PY 131 Chapter 16: Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer
- Heat moves due to temperature differences.
- Heat energy always moves from hot to cold.
- Heat is transferred from one object to another via three mechanisms:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
- During conduction the atoms/molecules of the object transferring the heat do not move.
- Conduction is the only method of moving heat through a solid.
- During convection the atoms/molecules do move.
- Convection occurs in liquids and gases.
- During radiation heat (energy) is transferred through space by electromagnetic waves (light) or gravitational waves.
Conduction
- Conduction is the flow of energy between objects or from one object to another due to collisions between the atoms/molecules and without net motion of the material.
- No net motion means the body does not move as a whole i.e. there is no bulk flow.
- Conduction can occur in solids, liquid and gases.
- In a solid the atoms are largely confined and collisions are the main mechanism by which the heat flows.
- In a liquid or gas the heat flows due to collisions of the atoms/molecules but also atoms/molecules can diffuse.
- Materials through which heat travels easily are called ==(thermal) conductors.==
- Examples include metals, diamond (diamond is 250% better thermal conductor than copper).
- Materials through which heat travels with difficulty are called ==(thermal) insulators.==
- Examples include glass, wood, plastic, air.
EXAMPLE 1
If you hold one end of a metal bar against a piece of ice, the end in your hand will become cold. In which direction is energy moving?
- ==From your hand to the ice==
Convection
Convection is heat transfer through an object due to the bulk motion of the material.
Convection requires there be a net force on a fluid element.
Convection can occur in different ways depending upon the force e.g. buoyant convection or forced convection.
- In buoyant convection, the force is buoyancy so buoyant convection requires there be gravity – without it buoyant convection cannot occur.
- Forced convection is when you blow or pump the fluid.
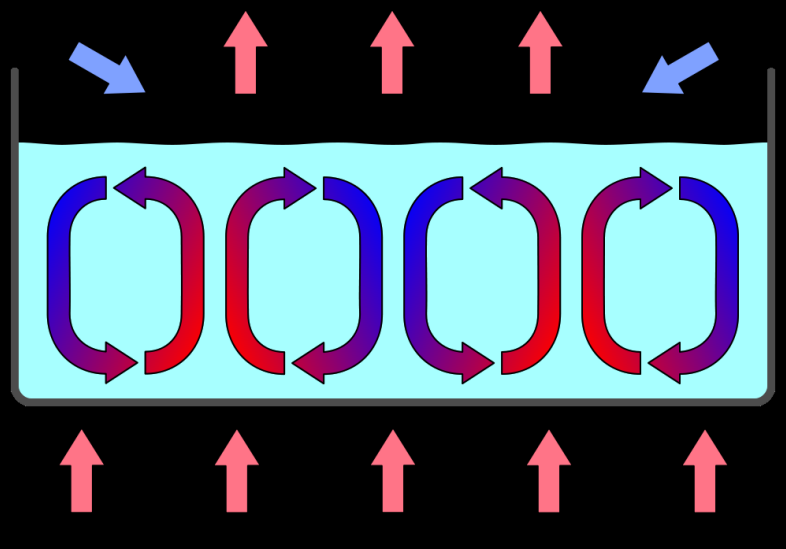
Consider a ‘fluid element’ with density ρb
- Here b stands for ‘bubble’.
The surrounding fluid has the same density ρ.
What happens if this element moves upward by an amount Δy?
The density will change to ρb +Δρb .
At the new location, the surrounding fluid has a density ρ +Δρ.
If ρb +Δρb < ρ+Δρ then the element will continue to rise due to the buoyancy force and the fluid is unstable to convection.
Since ρb = ρ the criterion for instability is that Δρb < Δρ or Δρb Δ y ≤ Δρ Δ y A buoyantly convecting fluid forms Bénard (convection) cells.
High-resolution images of the Sun show its surface is broken up into granules: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W_Scoj4HqCQ
The Bénard cells on the Sun are huge: each is ~1000 km across and lives for ~ 10 minutes.
Careful observations indicate there are also supergranuales which are of order 30,000 km in size.
- It is thought these may be the imprint of deeper lying convective cells.
Convection is responsible for sea breezes.
- The land heats the air above it better than the water heats the air above it.
- The density of the air over the land decreases causing it to float (rise).
- The air over the sea is pushed in by pressure forces in to replace it.
Newton’s Law of Cooling
- Consider two points in space separated by a distance Δx and with a temperature difference ΔT.
- The ratio of ΔT to Δx is called the temperature gradient.
- ΔT/Δx
- The temperature gradient (which is a vector) will cause an amount of heat ΔQ to flow between the points in a time Δt.
- The thermal current I is
- I= ΔQ / Δt
- It is found from the experiment that the thermal current is proportional to the temperature gradient.
- I ∝ - (ΔT/Δx)
- The minus sign is because heat flows from hot to cold.
