Unit 7: Biological Bases of Behavior
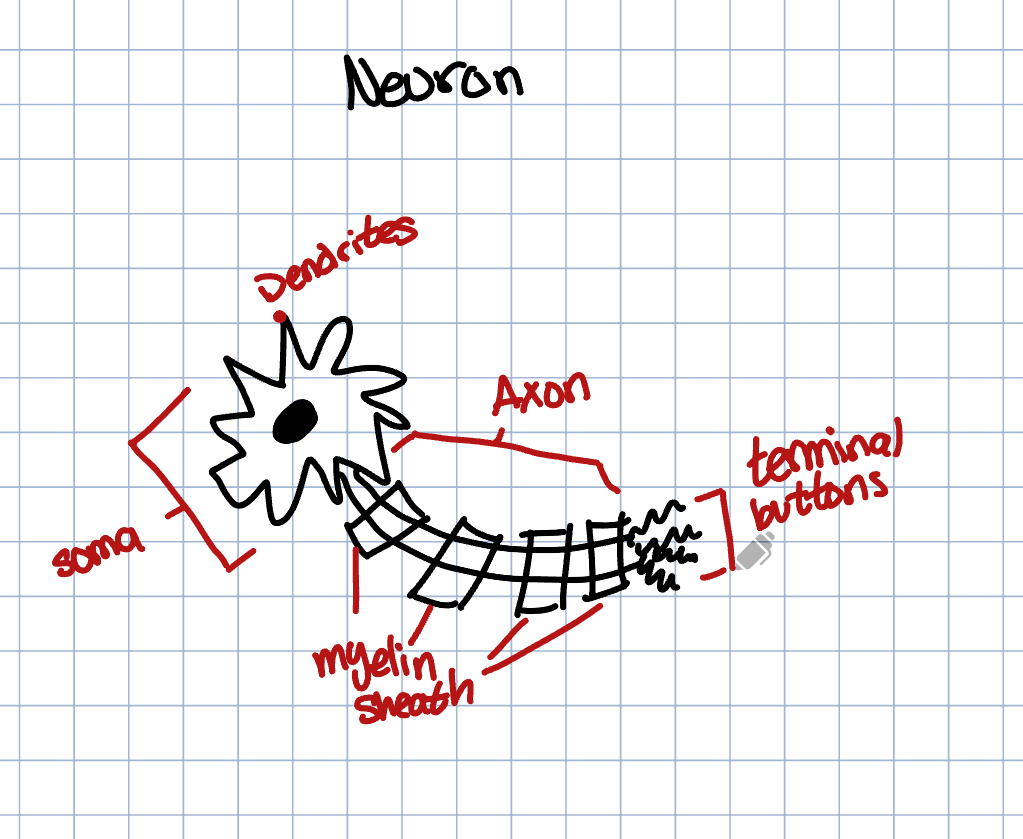
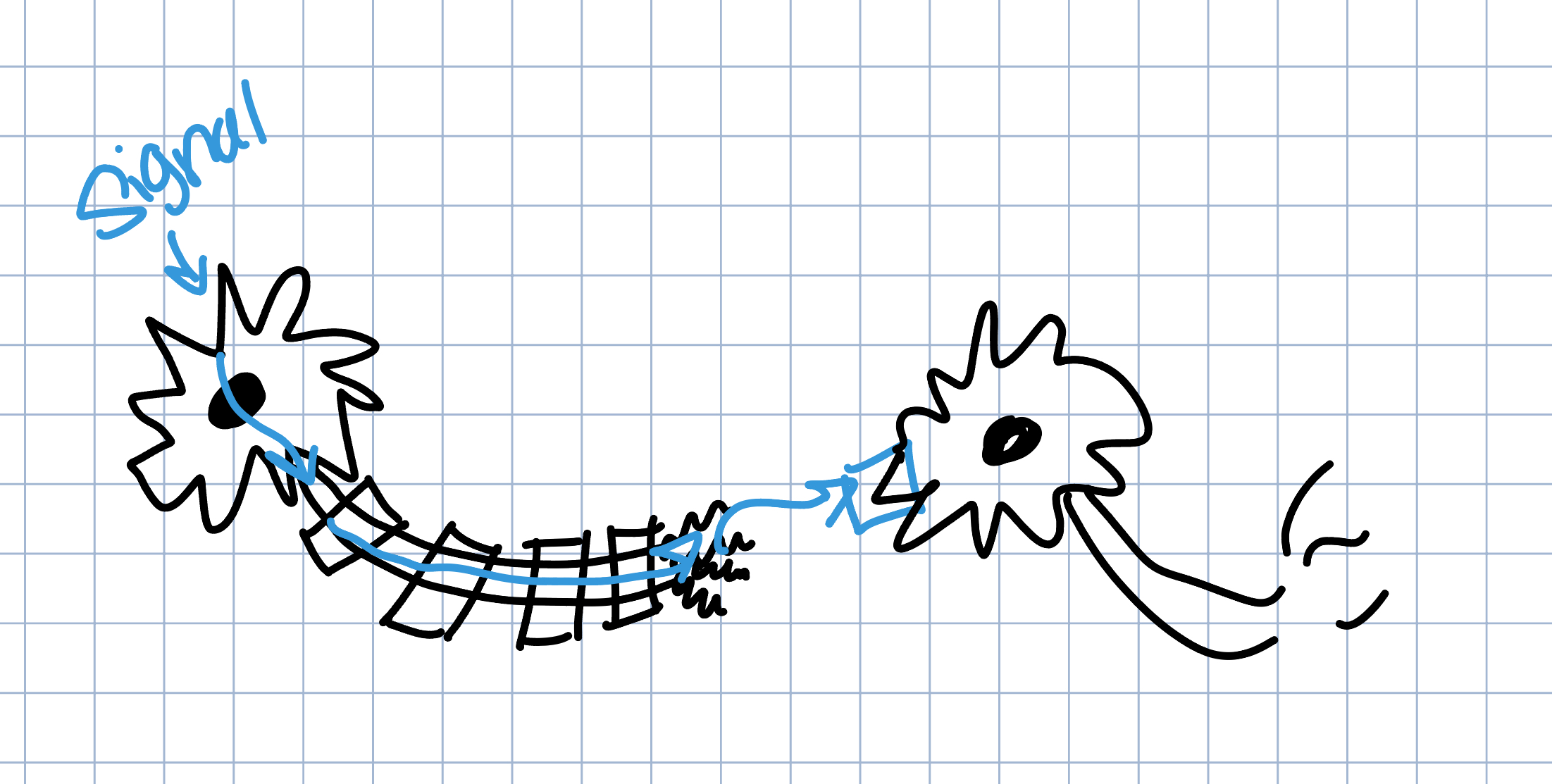
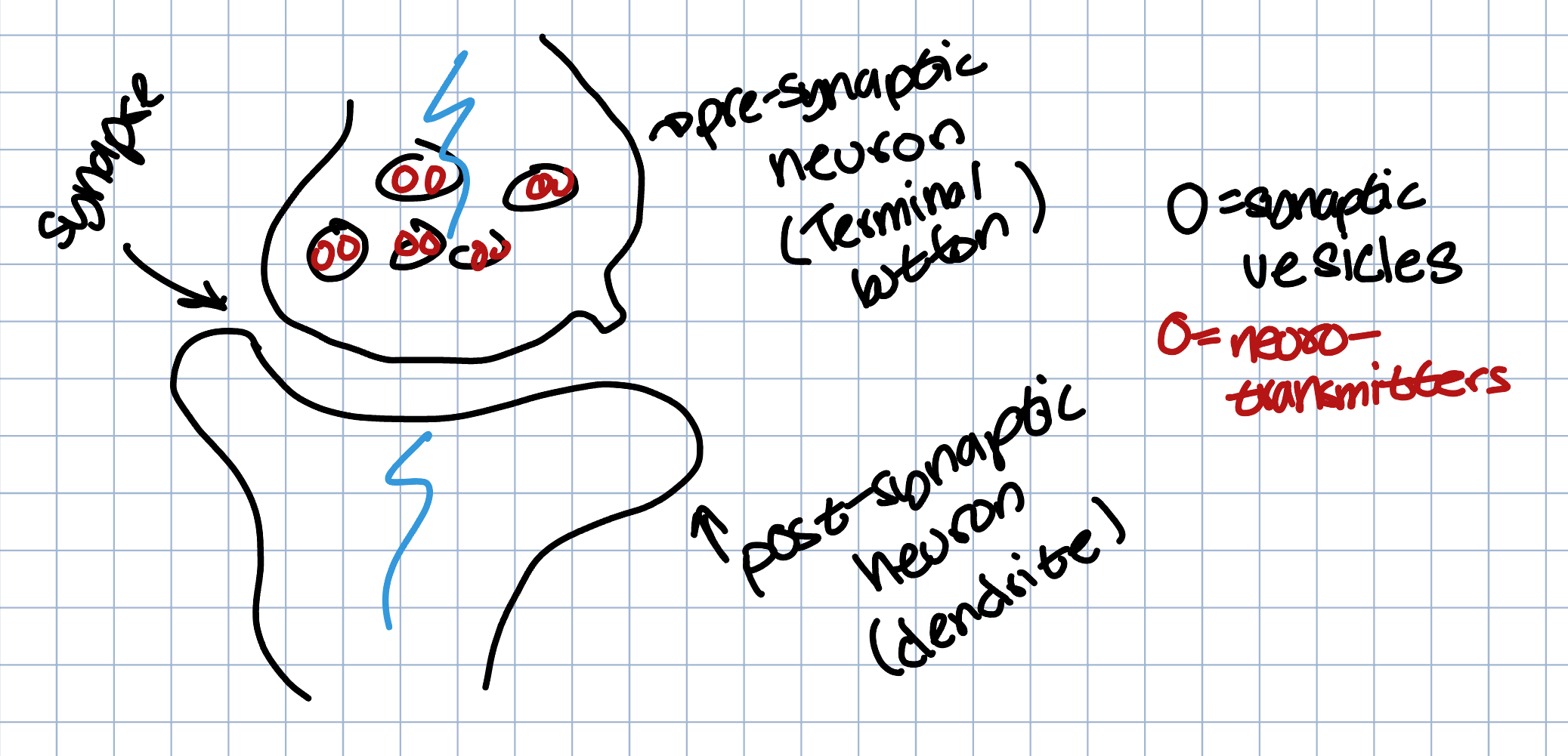
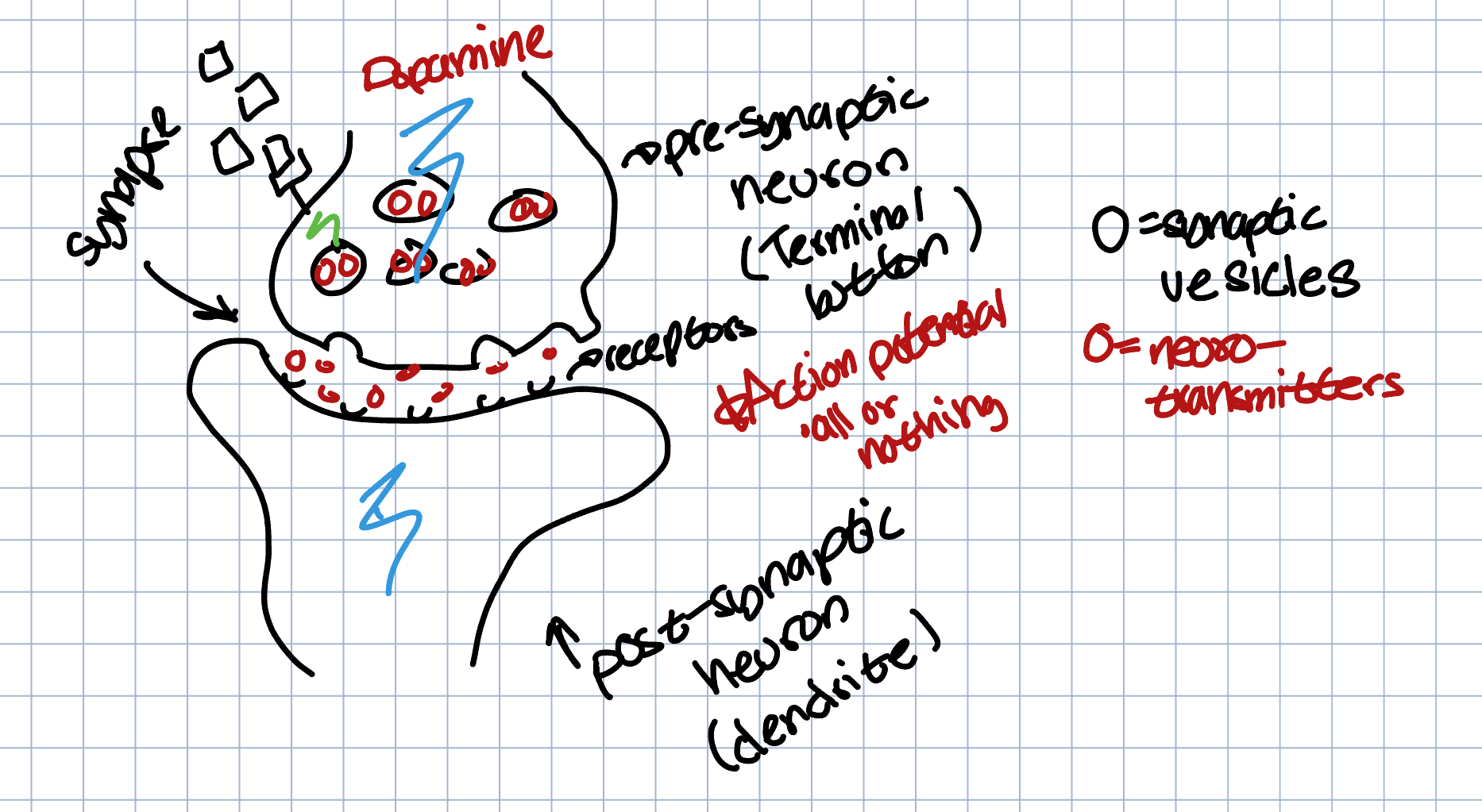
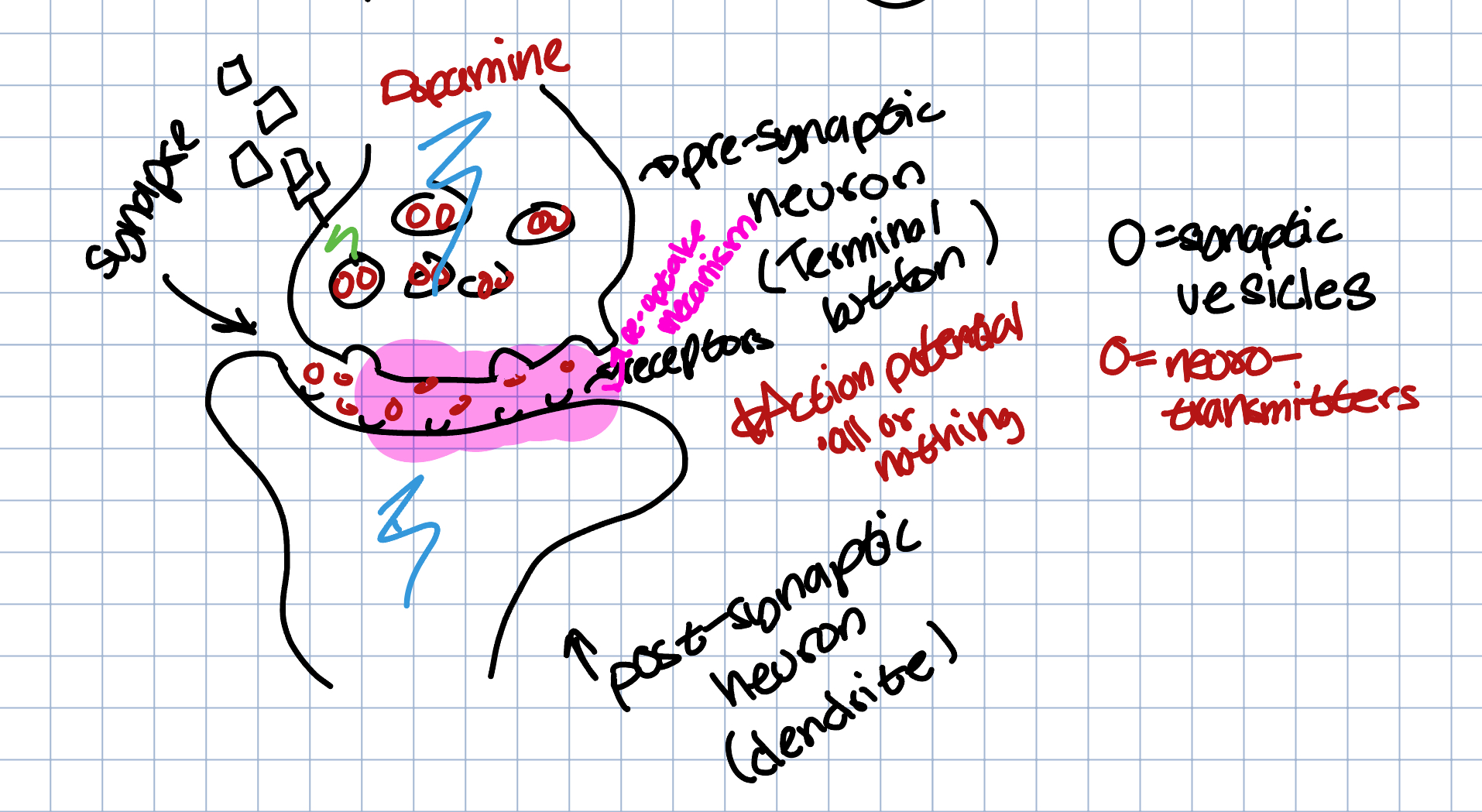
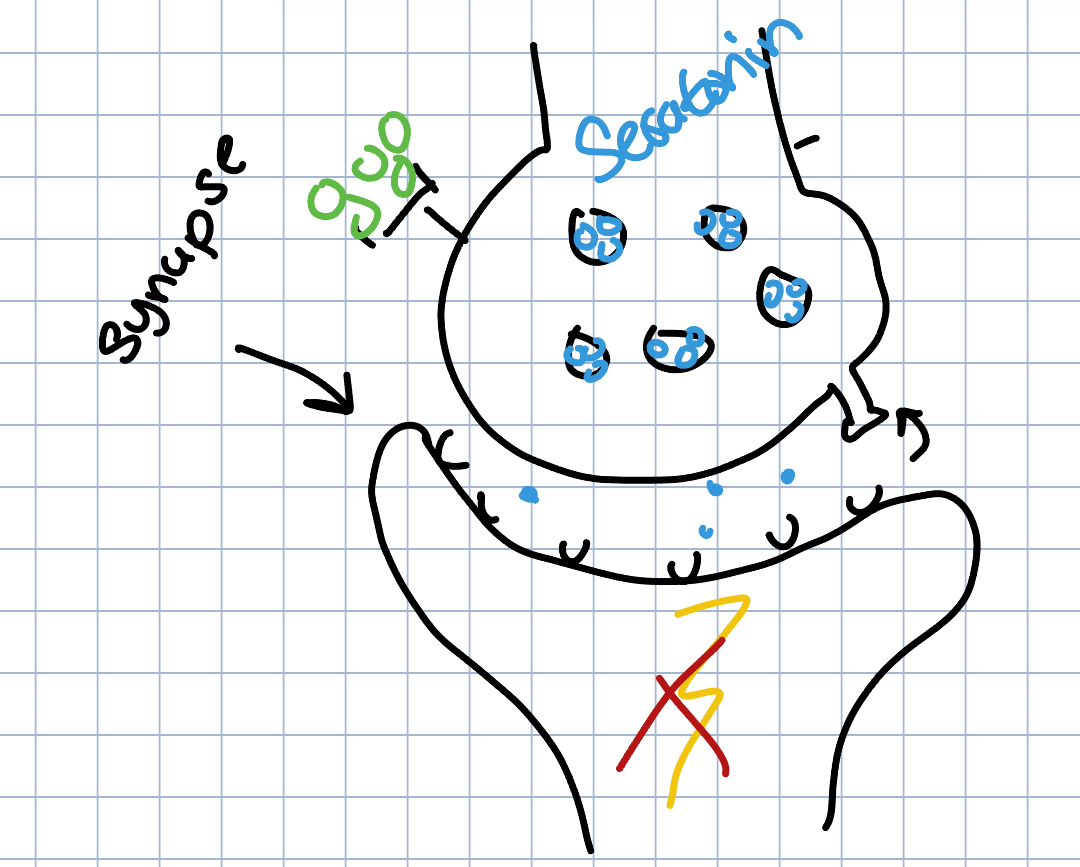
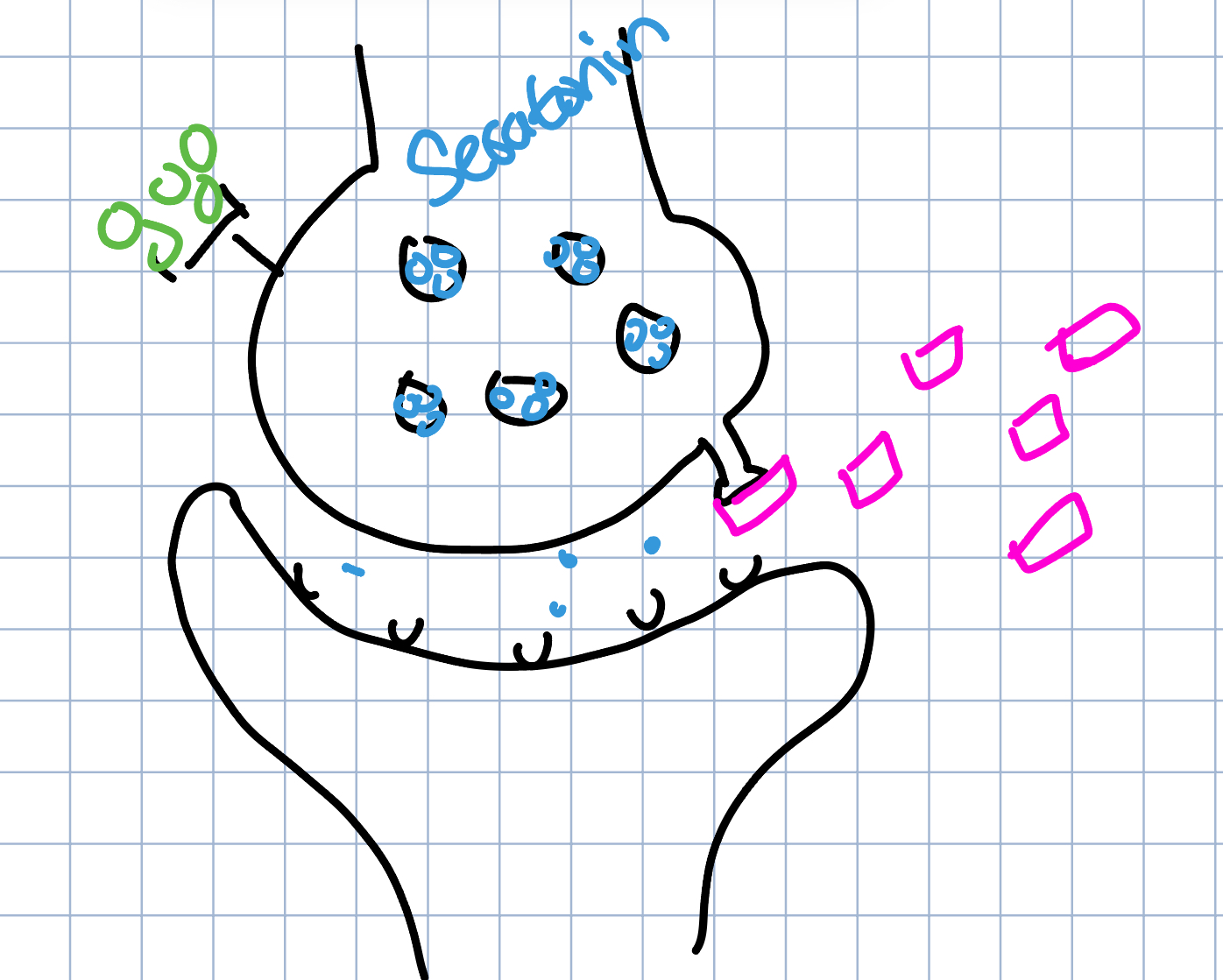
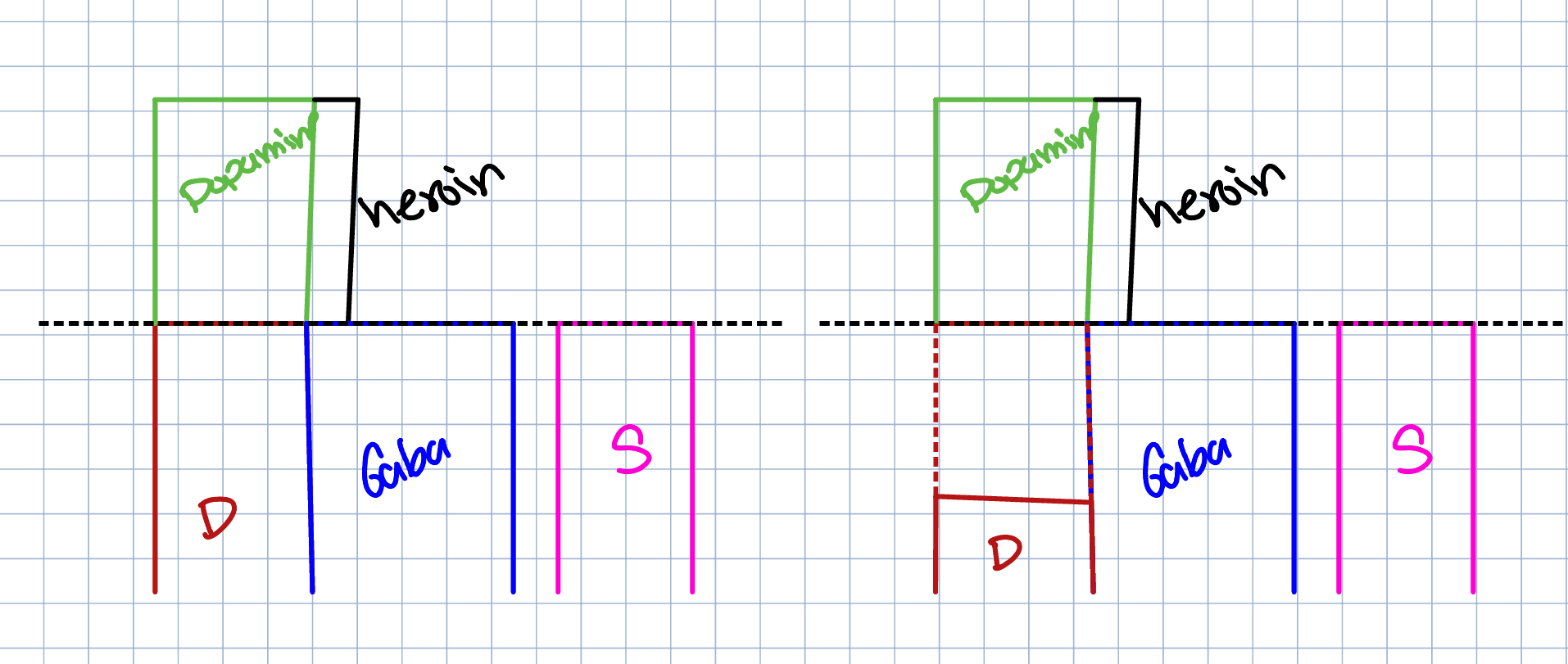
Agonist → mimics or stimulates neurotransmitters
Antagonist → blocks the production of a neurotransmitter
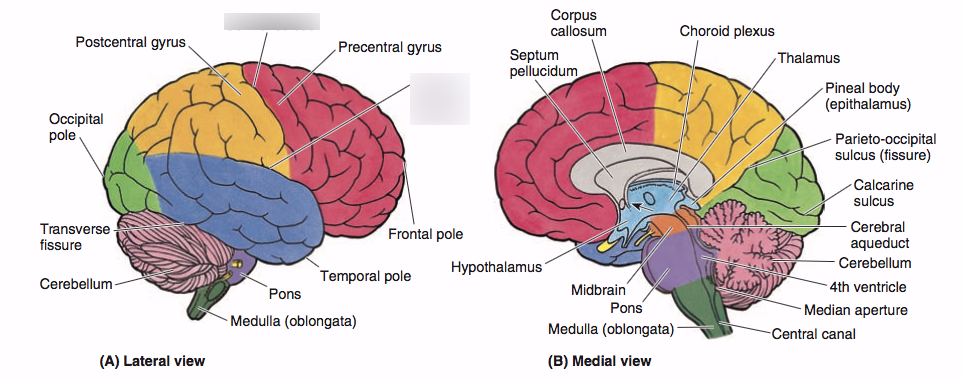
Corpus Callosum → connects the right and left hemisphere of the brain and allows them to communicate
Hemispheric Specialization → specilization occurs between the two hemispheres but a person is never left or right brained
Can be seen in split-brained patients
