Note
5.0(1)
Explore Top Notes Note
Note Studied by 155 people
Studied by 155 people Note
Note Studied by 25 people
Studied by 25 people Note
Note Studied by 2 people
Studied by 2 people Note
Note Studied by 84 people
Studied by 84 people Note
Note Studied by 12 people
Studied by 12 people Note
Note Studied by 7 people
Studied by 7 people
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
5.0(2)
CUSTOMER SERVICE
5.0(1)
CGO casus 8
5.0(1)
Unit 2 - Environmental research and data collection
5.0(2)
Electromagnetic Waves and Refraction
5.0(1)
New Worlds For All
5.0(1)
3.8 Investment appraisal
What is investment appraisal?
Investment appraisal: evaluating the profitability or desirability of an investment project.
</p>
Quantitative investment appraisal requires:
- Initial capital cost of the investment
- Estimated life expectancy
- Residual value of the investment
- Forecasted net returns or net cash flows from the project
</p>
Methods of quantitative investment appraisal:
- Payback period
- Average rate of return
- Net present value using discounted cash flows
\
- Quantitative techniques of investment appraisal
- Payback method
- Payback period: length of time it takes for the net cash inflows to pay back the original capital cost of the investment
- Average rate of return (ARR) measures the annual profitability of an investment as a percentage of the initial investment.
\
Higher level (discounting and net present value)
- Discounting future cash flows
- Present value of a future sum of money depends on two factors:
- The higher the interest rate, the less value future cash has in today’s money.
- The longer into the future cash is received, the less value it has today.
\
Net present value (NPV): today’s value of the estimated cash flows resulting from an investment.
- Calculating NPV:
- Multiply discount factors by the cash flows. Cash flows in year 0 are never discounted as they are today’s values already.
- Add the discounted cash flows.
- Subtract the capital cost to give the NPV.
Example:
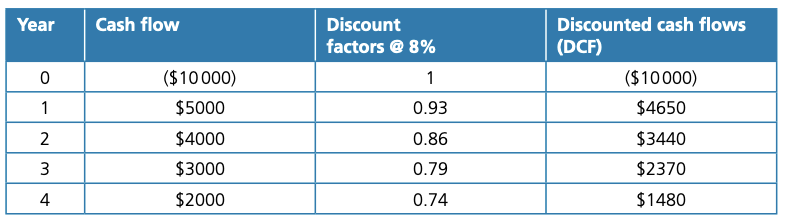
NPV = Total discounted cash flows - Original investment
→ $11,940 - $10,000 = $1,940
→ The project earns $1,940 in today’s money values. So, if the finance needed can be borrowed at an interest rate of 8% or less, the investment will be profitable.
\
Note
5.0(1)
Explore Top Notes Note
Note Studied by 155 people
Studied by 155 people Note
Note Studied by 25 people
Studied by 25 people Note
Note Studied by 2 people
Studied by 2 people Note
Note Studied by 84 people
Studied by 84 people Note
Note Studied by 12 people
Studied by 12 people Note
Note Studied by 7 people
Studied by 7 people
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
5.0(2)
CUSTOMER SERVICE
5.0(1)
CGO casus 8
5.0(1)
Unit 2 - Environmental research and data collection
5.0(2)
Electromagnetic Waves and Refraction
5.0(1)
New Worlds For All
5.0(1)