Metabolism
Introduction to Metabolism
Definition of Metabolism: Metabolism is the sum of all the reactions in a cell or the body.
Purpose of Metabolism: Metabolism involves chemical reactions that convert molecules to release energy or synthesize new substances necessary for life.
Key Reactions in Metabolism
Importance of Glucose
Glucose: A vital molecule in metabolism. It serves as a primary energy source and starting point for many new chemicals.
Energy Release: During respiration, energy is released from glucose, which is utilized by enzymes to help synthesize new molecules.
Metabolic Conversions In Plant Cells
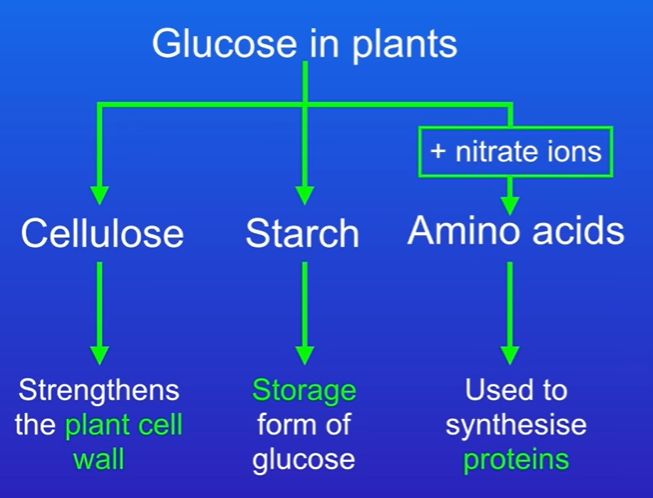
Glucose to Cellulose
Glucose is converted into cellulose, providing structural support for plant cell walls.
Glucose to Starch
Glucose is transformed into starch, which acts as a stored form of glucose in plants.
Glucose to Amino Acids
In the presence of nitrate ions, glucose is converted into amino acids, which are essential for protein synthesis.
Metabolic Conversions In Animals
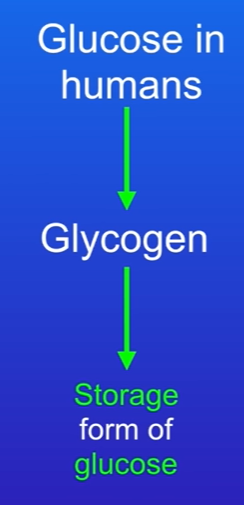
Glucose to Glycogen
In humans and animals, glucose is stored as glycogen, a form which allows for energy storage and release when needed.
Lipid and Protein Metabolism
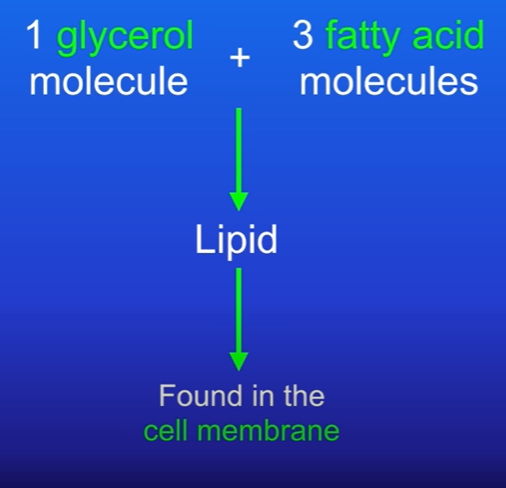
Lipid Synthesis
Formation of Lipids: Lipid synthesis: One glycerol molecule reacts with three fatty acids to form a lipid molecule, which is crucial for cell membrane structure.
Importance in Exams: Understanding the details of lipid synthesis is essential as it may appear in exam questions.
Protein Metabolism
Protein Breakdown: Humans require a small amount of dietary protein. Excess proteins are broken down into chemical urea, which is excreted by the kidneys.
Excretion: This process of protein breakdown and urea formation will be further explored in upcoming content.
By the end of the video, viewers should understand the concept of metabolism and the different biochemical transformations it encompasses, particularly how glucose is converted into other essential molecules.