Hindbrain
Medulia Oblongata → Located on top of the spinal cord; the very bottom of the brain
involved in the control of our blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing
Pons → Located on top of the medulla; larger swelling
connects the hindbrain with the midbrain and forebrain
involves the control of facial expressions
Reticular Formation → Located through the middle of the medulla & the pons; in between the ears
involved in various physiological functions, including pain sensitization, alertness, fatigue, sleep, and motivation
Cerebellum → Located in the rear of the brain; large & deeply folded structure; “little brain”
Coordinates some habitual muscle movements such as tracking a target with our eyes or playing the saxaphone
Brain Stem → Located in the lower part of the brain that connects to the spinal cord
helps regulate vital body functions that you don’t have to think about, like breathing and your heart rate
Forebrain
Limbic System → Located as a loosley connected netwrok of structures
responsible for mood & emotions, as well as the experience of pain and fear
Thalamus → Located on top of the brainstem
responsible for recieving the sensory signals coming up the spinal cord and sending them to the appropriate areas in the rest of the forebrain
smell is the only thing that does not go through the thalamus but is directly wired to the Limbic system
Hypothalamus → Located directly underneath the thalamus & directly above the pituitary gland
controls several metabolic functions including body temperature, sexual arousal, hunger,thirst, and the endocrine system
Hippocampus → Curved structure located within each temporal lobe; wraps around the back of the thalamus
vital to our memory system
memories are processed through this area and then sent to other locations in the cerebral cortex for permanent storage
Amygdala → Two almond shaped structures located near the hippocampus
vital to our experiences of emotion
Cerebrum
Frontal Lobe → Located in front of the brain; underneath the forehead, largest lobe
important for voluntary movement, expressive language and for managing higher level executive functions
Prefrontal Cortex→
thought to play a critical role in directing thought process
