Atomic Structure & Periodic Table – One Page Study Guide ⸻ Atomic Scientists (In Order) Democritus – matter made of indivisible particles (atomos) Dalton – modern atomic theory; atoms combine in whole-number ratios J.J
Atomic Scientists (In Order)
Democritus – matter made of indivisible particles (atomos)
John Dalton – modern atomic theory; atoms combine in whole-number ratios
J.J. Thomson – discovered the electron; plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford – discovered the nucleus; atom mostly empty space
Neils Bohr – electrons in fixed energy levels
James Chadwick- discovery of neutrons
Werner Heisenberg- uncertainty principle
Periodic Table: Element Types & Location
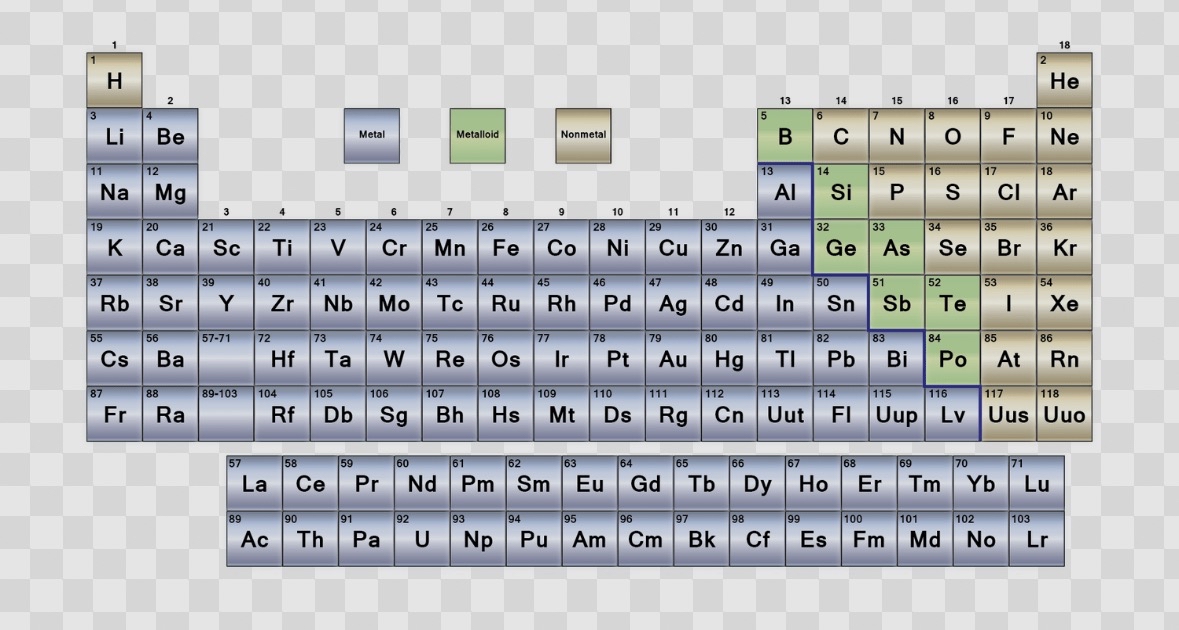
Metals – shiny, conductive, lose electrons
Nonmetals – dull, brittle, gain electrons
Metalloids – mixed properties
Ions & Isotopes
Ion – charged atom
• Cation: positive (lost electrons)
• Anion: negative (gained electrons)
Isotopes
• Same protons
• Different neutrons
• Different mass
Periodic Table Groups
Group Name | # | |
Alkali Metals | 1 | |
Alkaline Earth Metals | 2 | |
Transition Metals | 3-12 | |
Boron Group | 13 | |
Carbon Group | 14 | |
Nitrogen Group | 15 | |
Oxygen Group | 16 | |
Halogens | 17 | |
Noble Gases | 18 |
Total Electrons = atomic number (neutral atoms)
Valence Electrons =
• Outer shell electrons
• Control reactivity