Botany🌹🌲
Survival of Plants:
- Need sunlight (energy for photosynthesis)
- Water
- Minerals/Nutrients
- Phosphorous
- Potassium
- Magnesium
- Calcium
- Nitrogen
- Gas exchange with environment
- Movement of water and nutrients from roots to leaves
- Diffusion
- Specialized tissues
Early Plants:
- Origins in the water (algae)
- First plants evolved from plant-like protists (algae) similar to multicellular green algae of today (chlorophyta)
- Oldest known plant fossil: 450 mya
- Similar to mosses of today
4 Divisions
- [ ] %%Mosses%%
- [ ] ^^Ferns^^
- [ ] @@Conebearers@@
- [ ] ==Flowering plants==
%%Byrophytes (Parent Group):%%
These are %%Mosses%% and Relatives
%%Nonvascular%%
- They depend on osmosis to deliver water; this keeps them small
Groups:
- Mosses: most common
- tolerant in harsh environments
- Liverworts: “flat leaves”
- attached to the ground
- Hornworts: Phylum: Anthrocerophyta
%%Life Cycle:%%
- It is dependent on water because sperm of bryophyte must swim to an egg
- NO SEEDS
Human Uses:
- Sphagnum:
- Accumulates in peat deposits
- Retains water

%%Vascular Tissue%%%%: transportation system that allows for the movement of fluids against gravity%%
%%Two types:%%
- %%Xylem:%% %%carries water up%%
- %%Phloem%%%%: carries nutrients and carbohydrates down%%
^^Ferns and Relatives (Vascular):^^
- Club Mosses
- Horsetails
- Ferns
They all have true:
- Roots: underground organs used for absorption
- Leaves: photosynthetic organs
- Veins: gathering of xylem and phloem
- Stems: supporting and connecting structures
^^Life Cycle:^^
- Develop haploid spores on undersides of fronds called Sporangia
- Grouped in clusters of sori
- Fertilization requires at least a small film of water
Seed Plants:
- Gymnosperms
- Angiosperms
- These are the most successful plants
- Adaptations:
- Allows for reproduction without water
- Includes flowers and cones
- Pollination transfers sperm
- Embryos are protected in seeds
- Pollen grain: where entire male gametophyte is contained
- Sperm do not swim
- These are carried to female reproductive structure through: insects, wind, or small animals
- Seed: embryo of plant
@@Gymnosperms (Cone Bearers)@@ :
- Most ancient seed bearer
- Gymnosperms Includes:
- Gnetophytes, Cycads, Ginkgoes, Conifers
- Gnetophytes:
- Phylum: Gnetophyta
- Only 70 species
- Cycads:
- Phylum: Cycadophyta
- Palm-like plants
- Only 9 genera exist today
- Ginkgoes:
- Phylum: Gingkophyta
- Conifers:
- Phylum: Coniferophyta
- Most common gymnosperm
- 500 species
- Pines, spruces, redwoods, sequoias, cedars
- Ecology of Conifers:
- Wide variety of habitats
- Evergreens
- Have adaptations such as needle shaped leaves and waxy covering to protect from dry conditions
==Angiosperms (Flowering Plants)== :
Flowers: unique reproductive structures
Pollination through animals is more effective than wind pollination
Flowers contain ovaries, which surround and protect the seed
After pollination, ovary develops into a fruit (wall of tissue surrounding the seed)
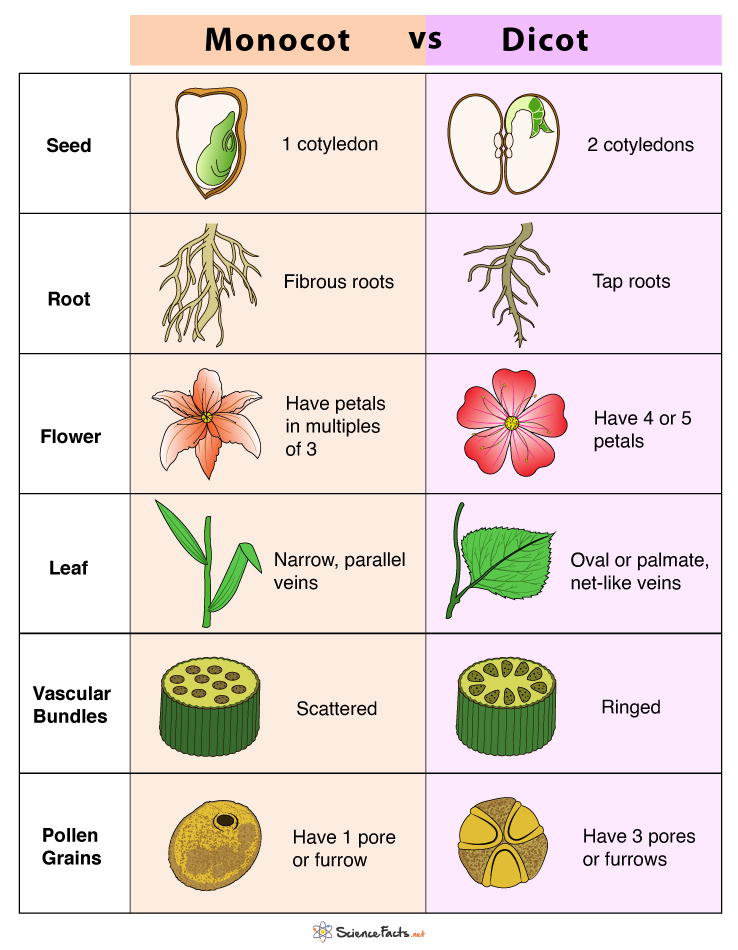
Two classes of Angiosperms:
- Named for the number of leaves (cotyledons) in plant embryo
- Monocots: one seed leaf
- Corn, wheat, lilies, orchids, palms
- Dicots: two seed leaves
- Roses, clover, tomatoes, oak, daisies
Groups By Stems:
- Woody: have thick cells
- Trees, shrubs, vines
- Herbaceous: do not produce woody stems
- Sunflowers, pansies, etc