Optional Study Guide
Lab Report
Difference between p-value >0.05 and p-value <0.05
If the p value is less than 0.05 we reject the null hypothesis.
If the p value is greater than 0.05 we fail to reject the null hypothesis
Be able to interpret if there is a significant difference if given t-stat and critical value.
If the test statistic lies outside of the boundaries defined by teh critical value, the result is statistically significant.
If the test statistics does not lie outside of the boundaries set by the critical value, the result is not statistically significant.
Know the chemical properties of both plant defense extracts: coffee and kava.
Coffee → contains caffiene which is a stimulant.
Kava → contain kavalactones which interact with neurotransmitter systems in the brain, promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety without impairing mental clarity.
Lavender → contains linalool which is a relaxant
What is the scientific name of the specimen we used?
Artemia salina
Be able to identify various fungi taxa:
Chytridiomycota:
Ancient fungi
Unicellular
Aquatic decomposers
Parasites living on water molds, insects, or snakes
Zygomycota:
Bread molds
Ex: Pilobolus spp., the “hat-throwing” fungus
Glomeromycota:
Mutualists that form a symbiotic relationships with the roots of plants
Mycorrhizae
Ascomycota:
Largest phylum of fungus
Examples: Truffles, Morels, Yeast,
Penicillium First “wonder drug,”
Basidiomycota:
Mushrooms
Shelf fungi
Puffballs
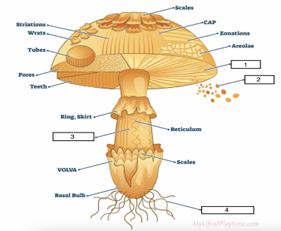
Be able to identify the different parts of the mushroom:
What are the 3 distinct types of Lichen?
Foliose (common ones that grow on trees)
Crustose (dense)
Fruticose (light and delicate)
Be able to identify the major anatomical structures in a typical fungus: Cap, Gills, Stipe/Stalk, Mycelial threads
Animal Blueprints
Be able to identify various taxa:
1. Phylum Porifera:
Evolved from choanoflagellates
No tissues or organs
Mostly marine sessile creatures
Reproduce asexually by budding
Reproduce sexually by being monoecious → containing both male and female reproductive organs
Respiration and excretion occur
through diffusion
2. Phylum Cnidaria:
Stinging cell: cnidoblast
Stinging organelle: nematocyst
Budding
Dioecious → two organisms contain separate male and female gametes.
Radial symmetry (Diploblastic) + incomplete GI tract
Dimorphism (two morphological forms): medusa
(jellyfish) vs polyp (coral)
3. Phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms):
Free-living or parasitic flatworms
Bilateral symmetry, triploblastic, acoelomate
Anterior and posterior ends
Only one opening (mouth)
No respiratory or circulatory systems → perform gas exchange through diffusion
Cephalization → formation of the head
Classes:
Turbellaria
Cestoda
Trematoda or Planaria
4. Phylum Nematoda (roundworms):
Cylindrical and elongated body shape
Bilateral symmetry and triploblastic structure
Psuedocoelomates with a complete digestive system
Many are parasitic, affecting a variety of hosts
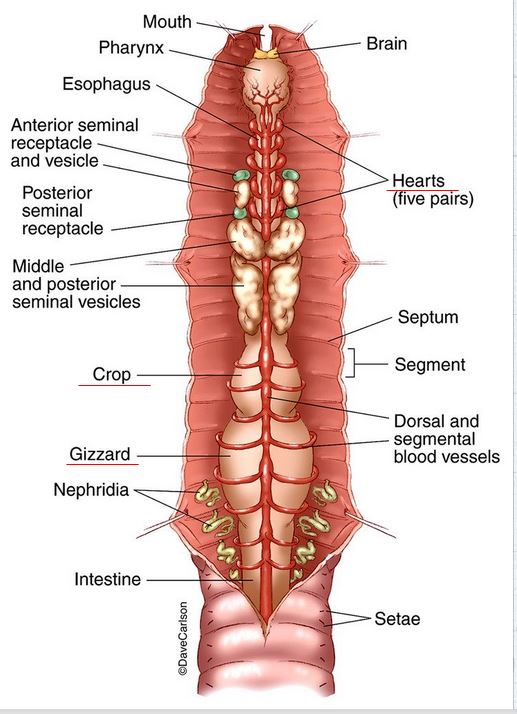
5. Phylum Annelida (earthworms or segmented worms):
Segmented body structures.
Bilateral symmetry, triploblastic.
Possesses a true coelom.
Closed circulatory system.
Contains a simple nervous system.
Reproduces both sexually and asexually.
Be able to identify Planaria and the background of it.
Planaria is a part of the Platyhelminthes
Looks like this:

Be able to identify the different parts of an earthworm:
What are the two life stages of cnidarians?
Polyp
Medusa
Understand major differences between Platyhelminthes vs. Annelida
Platyhelminthes (flatworms):
Acoelomates (lack a body cavity).
Generally have a flat, ribbon-like body structure.
Can be free-living or parasitic.
Possess bilateral symmetry and are triploblastic.
Gas exchange occurs through diffusion across the skin.
Annelida (segmented worms):
Coelomates (possess a true body cavity).
Characterized by segmented body structures.
Have a closed circulatory system.
Exhibits bilateral symmetry and is triploblastic.
Reproduce both sexually and asexually, with many being hermaphroditic.
More complex body systems compared to flatworms, including a nervous system with a brain and more specialized organs.
Animal Blueprints: part 2
What animals are in Mollusca:
Chitons, octopi, cuttlefish, squid, nautilus, bivalves, snails and slugs
What are Chelicerata(horseshoe crabs) more closely related to?
Spiders and ticks
What are the three tagmata of arthropods?
Head, thorax, abdomen
Identify radula and its function.
A radula breaks apart food particles fo reating and it looks like this:
What is the most diverse animal phylum?
Arthropods (more than 1000000 species
Difference between millipedes and centipedes.
Millipedes: two pairs of legs per body segment, slow-moving, feed on decaying plant matter.
Centipedes: one pair of legs per body segment, fast-moving, carnivorous,
What is ecdysis and who performs this?
Ecdysis is the molting process. Performed by arthropods, insects, crustaceans, reptiles.
Building a better tetrapod
Be able to identify and know the functions of the parts of a starfish.
Tube feet → movement
Madreporite →
Ring canal → Circulating water
Ambucatral ridge → Houses the tube feet, locomotion, feeding, adhesion
Distinguish between a hagfish and a lamprey.
What are the 5 major features of Chordata?
1. Notochord
2. Pharyngeal slits
3. Dorsal hollow nerve chord
4.
5.
Understand different symmetry.
What are the lateral lines and swim bladders used for in fishes?
What makes up Osteichthyes and Chondrichthyes?
Vertebrates
What are vestigial structures?
Define the following:
1. Endotherm:
2. Ectotherm:
3. Poikilotherm:
What type of teeth differentiation can animals have? (define the difference)
1.
2.
Major features of Class Reptilia
Why are amphibians restricted to water?
What animals possess amniotic eggs?
Be able to identify different parts of the frog.
Do all tetrapod’s have the same general internal structure and who did they evolve from?