
The Nervous System Biology Notes
Functions of the System
Responsible for the control of the body and communication among its parts
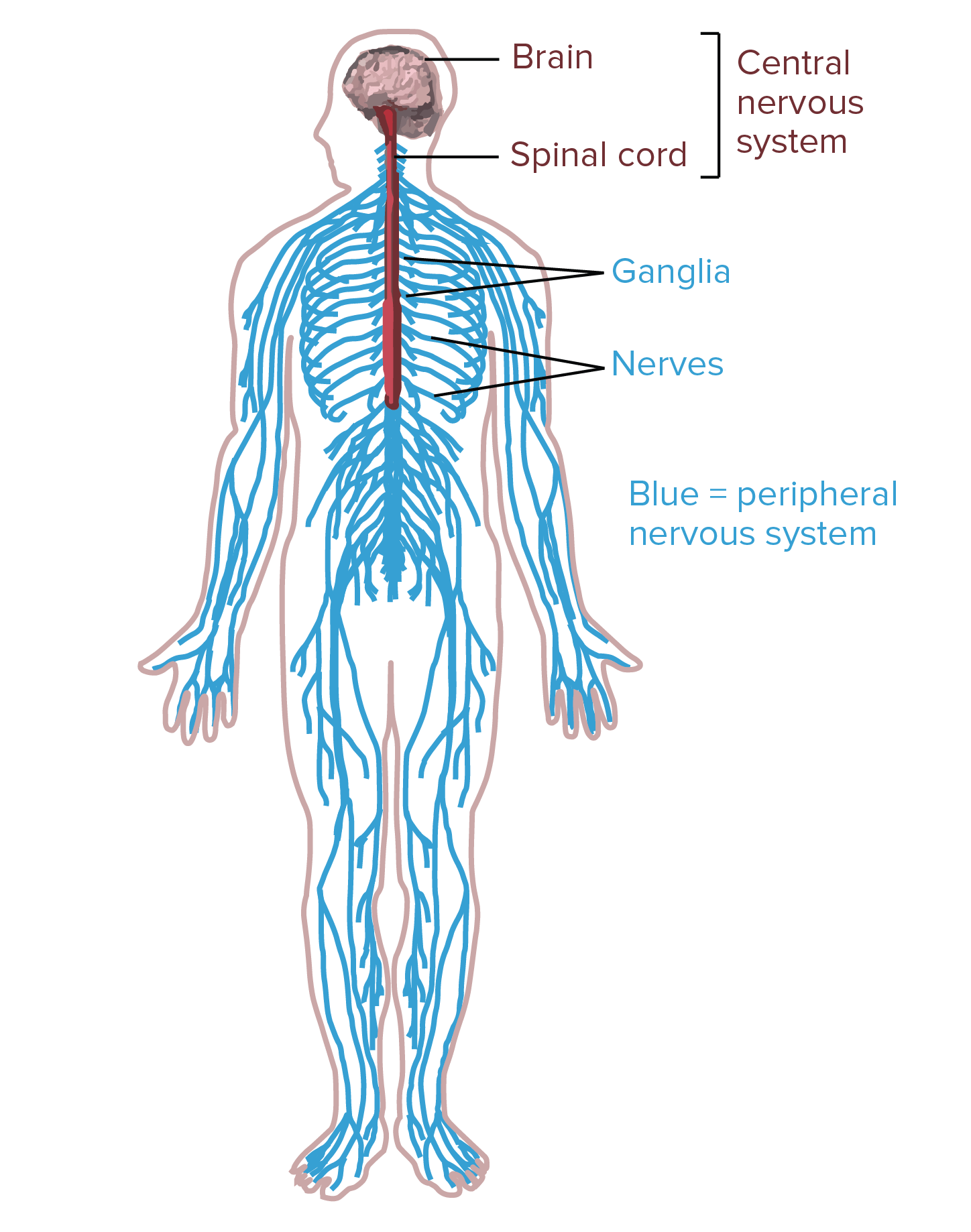
System Organs (and key parts)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain- controls bodily functions
Spinal cord- Connects the PNS and the CNS
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nerves (neuron)
Sensory: sends stimulus info to the CNS from the sensory organs (PNS → CNS)
Ears
Mouth
Skin
Nose
Eyes
Motor: sends stimulus info from CNS to the organs (CNS → PNS)
Ex: muscles
System Interactions
Nervous, Digestive & Endocrine Systems:
When an organism starts ingesting food, the nerves located on the tongue signal the stomach to start producing gastrin, a hormone that begins chemical digestion in the stomach.
Nervous & Muscular Systems:
Balance: receptors located in the muscles provide the brain with information about body position and movement
Common system disorders/medical issues
Stroke: When blood circulation is cut off from brain tissue and part of the brain tissue dies
The damage/symptoms can vary, depending on how long the stroke is and where it is located
Memory loss
Paralysis
Loss of sensory/organ function
Loss of limb function
Profession: Neurologists
Neurologists are specialists who treat diseases of the brain and spinal cord, peripheral nerves and muscles. Neurological conditions include epilepsy, stroke, multiple sclerosis (MS) and Parkinson's disease.
Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System: controls voluntary reactions
Autonomic Nervous System: controls involuntary actions
Parasympathetic: When nothing is stimulating/stressing the organism out
Rest and digest
Stimulates stomach activity, slows heart rate, inhibits glucose release
Sympathetic: When the body is introduced with a stimulus that causes the body to prepare for action
Fight or flight
Increased heart rate
Stimulate glucose release
Digestion stops
Adrenaline/ Cortisol is released from adrenal glands
Reflex Arc
A true reflex arc involves only a few neurons and the information goes only from your body to your spinal cord! Your brain does not dictate the response.
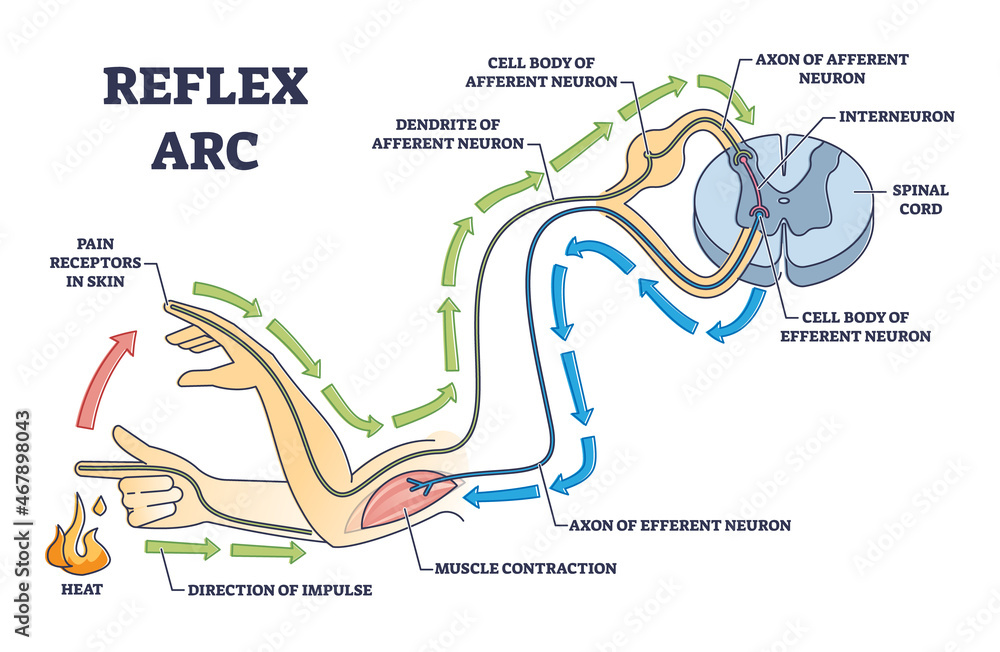 Steps in a reflex arc:
Steps in a reflex arc:
Sensory Receptor – receptor that responds to a signal in the environment
Sensory neuron - carries impulse to spinal cord
Motor neuron - carries impulse away from spinal cord to the effector
Effector - structure by which animal responds (muscle, gland, etc).
Functions of the System
Responsible for the control of the body and communication among its parts
System Organs (and key parts)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain- controls bodily functions
Spinal cord- Connects the PNS and the CNS
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nerves (neuron)
Sensory: sends stimulus info to the CNS from the sensory organs (PNS → CNS)
Ears
Mouth
Skin
Nose
Eyes
Motor: sends stimulus info from CNS to the organs (CNS → PNS)
Ex: muscles

System Interactions
Nervous, Digestive & Endocrine Systems:
When an organism starts ingesting food, the nerves located on the tongue signal the stomach to start producing gastrin, a hormone that begins chemical digestion in the stomach.
Nervous & Muscular Systems:
Balance: receptors located in the muscles provide the brain with information about body position and movement
Common system disorders/medical issues
Stroke: When blood circulation is cut off from brain tissue and part of the brain tissue dies
The damage/symptoms can vary, depending on how long the stroke is and where it is located
Memory loss
Paralysis
Loss of sensory/organ function
Loss of limb function
Profession: Neurologists
Neurologists are specialists who treat diseases of the brain and spinal cord, peripheral nerves and muscles. Neurological conditions include epilepsy, stroke, multiple sclerosis (MS) and Parkinson's disease.
Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System: controls voluntary reactions
Autonomic Nervous System: controls involuntary actions
Parasympathetic: When nothing is stimulating/stressing the organism out
Rest and digest
Stimulates stomach activity, slows heart rate, inhibits glucose release
Sympathetic: When the body is introduced with a stimulus that causes the body to prepare for action
Fight or flight
Increased heart rate
Stimulate glucose release
Digestion stops
Adrenaline/ Cortisol is released from adrenal glands
Reflex Arc
A true reflex arc involves only a few neurons and the information goes only from your body to your spinal cord! Your brain does not dictate the response.
 Steps in a reflex arc:
Steps in a reflex arc:
Sensory Receptor – receptor that responds to a signal in the environment
Sensory neuron - carries impulse to spinal cord
Motor neuron - carries impulse away from spinal cord to the effector
Effector - structure by which animal responds (muscle, gland, etc).