WEEK 2 (History of Science)
what are the examples of the curiosity of humankind?
Astronomy (Mesopotamians believed that Earth was at the center of the Universe)
Metallurgy (The extraction of iron, which led to the Iron Age) + (extraction of copper and tin which led to the Bronze Age)
Medicine (certain plants could be used to treat sickness and disease)
what is the history timeline of technology?
Paleolithic Age / The Old Stone Age (500.000 BC - 10.000 BC)
Mesolithic Age (10.000 BC - 4.000 BC)
Neolithic Age (4.000 BC - 2.300 BC)
Bronze Age (2.300 BC - 700 BC)
Iron Age (700 BC - 450 AD)
The Medieval Age (450 AD – 1,400 AD)
The Renaissance Age / Enlightenment (1,400 AD – 1,750 AD)
Industrial Age (1750 AD – 1950 AD)
what are the inventions + impacts of the (Paleolithic) Age?
Stone tools / helped humans in butchering carcasses, chopping wood, skinning an animal for clothing and making fire
what are the inventions + impacts of the (Mesolithic) Age?
Pressure flaking and prepared-core techniques / helped with the gradual domestication of animals and agriculture which led to settled communities
what are the inventions + impacts of the (Neolithic) Age?
polished stone tools / the first steps in mining technology. The polished axes were used for forest clearance and the establishment of crop farming
what are examples of Engineering Design during the Neolithic Age?
(Mesopotamian) engineers used clay tablets to document irrigation systems
(Babylonian) engineers used mathematical concepts such as algebra for land excavation calculations
(Egyptian) engineers built the pyramids
what are the inventions + impacts of the (Bronze) Age?
Bronze jewelry, tools and weapons / The use of bronze replaced stone tools and allowed humans to greatly alter their environment
what are the inventions + impacts of the (Iron) Age?
Iron farming equipment, Iron weapons / Military dominance for cultures that could produce iron weapons + increasing the food production
what are examples of Engineering Design during the Iron Age?
(Greek engineers) created the crossbow and catapult to conquer territories
(Roman engineers) created aqueduct systems, sanitary systems, and an extensive road system
what are the inventions + impacts of the (Medieval) Age?
Improved harness for horses, cast iron, cannons, mechanical clocks, compass
Early Middle Ages (increased pressure from invasion lead to depopulation and deurbanization)
High Middle Ages (the beginning of feudalism, population increase, and agricultural innovation)
Late Middle Ages (famine, plague and war, often marked by the Black Death, which killed approximately one-third of the population)
what are examples of Engineering Design during the Medieval Age?
(Technology) like the windmill, produced mechanical labor
The printing press was used to share information and knowledge
The word (engineer) began to appear as (ingeniare) or to design or devise
what are the inventions + impacts of the (Renaissance) Age?
Telescope, microscope, thermometer / The Instrumentation enabled scientists to observe and quantify natural phenomena
what are the inventions + impacts of the (Industrial) Age?
Electricity, automobile, airplane, radio, television, telephone, rocket / The rise of professionals, population expansion
The architectural period in the (Bronze age) included what?
combining copper and tin to produce bronze
The architectural period in the (Medieval age) included what?
The architectural period after the Roman Empire
The architectural period in the (Iron age) included what?
the prevalent use of iron or steel
The architectural period in the (Renaissance age) included what?
the revival of classical influence and the sharing of ideas (reborn in Italian)
The architectural period in the (Industrial age) included what?
the first use of complex machinery, factories, and urbanization.
what are the first mankind inventions?
fire, stone, stick, clothing, ceramic vessels, metal processing
what is the MAIN difference between humans and other animals?
their ability to work collaboratively and to transmit their knowledge to future generations
what is the first place where science flourished in? why there?
(Mesopotamia) near the Euphrates-Tigris, Indus and Nile rivers / The climate and soil were favorable (firstly invented the wheel)
what is the Classical antiquity?
it is the period of cultural history of Roman and Greek between the (8 BC-6 AD) centered on the Mediterranean Sea.
the period of the flourishment of Greek and Roman societies throughout much of Europe, Northern Africa, and Western Asia
who are the first people to try and develop the theory behind their observations?
