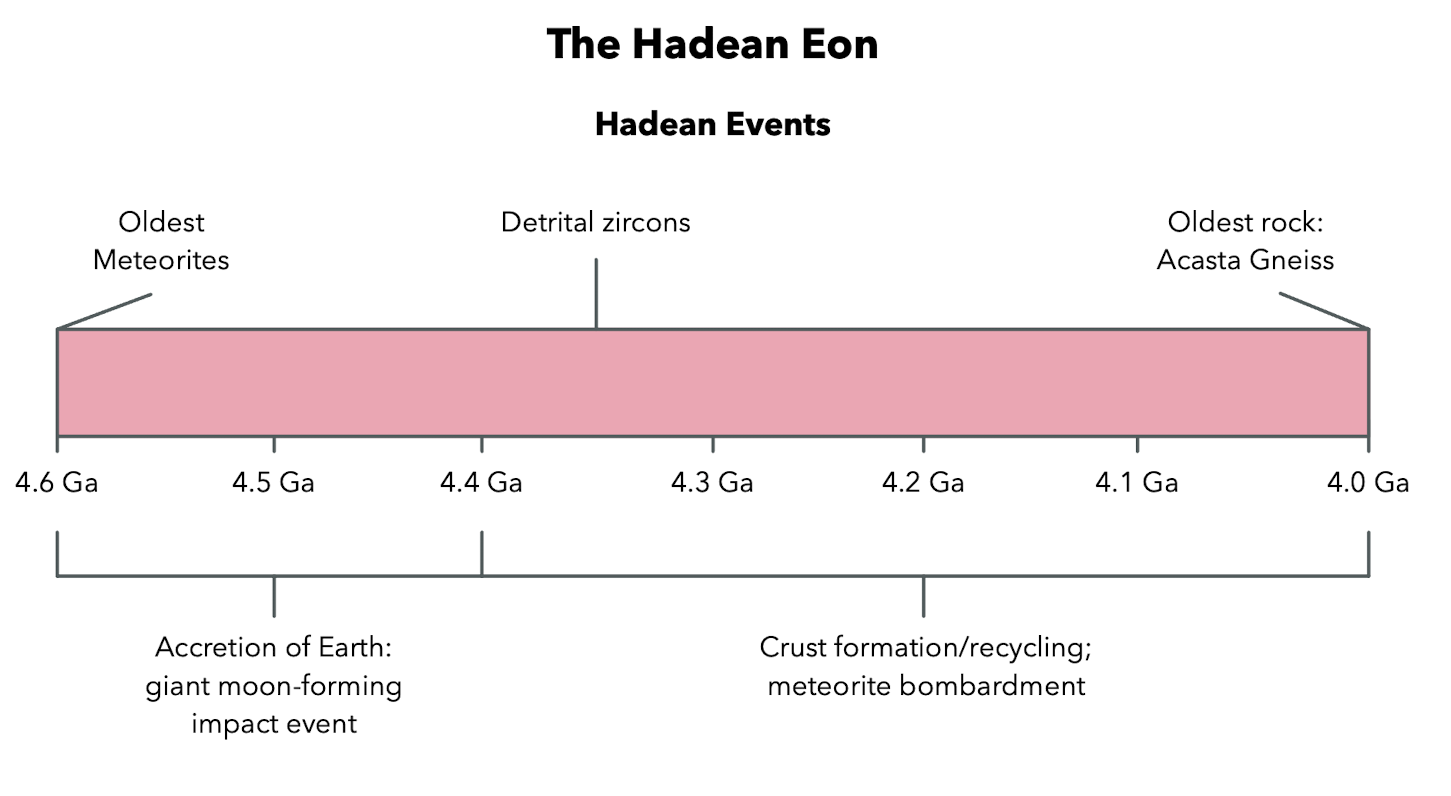
Eons Remembered
Precambrian: ~4.0 billion years
~87-88% of geologic time
Hadean: <0.6 billion years
Archean: 1.5 billion years
Proterozoic: 2 billion years
Phanerozoic: ~540 million years
~12-13% of geologic time
Early Earth
Early Earth took up debris from its orbital path
“Hadean” → Hades, Greek God of underworld, hot, melt, magma
Intense bombardment and extreme volcanism
Period of time from the formation of Earth until the surface cools enough to solidify
Any melt that cooled enough to form crust on surface didn’t last long.
No rock record from this eon
Period of time for differentiation
Differentiation: The process where a planet separates into different layers, like a core, mantle, and crust, based on density.
Melted or partially melted material start to separate into different layers based on their density.
Crust is the lightest, core is the densest
Materials separate into layers based on their density
“Giant Impact” Hypothesis - The Formation of the Moon
Now widely accepted
Impact of Mars-sized planetesimal on the early Earth resulted in formation of the moon.
Results in loss of volatile elements due to collisional heating - probably melted both bodies.
Modeling suggests Moon is formed from mantles of both bodies and Earth retains cores.
Collision also gives earth’s axis its 23° tilt, produces the high angular momentum of the Earth-moon system.
