Chapter 4

Patterns of Growth
Cephalocaudal pattern is the sequence in which the earliest growth always occurs at the top - the head
Infants’ eyes and brains grow faster than their jaw
Proximodistal pattern is the sequence in which growth starts at the center of the body and moves toward the extremities
Infants control the muscles of their trunk and arms before they control their hands and fingers
Height and Weight
Most newborns are 18 to 22 inches long and weigh between 5 and 10 pounds.
Infants grow about 1 inch per month during the first year
By 2 years of age
Approx weight - 26 to 32 pounds
Approx height - 32 to 35
The Brain
Contains approximately 100 billion neurons at birth
Because the brain is still developing rapidly in infancy, the head should be protected from falls and other injuries
Shaken baby syndrome - brain swelling and hemorraging
Newborn’s brain is about 25% of its adult weight
By the 2nd birthday, it is about 75% of its adult weight
However, the brains areas do not mature uniformly
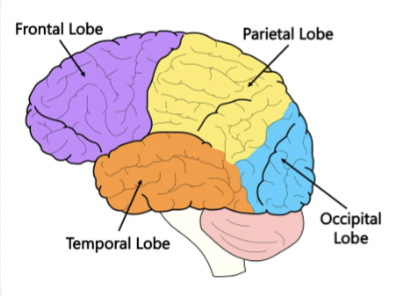
Mapping the Brain
Frontal lobe is involved in thinking, decision making, personality, and intentionality
Occipital lobe functions in vision
Temporal lobe facilitates hearing, language processing, and memory
Paretial lobe plays important roles involving spatial location, attention, and motor control.
Early Experience and the Brain
Children who grow up in a deprived environment may have depressed brain activity
Sensory stimuli is important
exaggerated speech
Basic colors and shapes
Observational learning
learning by observing others
following the example
However, the brain tends to demonstrate both flexibility and resilience
Studies have shown specific cases in which the effects of deprived environments were reversible
But if it’s later in development it’s harder to reverse and won’t be able to fully develop as intended
Sleep
Typical newborn sleeps approximately 18 hours a day
The most common infant sleep-related problem is nighttime waking
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) occurs when an infant stops breathing, usually at night
Infant dies suddenly without an apparent cause
Less likely to occur in infants who use a pacifier when they go to sleep
Shared sleeping is linked with a higher incidence of SIDS
Low birth weight infants are 5-10x more liley to die of it
Nutrition
Nutritional needs and eating behavior:
Infants should consume approximately 50 calories per day for each pound they weigh
As motor skills improve, infants change from using suck-and-swallow movements to shew-and swallow movements with semisolid and then complex foods
Infants need to have a diet that includes fruits and vegetables
Breast vs Bottle feeding
During the first 4-6 months of life, human milk or an alternative formula is the baby’s source of nutrients and energy
Although the consensus states “fed is Best,” there are some benefits to breastfeeding:
Fewer gastrointestinal infections
Fewer respiratory tract infections
Lower likelihood of obesity
Lower likelihood of type 1 diabetes in childhood
Motor Development
Dynamic systems theory
Reflexes
Gross motor skills
Fine motor skills
The dynamic systems theory
According to the dynamic systems theory, infants assemble motor skills for perceiving and acting
Motor skills initially develop alongside the development of the nervous system
To continue the development of motor skills, infants must perceive something in their environment that motivates them to act and fine-tune their movements
Reflexes
Reflexes are built-in reactions to stimuli
They are automatic and govern the newborn’s movements
Rooting reflex occurs when the infant’s cheek is stroked or the side of the mouth is touched
Infants turn their head trying to find something to suck
Sucking reflex occurs when newborns automatically suck and object places in their mouth
Moro reflex is a neonatal startle response that occurs in reaction to a sudden, intense noise or movement
Grasping reflex occurs when something touches the infants’ palms
Gross Motor Skills
Gross motor skills involve large-muscle activities:
Lifting head
Rollin over
Sitting
Crawling
Walking
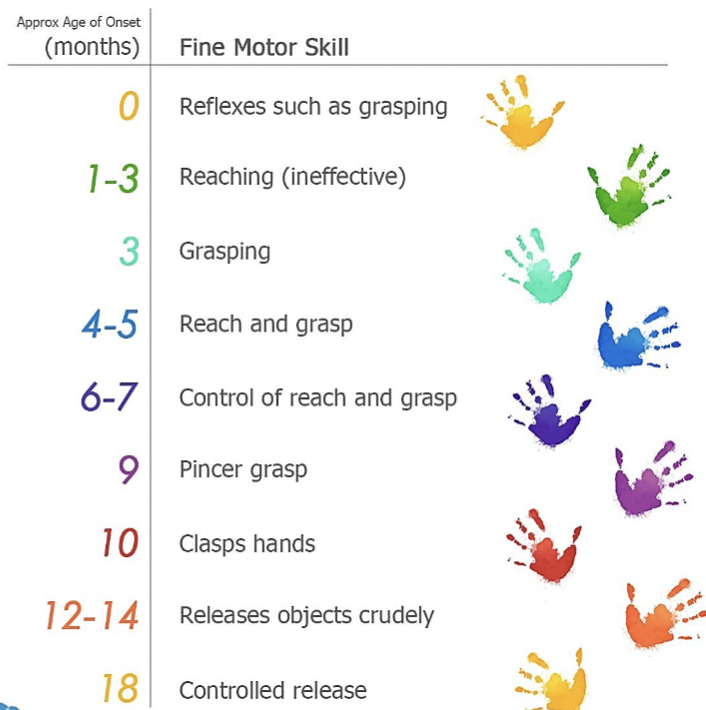
Fine Motor Skills
Fine motor skills involve finely tuned movements:
Grasping a toy
Using a spoon
Buttoning a shirt
Any activity that requires finger dexterity
Problem solving
What are sensation and Perception?
Sensation occurs when information interacts with sensory receptors - the eyes, ears, tongue, nostrils, and skin
Perception is the brain’s interpretations of what is sensed
At birth, the nerves and muscles and lens of the eye are still developing
Newborns cannot see small things that are far away
Faces are the most important visual stimuli in children’s social environment; they extract a lot of information from other’s faces.
Vision
By 8 weeks, infants can discriminate some colors; by 4 months, they have color preferences
Perceptual consitancy is the perception of an object as constant even though our sensation of the object changes.
Perception of size and shape of an object remains the same even if the distance or orientation of the object has changes
Presented in babies as young as 3 months of age
Depth perception is the ability to judge if objects are nearer or farther away then other objects
This begins to develop around the 5th month but will not be fully developed after 2 years of age.