Chapter 2
Constitutional Government
Outlines powers of government
example of the US Constitution
Ideally brief AND flexible
explains how to structure power
Fundamental provisions require less updating
constitutions are meant to say the fundamentals so they’re flexible to what the future requires
Protect individual rights but remain relevant
Founders’ checks on tyranny
tyranny- abuse of power
vicious or oppressive
use of force without a right to do so
(check recording)
Federalism
the fancy word for “power sharing between different levels of government”
Separation of powers
legislative, executive, judicial
Popular sovereignty
one thing
think of a pie
splitting up responsibilities
but as a whole operates the government
Texas modeled after US constitution
The Federal System of the United States
Unitary system
Confederal system
Federalism
The Federal System of the United States
Enumerated powers
Implied powers
State powers
Concurrent powers
Vertical Federalism
Definition
Supremacy clause
Reserved powers
Horizontal Federalism
Definition
Privileges and immunities
Full faith and credit clause
Extradition
The Evolving Idea of Federalism
Dual federalism
Cooperative federalism
Fiscal federalism
Unfunded mandate
State-Local Power
The federal-state conflict mirrored on the state-local level
Dillon’s Rule
Home rule city
State infringes on local governments
Texas Constitutions
Spanish Empire
The 1827 Constitution of Coahuila y Tejas
Limited rights in Mexico
Mexican fears of Anglo immigration
Immigration Rights
Texas’ complaints about Mexico
Mexico cracked down on immigration
Language barriers
Constitution designed for future citizens
The Republic of Texas: The Constitution of 1836
Iconic in the mythology of Texas
Laws Influenced by the US Constitution
Free persons of color
Prohibited priests from holding office
Enslaved person population increased
Republic of Texas relatively short-lived
Statehood: The Constitution of 1845
Changes to the new Constitution
Provisions that enforced inequality
Lincoln’s election
Secession and the Confederacy: The Constitution of 1861
United States changed to the Confederate States of America
Slavery even stronger protection
The First Reconstruction: The Constitution of 1866
Loyalty oath
Requirements for State readmission
Granted abolition but no suffrage
Short-lived due to Radical Republicans
The Second Reconstruction: The Constitution of 1869
Reconstruction Acts
Prohibition of ex-Confederate involvement
Legitimacy of the process doubted
The Current System: Constitution of 1876
Resentment toward northerners and Republicans (continued for 100 years)
1869 Constitution was hated - it was at odds with Texas’ dominant political culture
A sign of being on the losing side of the Civil War
Consolidated power at the state level, away from local
redeemer constitution is the constitution that heals the sins that the prev constitution had
1876 Constitution’s delegates largely farmers
Popular sovereignty
Power derived from the people
Separation of powers
No one branch holds all the power
In Texas specifically, the “plural executive”
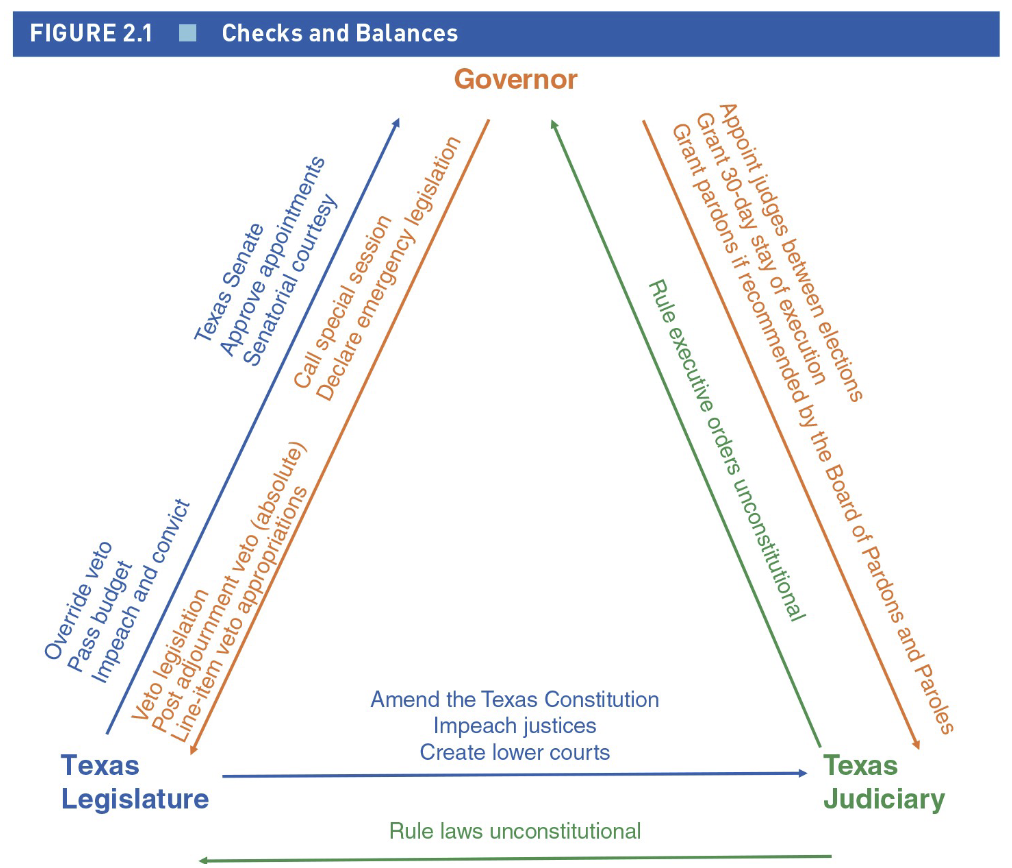
Checks and balances
Each branch can get in the others’ way
The Current System: Constitution of 1876
Distrust of Government (prominent)
Taxation and debt rules for government
Limits to powers, terms, and salaries
Long ballot
Most political positions elected, not appointed
The Current System: Constitution of 1876
The Legislative Branch
Part-time “citizen-legislature” ideal
Meets every other year for 140 days
Salary of $7,200 per year + per diem of $221 for 140 days legislature is in session
$7,200+(140*$221) = $7,200 + $30,940 = $38,140
Limited by constitution
Texas House has 150 members
2 year terms
Texas Senate has 31 members
4 year terms
Property taxes cannot be collected by state
Limits amount of property taxes local governments can collect
State income tax is forbidden - unless approved by majority of voters
The Executive Branch
Governor’s power reduced and divided
“Plural executive”
6 elected positions (excluding Sec. of State)
Limited power:
Shortened term to two years, reduced salary
Two-term limit (later amended to 4 year term and no term limit)
Texas Judiciary
A variety of courts in the Texas judiciary
Elected judges, not appointed
Criticisms of the Texas Constitution
Modern diversity and advancement
Growing Hispanic and Asian American populations
Demographic changes
1.5 million (1880s) to 29.5 million people (today)
Economic changes
Farms/ranches (1880s) to aerospace and defense, telecommunications and computers, shipping, etc…
How to move past Reconstruction version
Fjk
Only wealthy become legislators
Texan judge elections expensive
Amending the Constitution
Approval process
Publishing requirements
Approved by simple majority
On ballot
Constitutional Revision
Current constitution thoroughly criticized
Revision in the 1970s
1998’s Ratliff-Junell proposal
Cost of frequent elections, rejected proposals
Winners and Losers
Unyieldiing fundamental law
Limits state power
Long ballots overwhelming
Difficult for average citizens
Judicial elections contribute to overwhelming environment