Early Atmosphere and Oceans
First (primordial) atmosphere from degassing, melting, evaporation. H and He lost quickly
Liquid water was present by 4.4 Ga
Moon was much closer in the sky because it had just broken away, and it would have had enormous pull, causing true tidal waves to sweep across the earth.
Earth spun faster, so a complete day-night cycle was only 10 hours long
The Archean Eon
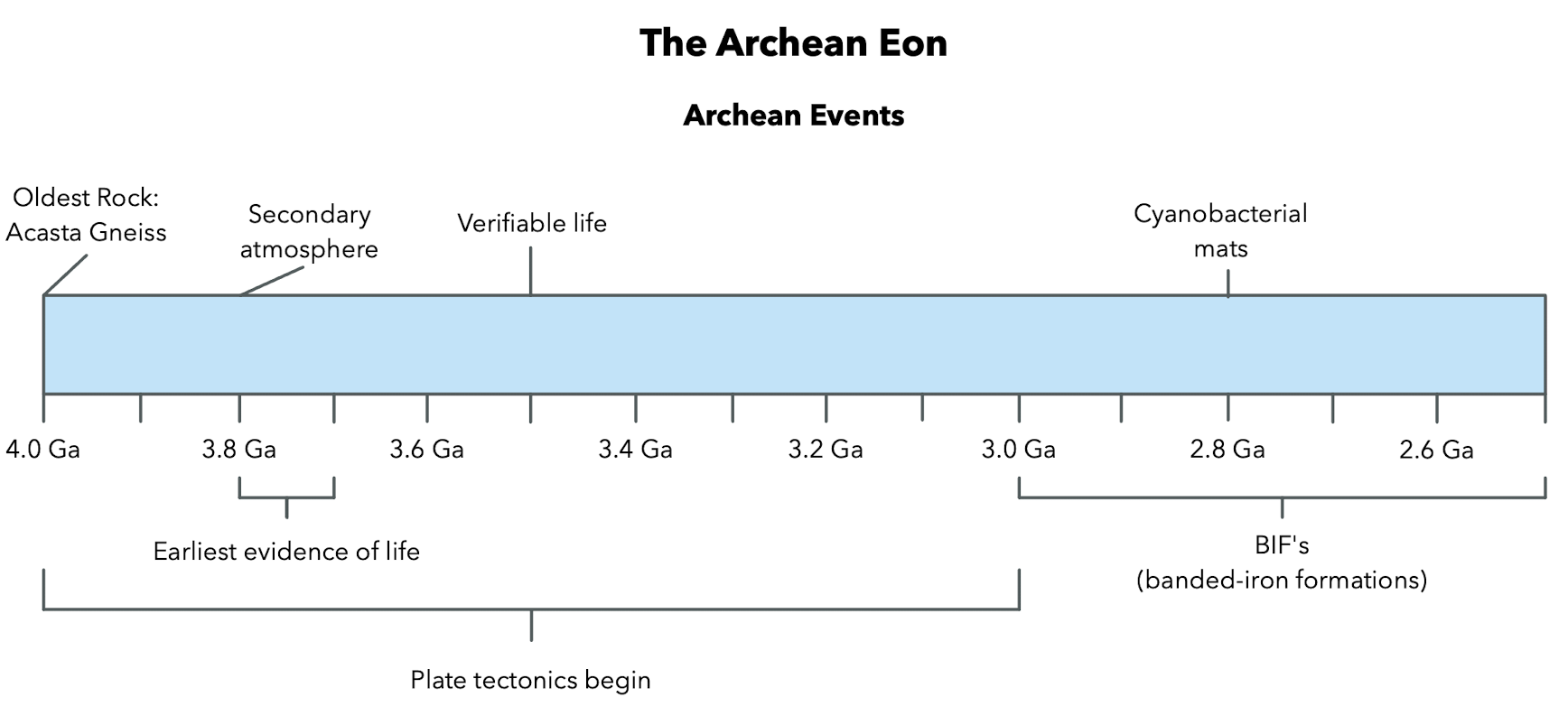
Secondary Atmosphere
Very different from today
H and He (most abundant in the universe) and H2O vapor (too hot for condensation)
Was likely lost to space
Lack of atmospheric pressure (Earth’s gravitational attraction is insufficient to retain gases)
Before Earth differentiated, it lacked a magnetosphere → solar winds (stream of charged particles released from the sun) can blow it away
Magnetosphere is produced because of our core.
Earth’s Early Atmosphere
Earth’s early Archean atmosphere (before 3.8 Ga) had nearly 0% O; any that existed combined with Fe.
Air consisted of H2O vapor, CO2, N, other (e.g. modern volcanoes)
Earth differentiation and magnetosphere formed
Atmosphere began accumulating as a result of volcanic outgassing.
O2 in Earth’s Early Atmosphere
Lack of free oxygen in Earth’s early atmosphere
Oldest sedimentary rocks lacked oxidized iron
Level of O in the early Earth’s atmosphere was < 0.01% of present day level
Banded Iron Formations (BIF)
Banded Iron Formations (BIFs): Layers of iron-rich rocks that show evidence of early oxygen production by ancient bacteria.
Archean-Proterozoic (~3.0-1.8)
What was the Eventual Source of O2?
Evolution of the atmosphere and living things occurred independently
2 main processes generated oxygen:
Photochemical dissociation: the breakup of H2O molecules into H and O
Photosynthesis: the splitting of carbon dioxide into carbon and free oxygen
Where did Oceans Come From?
Water from volcanic outgassing
Outgassing: gases coming out of volcanos, the gases can have water, carbon dioxide, and more.
Water from comet/asteroid bombardment (~3.9 Ga)
Rain accumulated in ocean
Originally all waters are freshwater
Not sure the exact hydrological cycle in early days
How Did Life Originate?
Spontaneous Generation: Life spontaneously originates from inorganic matter (abiogenesis); disproven.
Pasteur’s experiment → life was spawning from insects laying eggs on spoiled food.
Panspermia: Life is extraterrestrial in origin.
Biochemical Theory
Biochemical Theory: Chemical evolution from simple organic compounds (inorganic model)
Primordial Soup
The Miller - Urey Experiment
Warm ocean (water)
Lightning (energy source)
Condenser to turn water vapor back to liquid
Reduced atmosphere (lack of O2)
Accumulation of primordial soup in a “warm little pond” (Darwin)
What do Amino Acids Mean
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins.
Not life, just one piece of of building something to become alive.
Miller’s experiment showed that natural processes could easily produce amino acids.
Later experiments found 20 amino acids
74 amino acids found in chondritic meteorites.
The Origin of Life: Warm Little Pond or Deep Sea Hot Spring?
It is possible for life to have originated from deep-sea hot springs.
A lot of uncertainties remain: including the CO2 and O2 levels at the time of life origin
Hydrothermal Vents: Evidence of Life
Hyperthermophiles: Microorganisms that live in high-temperature environments; some of them are chemoautotrophs
Organisms that make their own good using chemical energy.
Life of the Archean
Earliest evidence for life is 3.7-3.8 Ga (in Greenland)
Verifiable evidence for life is 3.5 Ga (Australia)
Fossil bacteria
Life for a majority of Earth’s history has been single-celled
By 2.8 Ga, cyanobacterial mats and other photosynthesizing organisms had dramatically changed the atmosphere.
Leading to the Proterozoic
2.8 Ga Stromatolites
Cyanobacterial mats
Photosynthetic - energy from sunlight
Still around today
When Tectonics Begin?
Plate tectonics is believed to begin during early to mid-Archean (3 to 4 billion years ago)
3.8 billion year old rock from Greenland
Consist of deep ocean sediments and sea-floor volcanics (pillow basalts) pushed up onto continental crust
When lava pours out from the bottom of the ocean, the cold water cools it quickly forming the basalt pillows.
Show signs of having been subducted
Pillow basalts commonly found in subduction zones.
Hydraulically altered (because of subduction)
Review Questions
What is the Nebular Theory? What is accretion? How do these processes explain formation of our solar system and planets? What is the Giant Impact Hypothesis (formation of the moon)?
The Nebular Theory posits that the solar system formed from a large cloud of gas and dust, known as a nebula, which collapsed under gravity to form the Sun and planets.
Accretion is the process by which particles and small objects collide and stick together, gradually forming larger bodies like planetesimals and eventually planets.
The Nebular Theory describes the initial collapse of the nebula leading to the formation of the Sun, while accretion explains how particles within the surrounding disk clumped together to form planetesimals, which further coalesced into planets.
The Giant Impact Hypothesis suggests that the Moon formed from debris ejected into orbit around Earth after a colossal collision with a Mars-sized body; collision gave earth’s axis its 23° tilt.
What were the early atmospheres like? How did they form?
They were mostly made of gases like hydrogen and helium, along with volcanic gases such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and methane. These atmospheres were very different from the ones we have today because of their lack of oxygen.
These early atmospheres formed from the leftover gases in the nebula that created the solar system, along with gases released from volcanic eruptions on the young planets. Over time, the composition of Earth's atmosphere changed significantly due to processes like volcanic activity, chemical reactions, and the emergence of life, which added oxygen through photosynthesis.
What are three theory’s on how life formed?
Biochemical Theory (Primordial Soup): Life started in a "soup" of chemicals in the ocean, with lightning or sunlight helping these chemicals turn into the first living things.
Hydrothermal Vent Theory: Life began at hot vents on the ocean floor, where heat and minerals created the right conditions for life to start.
Panspermia Theory: Life came to Earth from space, possibly on comets or meteorites that brought tiny life forms or the building blocks of life.
What evidence of life is there? When did life begin?
Fossils, stromatolites, hyperthermophiles, and BIF’s.
Earliest evidence for life is 3.7-3.8 Ga; Verifiable evidence for life is 3.5 Ga (fossil bacteria).
What happened during the Hadean Eon? What happened during the Archean Eon?
Hadean Eon: Accretion of Earth, meteorite bombardment, detrital zircons, crust formation, oldest intact rock (Acasta Gneiss)
Archean Eon: Secondary atmosphere formed, found earliest evidence of life, found evidence verifiable life, plate tectonics begin, cyanobacterial mats, BIF’s