1.1.2 Market Research
Market research is the action or activity of gathering information about consumers’ needs and preferences. It helps companies to identify potential opportunities and threats, better understand their customers and the competitive landscape, and make informed decisions
Market Oriented vs Product Oriented:
When a business is market oriented the consumer is the most important factor when provididng products for the market.
When a business is product oriented, the product is the most important factor when providing products for a market.
Primary Research
Primary research is finding out original information first hand - for example going on the street and asking questions.
primary research is original data gathered by the researcher
The information does not exist yet so it couldn’t be found on the internet
Brand new data which the business will gather specific to their product or service
They will then use this data to make decisions about the business - ie new products.
methods of conducting primary research include:
Questionaries / Surveys
Consumer Panels
Interviews
Observation
Loyalty cards (businesses use these to track customers purchases)
Focus Groups
Test Marketing
Retailer Research
Secondary Research
Secondary research is finding out information that has already been gathered - for example finding data online or from the government.
examples of these could be:
Internet
Trade Press
Annual Reports
Internal Data
Government - produced data
Specialist Organisation Publications
News Stories
Types Of Data
Quantitative Data
Quantitative data is information that can be measured using numbers and analysed using mathematical or statistical methods.
Examples of quantitative data include sales figures, population demographics, experiment results, and financial data.
Qualitative Data
Qualitative data is non-numerical information that is descriptive and subjective.
It's collected through observations, interviews, and open-ended questions and used to gain a deeper understanding of people's experiences and behaviours.
Examples of qualitative data include interview transcripts, survey responses, field notes, and case studies.
Limitations Of Market Research
Market research is very helpful but it can have limits if the data is not accurate.
How to analyse data:
Validity
does the market research tell you something meaningful?
Reliability
when you take opinions of a group of people they need to be representative of the whole target population. THe smaller the sameple size the more you can question the validity of that sample because you cannot have statistical confidence in the results.
Bias
when picking your sample population it is important that they are representative of the whole population.
Other examples of bad market research:
research carried out doesnt give enough information
inaccurate or misleading data
data non specific to the organisation
time limitations
budget limitations
asking wrong questions in primary research would gather wrong data
reluctance of respondents to participate in research
data taken a while ago
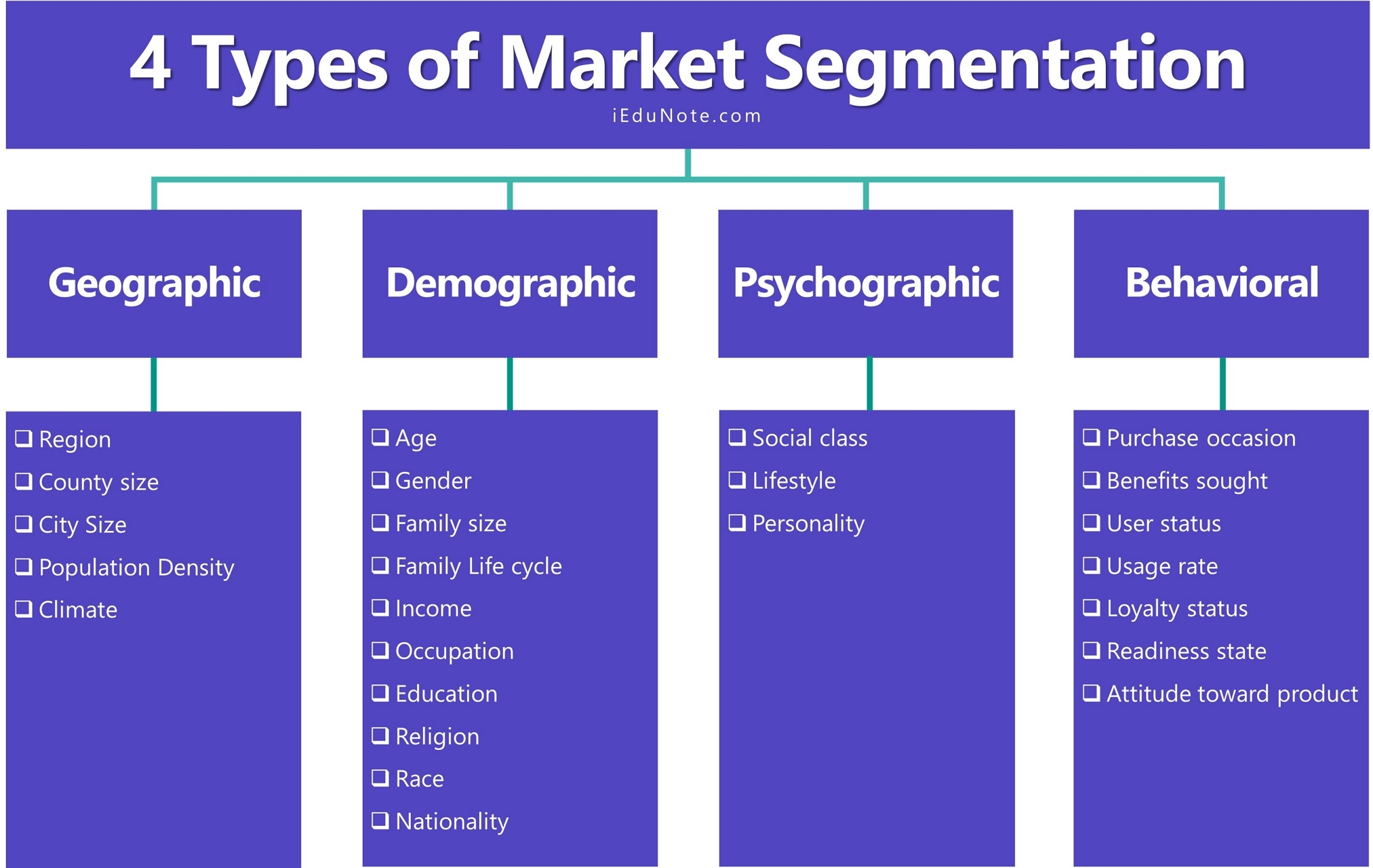
Market Segmentation
an identifiable group of individuals (or part of a market) where consumer share one or more characteristics or needs.
Market segmentation can be done through
demographic
geographic / location
behavioural, based on usage or attitude to product e.g occasional, everyday
Psychographic - personality types
Religion or ethnicity - eg halal or kosher food seekers
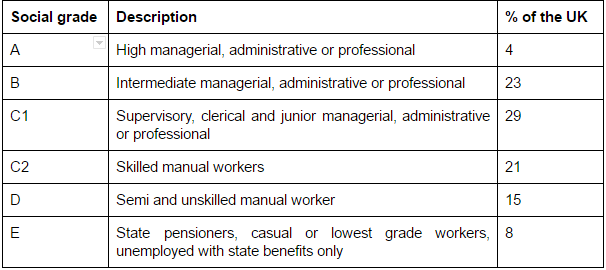
For example if you wanted to segment the market according to social class you may targetto A,B,C1 or D,E consumers: