
19) Pharmacogenomics (copy)

Pharmacogenetics: science on how heritability impacts drug response
Pharmacogenomics: how identifying human genes, their products, their variations, their expression & function affects drug response
Personalized medicine: using genetic profiles to make treatment decisions
Genes encoding target molecules or pathways can influence drug responses.
Examples of genetic variants affecting drug responses through interactions with target molecules.

Polymorphisms in multiple genes may collectively impact drug responses.
Variations in genes unrelated to therapeutic response can affect drug responses.
E.g. HLA system variants (HLA B*5701 risks fatal skin reaction in response to abacavir)
Some variations may affect both pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic targets
E.g. Warfarin (metabolism affected- CYP2C9/ codes for warfarin target enzyme- VKORC1)
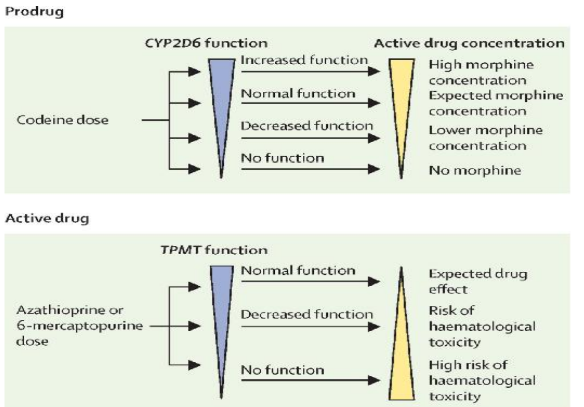
Influence of genetic polymorphisms on drug responses variability (from TPMT gene variation)
Role of CYP2D6 in metabolizing codeine into active morphine
Impact of genetic variations in CYP2D6 on codeine effectiveness in certain populations (7% Caucasians missing one copy of gene)
Genetic variations in CYP2C9 and VKORC1 affecting warfarin metabolism and dose requirements.
Rare variations leading to challenges in managing warfarin therapy clinically.
Metabolised by slow & fast acetylators (high-risk pharmacokinetic groups)
Metabolised by CYP2C19 (polymorphism (genetic variation) > reduced efficacy of gene)
Beta adrenergic receptor: variable response (treatment for hypertension, heart failure, bronchial asthma)
Adrenoreceptor alpha 2A: variable response (treatment for hypertension)
Hydrochlorothiazide variable response: sodium channel polymorphism
Polymorphism of dopamine D2 & D3 receptors: variable response to antipsychotic drugs & enhance toxicity
CYP2C9 variations: variable response to anti-epileptic drugs
Patients with HLA-B*5701 allele are at high risk for hypersensitivity to abacavir
Label recommends pre-therapy screening for this allele.
Use of alternative therapy is suggested for subjects with the HLA-B*5701 allele.
Patients on carbamazepine may face severe skin conditions (Stevens-Johnson syndrome & toxic epidermal necrolysis)
HLAB1502 in Asian populations and HLA-A3101 in Caucasians are linked to these reactions.
30% of breast cancers have a surface protein corresponding to Her2 gene
Personalized treatment with drugs like Herceptin benefits patients by blocking these surface proteins

Pharmacogenetics: science on how heritability impacts drug response
Pharmacogenomics: how identifying human genes, their products, their variations, their expression & function affects drug response
Personalized medicine: using genetic profiles to make treatment decisions

Genes encoding target molecules or pathways can influence drug responses.
Examples of genetic variants affecting drug responses through interactions with target molecules.

Polymorphisms in multiple genes may collectively impact drug responses.
Variations in genes unrelated to therapeutic response can affect drug responses.
E.g. HLA system variants (HLA B*5701 risks fatal skin reaction in response to abacavir)
Some variations may affect both pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic targets
E.g. Warfarin (metabolism affected- CYP2C9/ codes for warfarin target enzyme- VKORC1)
Influence of genetic polymorphisms on drug responses variability (from TPMT gene variation)
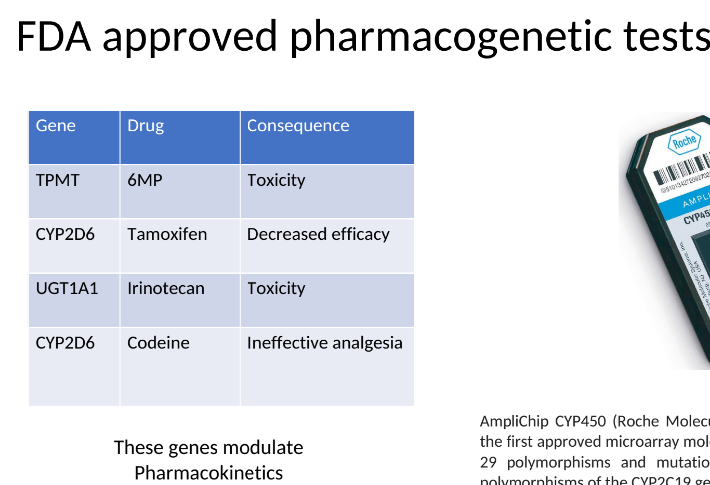
Role of CYP2D6 in metabolizing codeine into active morphine
Impact of genetic variations in CYP2D6 on codeine effectiveness in certain populations (7% Caucasians missing one copy of gene)
Genetic variations in CYP2C9 and VKORC1 affecting warfarin metabolism and dose requirements.
Rare variations leading to challenges in managing warfarin therapy clinically.
Metabolised by slow & fast acetylators (high-risk pharmacokinetic groups)
Metabolised by CYP2C19 (polymorphism (genetic variation) > reduced efficacy of gene)
Beta adrenergic receptor: variable response (treatment for hypertension, heart failure, bronchial asthma)
Adrenoreceptor alpha 2A: variable response (treatment for hypertension)
Hydrochlorothiazide variable response: sodium channel polymorphism
Polymorphism of dopamine D2 & D3 receptors: variable response to antipsychotic drugs & enhance toxicity
CYP2C9 variations: variable response to anti-epileptic drugs
Patients with HLA-B*5701 allele are at high risk for hypersensitivity to abacavir
Label recommends pre-therapy screening for this allele.
Use of alternative therapy is suggested for subjects with the HLA-B*5701 allele.
Patients on carbamazepine may face severe skin conditions (Stevens-Johnson syndrome & toxic epidermal necrolysis)
HLAB1502 in Asian populations and HLA-A3101 in Caucasians are linked to these reactions.
30% of breast cancers have a surface protein corresponding to Her2 gene
Personalized treatment with drugs like Herceptin benefits patients by blocking these surface proteins