Greeks (Pythagoras + Aristotle + Plato)
who are the first people to suggest that matter is made out of atoms?
Greeks
how was the development process of science?
wasn’t fast but slow as a result of religious dogma (took LONG TIME (16th century) for Copernicus to revolutionize the way that we look at the Universe + for Harvey to put forward his ideas on how blood circulated round the human body
was in Greece (in the end) + India + Middle East + China + South America / each developed their own (gunpowder, soap, paper)
During the (13th century) scientific work was brought together in (European universities) to produce what we know now as science
what was the biggest breaking point in science?
the invention of writing by the Sumerians for the first time (3500 BC)
helped for the information to no longer orally be transmitted to the next generations but in writing
how did the Egyptians use the writing invention?
They used ink on a paper (papyrus)
They knew the number Pi (3.14) + the properties of geometric shapes and used them in their daily work
how did the Babylonians use mathematical methods?
their mathematics is built on the (sexagesimal system) 60/60
why did the Babylonians use the sexagesimal system?
Cuz the number 60 is divided equally by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20 and 30 so that the division of property can be done without a fraction
which number had a special place in the Sumerians?
The number (12)
who were able to calculate the length of the year with an error of only about four minutes?
The Babylonians
the foundations of (astronomy) were laid by who?
The Babylonians because of their very advanced mathematical among others
How observing the periodic movements of celestial bodies and expressing these movements in a mathematical form helped the Babylonians in what?
Agriculture
Who firstly developed and carried forward science and philosophy where there are no oppressive regimes?
Greeks and that’s because they lived in small independent city-states and were acquainted with democracy
Science before the Greeks was all about what?
Observations
How did Ancient Greeks deal with science?
speculating
Institutionalization of science and connecting it to a systematic took place in which period?
the Hellenistic period
The explanation of nature in ancient Greeks was mostly through what?
Metaphysics
what is Metaphysics?
The nature of existence, being and the world
Aristotle called it the "first philosophy" or "wisdom" and saw it as a branch that studies the "first causes" of events
usually asks the following questions (is there God or not? How did the world come into existence and what is the origin of creation? If bodies exist, what is their objective nature?)
many philosophers do not think positively about it
can be considered reasonable but CANNOT be verified, tested, or proven by observation and experiment
the first clear example of the scientific method
who is the distinguished researcher of the Hellenistic period?
Archimedes
Life in ancient Greece was oriented towards what type of problems?
(theoretical) debates rather than (practical) problems
what was the striking example throughout history that demonstrates the power of deductive thinking and the greatest mathematic success for the Greeks?
The axiomatic system established by Euclid
Prehistoric people explained all natural phenomena with what?
God + Heroes
what is the (Conspiracy theory)?
it’s when he hears a rustle, the person who thinks it is a predator runs away from there, although this rustle may have been made by a harmless animal. But if it was a predatory and dangerous animal, the person could escape and save his life
it’s not particularly harmful as long as they don't go to extremes and can sometimes even save lives.
who is the pioneer of philosophy and science which Philosophy began with him?
Thales of Miletus
who is Thales?
He is a Greek Mathematician astronomer and philosopher
he believed in rational explanations rather than mythological explanations
The Greeks before Thales believed in what?
Mythology + God + Heroes
what is the main substance According to Thales?
Water
who is considered as the first true Scientist + the founder of astronomy?
Anaximander
who is Anaximander?
the student of Thales
the first philosopher and physicist to write his teachings according to historical sources
He is an Ionian natural philosopher AND a nature researcher
first to develop a cosmology or systematic view of philosophy on the world + introduced the term (arkhe)
he studied the movements of celestial bodies relative to the earth
what is the main substance According to Anaximander?
a single substance not similar to the substances and objects we know called (infinity) he believed that everything we perceive in the universe is (derived from this mysterious infinite substance)
he believed that the universe is a kind of organism powered by "cosmic breath"
who is the natural philosopher considered as the last Miletos thinker?
