Unit 12.2 Program Design
Aims
Know different tools that can be used to design a new program
Know what a structure chart is used for and construct these to show the different components in a program
Know what a state-transition diagram is used for and construct these to show the different states a program can have.
Program Design Tools
Design stage - structure of new program is defined - components, modules and their interactions, done by:
Structure Charts
Pros
Gain overview of whole program e.g. easily identify: modules and their hierarchy, task order, different parameters passed between modules.
easily identify parts of solutions that can be re-used elsewhere
Additional steps/refinement, new parts become simpler and easier to work with.
Unit 9.1 Computational Thinking Skills -
problem decomposition - breaking big problems into smaller sub-problems.
stepwise refinement - to break down big problems into smaller single-task problems, the smaller problems can be programmed independently of others.
Structure chart - shows small problems and how they interact with each other to form whole program.
Example

4 different modules: UpdateLoan, LoanExtend, CheckReserve, LoanReturn
Arrows show parameters passed between the modules
The structure chart shows:
UpdateLoan
Calls either module LoanExtend or module LoanReturn
LoanExtend
Is called with parameters LoanID and BookID
Calls module CheckReserve to whether books been reserved with another user
Returns TRUE if loan has been extended otherwise returns FALSE
CheckReserve
Is called with parameter BookID
Returns TRUE if book has been reserved otherwise returns FALSE
LoanReturn
Is called with parameters LoanID and BookID
Will return REAL value (fine value of overdue loan)
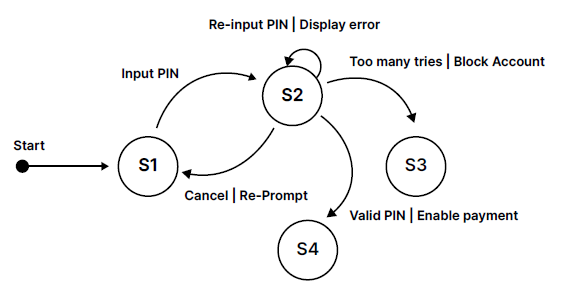
State-Transition Diagrams
Picture representation of program behaviour, showing various states the program can be in and the transition and triggers of them.
Start State - State the program begins, represented by incoming arrow usually labelled “Start”.
States - different situations the program can be in, each state shown as a circle, program can only be in one state at a time.
Transitions - join states together and show changes from one state to another, shown as directional arrows.
Conditions - condition or input that causes program to transition - labelled onto transition arrows.
Examples
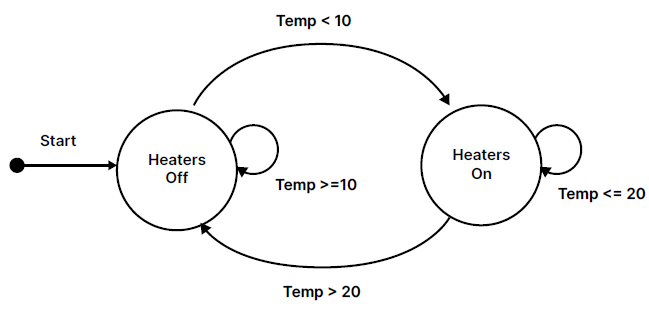
Start State - Heaters off (incoming arrow) and one other state - Heaters off
Transition arrows show changes from one state to another, and are labelled with the conditions that trigger them.
States can be used to determine inputs and outputs (think truth table)
Current State | Input | Output | Next State |
S1 | Input Pin | - | S2 |
S2 | Re-input Pin | Display Error | S2 |
S3 | Cancel | Re-Prompt | S1 |
S4 | Valid Pin | Enable Payment | S4 |
S5 (?) | Too Many Tries | Block Account | S3 |