Science Term 4: Chemistry
Periodic table:
Actinides: A special block metallic elements with atomic numbers 89-103
Alkali metals: Group 1 elements
Alkaline earth metals: Group 2 elements
allotropes: forms of the same element that have different molecular structures and therefore different properties
atomic number: the number of protons in an atom
atoms: the particles that make up all materials; the smallest part of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction
electron configuration: arrangements of electrons in electron shells
electron shells: also known as energy levels; the regions surrounding the nucleus where electrons may be found
element: a substance composed of atoms with the same atomic number; 119 are known to exist
fluoresce: to absorb UV light and re-emit light that is visible
ground state: the lowest energy arrangement of an atom’s electrons in energy levels
groups: also known as family; vertical columns of period tables
halogens: group 17 elements
indirect evidence: evidence that does not involve direct observation
nobles gases: inert gases; known for their stability (non-reactivity), group 18
isotopes: atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons
lanthanides: a special block of metallic elements with atomic numbers 57-71
mass number: the weight and number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
nucleus: the heavy core at the center of an atom, made of protons and neutrons
organic: describes a compound that is or was a part of a living thing; containing carbon.
organic molecules: molecules that have a skeleton of carbon atoms
periodic table: a list of all the known elements, arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
periods: series; horizontal rows of the periodic table
transition metals: a special block of metallic elements covering elements in groups 3-12.
2n^2: max number of electrons
metalloids: a chemical element that forms a simple substance having properties intermediate between those of a typical metal and a typical nonmetal. Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic, Antimony, Tellurium, Astatine '
Reactive nonmetals: Hydrogen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Flourine, Phosphorous, Sulfur, Chlorine, Selenium, Bromine, Iodine
Chemical reactions:
acid: a substance that produces hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water
agitation: stirring
alkaline: describes the solution made when a base is dissolved
anion: a negatively charged ion
balanced equation: a formula equation that has the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation
base: a substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water
biofuel: renewable fuel made from the fermentation of organic materials such as potato and grains
biodiesel: renewable fuel made from plant-based or animal-based fatty acids
catalyst: a chemical that helps to speed up a chemical reaction but is not used up by the reaction
cation: a positively charged ion
caustic: the term given to corrosive bases
chemical equation: a short-hand notation that scientists use to communicate what happens during a chemical reaction
chemical potential energy: energy that is stored in molecules
combination reaction: occurs when two reactants combine to form a single product
combustion: a chemical reaction in which a substance burns in oxygen gas to produce light and heat
concentration: the amount of a chemical in a certain volume of liquid gas
corrosion: a chemical reaction in which a metal reacts with oxygen to produce a metal oxide but does not produce significant amounts of heat and light
Decomposition reaction: A chemical reaction in which one reactant breaks apart into two or more products
endothermic: describes a physical or chemical process that absorbs energy
enzyme: a biological catalyst
exothermic: describes a physical or chemical process that produces energy in the form of heat and light
formula equation: a chemical equation in which the reactants and products are identified by their chemical formulas
hydrocarbon: all substances made out of just hydrogen and carbon atoms; commonly used as fuels
incomplete combustion: combustion that occurs in an environment with limited supply of oxygen
insoluble: does not dissolve
ion: an atom that has gained or lost an electron and became electrically charged.
ionic compound: a substance made up of positive and negative ions
neutral: neither acidic nor basic
polyatomic: having many atoms
precipitate: the insoluble product of a precipitation reaction
precipitation reaction: when two clear solutions react to produce an insoluble solid.
product: a substance produced by a chemical reaction
rate of reaction: how fast a chemical reaction proceeds
reactant: the initial substance of a chemical reaction
respiration: an exothermic chemical reaction that takes place in the cells of living things. Sugar + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
salt: ionic compound formed by the chemical reaction of an acid with another element or compound
soluble: able to dissolve
word equation: a chemical equation in which the reactants and products are identified by their chemical names.
Factors of reaction rates: temperature, concentration, agitation, surface area of reactants, catalysts, enzymes,
binary compounds: chemical compounds comprised of two distinct elements
polyatomic ion: an ion made from a charged group of bonded atoms consisting of more than one element.
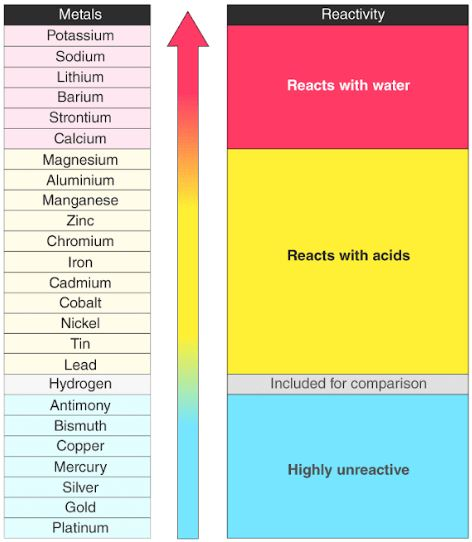
Reactive series of metals and elements:
Naming conventions:
Binary compounds:
- Write name of metal
- Write name of nonmetal, changing the ending to -ide.
Polyatomic ion:
- identify. Polyatomic ions contain more then two letters
- Written after the metal (except for NH4+ - Ammonia)
- Name of metal ion and then name of memorised polyatomic ion.