- This relationship is called ==Newton’s Law of Cooling.==
- The larger the temperature difference, the faster a hot object loses energy or a cool object gains it.
- As the object cools, the heat flow slows down.
- In addition to the temperature gradient, the thermal current depends on the contact area and what the material is.
- The smaller the contact area the smaller the heat flow.
- Heat finds it harder to pass through some materials than others.
- Newton’s Law of Cooling works well for conduction. For convective cooling it works if the cooling liquid/gas is pumped/forced/blown: if the convective cooling is buoyancy driven then it doesn’t work as well.
- It doesn’t take into account the fluid speed.
EXAMPLE 1
Why does it take an ice cube longer to melt on a winter day than on a summer day?
- ==The atmosphere is cooler==
Radiation
Heat Transfer by Radiation is the transfer of heat via the emission and absorption of light.
All objects with a temperature emit light.
- This is not the light reflected from a light source e.g. the Sun.
Usually, we don’t notice this radiation because, at typical everyday temperatures, the emitted light is mostly infrared.
- It takes temperatures of ~ 500 Celsius before the emitted light starts to
become visible light. - At very high temperatures the emitted light can be UV or X-rays.
- It takes temperatures of ~ 500 Celsius before the emitted light starts to
The emission of radiation causes an object to cool.
- it’s the emission of radiation into space that cools the Earth at night.
The temperature of an object is related to the frequency or wavelength of the light it emits which has the maximum intensity
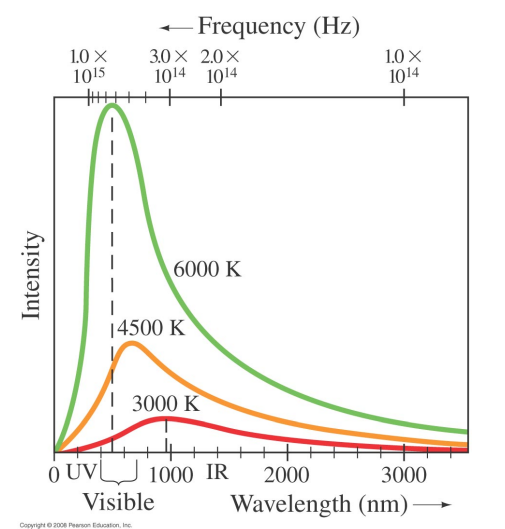
This relationship is known as ==Wien's Displacement Law==.
When radiation is incident upon an object, some of the light is absorbed, some is reflected, and some passes through.
- The absorbed radiation will cause an increase in the object’s
temperature. - The absorption of radiation emitted by the Sun heats the Earth during the day.
- The absorbed radiation will cause an increase in the object’s
An object which absorbs all the radiation incident upon it is called a blackbody.
Objects which are good emitters of radiation are also good absorbers of radiation (and vice versa).
To make life complicated, the amount of radiation absorbed and emitted depends on the type of light.
- Some objects reflect visible light well but absorb all the IR, for example.
Assuming a black object is black for all types of light, and a white object is white for all types of light, a black object radiates energy faster than a white object.
An object’s opacity is a measure of the amount of light it absorbs as light travels through the object.
The opacity can change with the ‘type’ of light.
- an object (e.g. glass) can be very transparent to visible light but not transparent (opaque) to infrared or UV.
The opacity of the atmosphere is very important to astronomers.
- If the atmosphere is opaque, a telescope can’t see through it.

The Greenhouse Effect
- It is the difference of the opacity of the atmosphere to visible and infrared light which keeps Earth warmer than it should be given our distance from the Sun.
- If Earth were a blackbody with no atmosphere it would have an average temperature of ~ +5 °C.
- Given that Earth reflects about 30% of the incident sunlight, an Earth without an atmosphere would have an average temperature of ~ -20 °C.
- Earth’s actual average temperature is ~ +15 °C.
- The Sun emits a lot of its light as visible light. Visible light can largely pass through the atmosphere and be absorbed by the Earth causing Earth to be heated.
- Earth emits most of its radiation as infrared light.
- This should cool the Earth but the atmosphere is opaque to infrared light so energy gets absorbed.
- The heated atmosphere radiates some of its energy back toward the Earth.
- The net effect is that radiation finds it difficult to escape and the Earth is warmer than it would be if it could easily escape.
- This is called the ==Greenhouse Effect.==
- Even though actual greenhouses work slightly differently.
- The same effects occur on other planets or moons with atmospheres.
- On Venus the Greenhouse Effect has runaway and the temperature is 450 °C.
- The gases in Earth’s atmosphere which absorb most of the infrared radiation are water vapor and carbon dioxide.
- The amount of these gases in the atmosphere changes over time due to natural processes such as volcanoes, ice ages, sun cycles etc.
- It even changes over the cycle of the year.
- Over the last 200 years the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has roughly doubled.
- Since 1960 the average temperature of the Earth has increased by ~1 °C.