Anaximenes
who is Anaximenes?
a natural philosopher and a physicist which his thoughts were very influential in (Antiquity)
his thoughts interpretations often contradict each other because of people taking them into their own work.
his thoughts were spread over a wide area
believed in rational explanations rather than mythological explanations THAT’S WHY there are no religious interpretations
He wrote his work in a measured and unbiased manner
what is the main substance According to Anaximenes?
Air
Solid substances (tight contraction of air) + liquid substances (less closely spaced air)
who are the three Miletus thinkers of the western world?
Thales > Anaximander > Anaximenes
who was the first to suggest that the thinking process and the soul are in the brain and not in the heart?
Pythagoras
who was the first to say that the world was (round), and planets revolve around a single center of (fire) but did not know that this fire was the sun?
Pythagoras
who is Pythagoras?
Believed that the (religious and scientific views) are inextricably (linked)
He believed in transmigration and reincarnation
he believed that the essence of existence is hidden in (numbers) and that the essence of existence can be reached with mathematics. Even the reason why a person is healthy or sick can be explained by mathematics (the ratio of elements that should be in a healthy person is at a normal level, but in an unhealthy person, this ratio is either too little or too much)
what is Pythagoras theorem?
the square of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
it was used by the Babylonians and Indians before BUT he was the first person to prove it
who thinks that everything is relative, and the universe is a harmony formed by the war of opposites?
Heraclitus
what is the main substance According to Heraclitus?
Fire that flows and changes constantly
who is Heraclitus?
he believes that our world was formed from eternal and living fire + Neither a god nor a human created this universe but the Fire itself
he thinks that everything is relative (Sea water is the cleanest and dirtiest. Fish can drink it, and for them it is the savior." On the other hand, it is undrinkable and deadly for humans) + (without the opposite sexes, male and female, there would be no living beings)
he thinks that the universe is relativity of good, bad + right, wrong
(Different waters flow over those who enter the same rivers)
who is the first thinker to use the (water, fire and air) as the basic elements + add (earth) to it for the first time?
Empedocles
who is Empedocles?
was one of the pre-Socratic thinkers
he thinks that everything consists of certain combinations of these four elements + they have no beginning and no end + their quantities in the universe always remain the same
After Empedocles (Aristotle) added to these four elements the (ether) which he claimed to exist in heaven
he thinks that these 4 elements are moved by two opposing forces (Love and Hate) where (Love serves to keep matter together + hatred serves to separate substances and keep them away from each other)
who is the owner of the (formulation of an atomic theory of the universe)?
Democritus
who is Democritus?
pre-Socratic philosopher and the student of (Leucippus)
he asserted that (space or Void), had an equal right with reality in which moved an infinite number of (very small atoms) that made up Being + these atoms are eternal and indivisible
he thinks that all phenomena are composed of the same eternal atoms SO it may be said that nothing comes into being or perishes in the absolute sense of the words
who believed that philosophy should achieve (practical results) for the greater well-being of society?
Socrates
who is Socrates?
He attempted to establish an ethical system based on human reason rather than theological doctrine
human choice was motivated by the desire for happiness + wisdom comes from knowing oneself (The more a person knows, the greater his or her ability to reason and make choices that will bring true happiness)
he believed that the best form of government being neither a (tyranny nor a democracy) BUT instead ruled by (individuals who had the greatest ability)
who was the thinker that founded the first institutions of higher learning in the Western world (Academy of Athens)?
Plato
who is Plato?
a student of (Socrates) and a teacher of (Aristotle)
Plato founded the Academy in Athens, one of the first institutions of higher learning in the Western world
In his writings on the (Theory of Forms) he suggests that the (world of ideas) is the only (constant) and that the perceived world through our senses is (deceptive and changeable)
who is the thinker who provided a complex synthesis of the various philosophies existing prior to him about the (water cycle)?