acts as the brains central executive and is beleived to be important in forseeing consequences, pursuing goals, and maintaing emotional control
also beleived to be responsible for abstract thought
Primary Motor Cortex →
provides the most important signal for the production of skilled movements
Broca’s Area →
responsible for controlling the muscles involved in producing speech
if damaged, you may be unable to make the muscle movements needed for speech
Temporal Lobe → Located just behind the temples; below the parietal lobe
process’s sound sensed by our ears
sound waves are processed by the ears, turned into neutral impulses, and interpreted in our auditory cortices
Auditory Cortex →
processes auditory information
Wernicke’s Area →
interprets both written and spoken speech
if damaged, the ability to understand language would be affected and our speech might sound fluent but lack the proper syntax and grammatical structure needed for meaningful communication
Parietal Lobe → Located on top of the head; between the frontal & occipital lobes
Sensory cortex → which recives incoming touch sensations from the rest of the body
integrating sensory information, including touch, temperature, pressure and pain
Somatosensory Strip →
recieves sensory input like heat or pain
Occipital Lobe → Located towards the back of the brain; at the base of the cortex
processes visual signals and works cooperatively with many other brain areas
Visual Cortex →
region of the brain that recieves, integrates, and processes visual information relayed from the retinas
Ways to See the Brain
EEG → used majorily in sleep studies
gives us brain function but not structures
CAT/CT → uses x-rays to see how the brain is operating in a region
used mostly on heads
will show a structure but not function
MRI → show structure but not function
most commonly used
PET→ injected with an isotope to see how your brain is reacting
shows function but not structure
fMRI → only imagining technique that shows both function and structure
combined an MRI with a PET scan
Brain Mapping → occurs when a doctor identifies what part of your brain controlls vision, speech, and movement to determine the precise location to perform brain surgery without reducing yout brain function
Case Study → Phineas Gage
railroad worker who packed the explosives into the rock
explosives ignited while he was packing it in
rod blew through his left eye and through his head
survived the incident
the rod went through his face and destroyed a portion of his brain
after this incident, his personaity changed
went from friendley and a family man to bitter
Blindsight
large amoun of places in the brain where eyesight can be effected
sight passes through the thalamus
even if you are blind, the thalamus continues to function and send signals
Sensory Homunculus
picture
Case Study → Joe
suffered from epilepsy that would travel between the left and right parts of the brain via the corpus callosum
as. a last ditch effort, they removed the corpus callosum to stop the transfer between the two parts