Aristotle
who is Aristotle?
a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece and a student of Plato
his views profoundly shaped medieval scholarship (developed the classical mechanics)
was revered among medieval Muslim scholars as (The First Teacher), and among medieval Christians as simply (The Philosopher), while the poet Dante called him (the master of those who know)
who is the thinker who was important for his discovery of the relation between the surface and volume of a sphere and its circumscribing cylinder?
Archimedes
who is Archimedes?
Italian philosopher and inventor
known for his formulation of a hydrostatic principle (known as Archimedes’ principle) + a device for raising water known as the (Archimedes screw)
who is Eratosthenes?
a philosopher who measured the angle cast by the sun at noonday in midsummer in both (Syene + Alexandria)
what is the difference between Plato and Aristotle?
Plato believed in rationalism (Knowledge comes before experience) + the man was born with knowledge
Aristotle believed in Empiricism ( Knowledge comes after experience)
what is the Aristotle’s geocentric universe?
the earth is the centre
sun + moon + planets move in crystal spheres around the earth
stars are on a single sphere
the universe remained uncganged since it was created
who was the first to propose a Heliocentric universe?
Aristarchus
who is Aristarchus?
he postulated that the starts are infinitely far away
he thinks that the radius of the moon is bigger than the earth (0.5)
he measured the angular diameter of the moon to be (2)
he measured the distances between earth + moon (114.6)
he thinks that the distance to the sun is bigger than to the moon (19.1)
who is Ptolemy?
he predicted the motions of the planet + the sun and the moon in his (Ptolemaic Model)
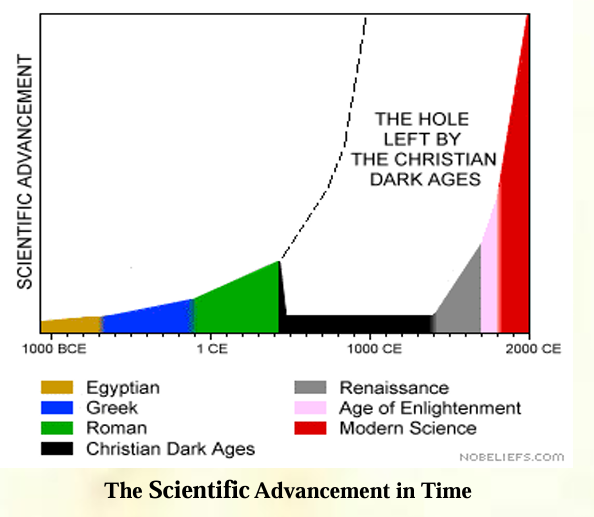
How was the science in the Islamic World?
Most scientific advancements were in (Medicine, astronomy, and chemistry)
Ibn Sina was the pioneer of these
The modern method was developed by Muslim scholars during the Golden age of Islam
they began to absorb Greek science from the former Byzantine lands
The situation was Christendom's loss and Islam's gain
During the (Abbasid) period, Arabic science entered its golden age
Al-Mamun sent a mission to Constantinople and brought Greek manuscripts
The establishment of (Wise Houses or Bayt al-Hikmet) which are the translation and original research institute, was the biggest contribution of the Abbasid caliphs to science
(Bayt al-Hikmet) served the Arabs in some sense the same function that the Museum and Library of Alexandria served the Greeks
(Bayt al-Hikmat) was the largest translation and research center in Baghdad during the time of (Al-Mamun + Al-Rashid
Participants in this study include not only Arabs, but also Iranians, Jews and Turks
Evidence of the influence of Arabic science on Europe exists in a long list of words derived from Arabic (Algebra + algorithm) / names of stars (Aldebaran, Algol, Alphecca, Altair, Betelgeuse, Mizar, Rigel, Vega) / chemical terms such as (alkaline, alembic, alcohol, alizarin, alchemy)
(Abu Hamid al-Ghazali) opposed the idea that there were (laws in nature) because he was thinking that having them would tie God's hands
Arabic science had begun to (decline) before the end of the Abbasid caliphate