Aquatic and Terrestrial Pollution
Water Quality Indicators
Nitrate
Nutrients for growth
Too much can cause algae blooms = nutrient pollution
Phosphate
Found in fertilizers
Found in detergents
Fecal Coliform
Fecal matter in the water
Can cause cholera and dysentery (sewage pollution)]
Turbidity
How clear the water is
The water can become cloudy from sediment pollution
Decrease in photosynthesis
Stoppage of water
pH
Ocean Acidification
→ Climate change
→ Can affect shells of organisms
Temperature
(Thermal pollution)
Range of Tolerance
Coral reefs get stressed with hot water
When exposed to hot water, coral reefs undergo coral bleaching, where they expel the algae living in their tissues, causing them to turn white and potentially die.
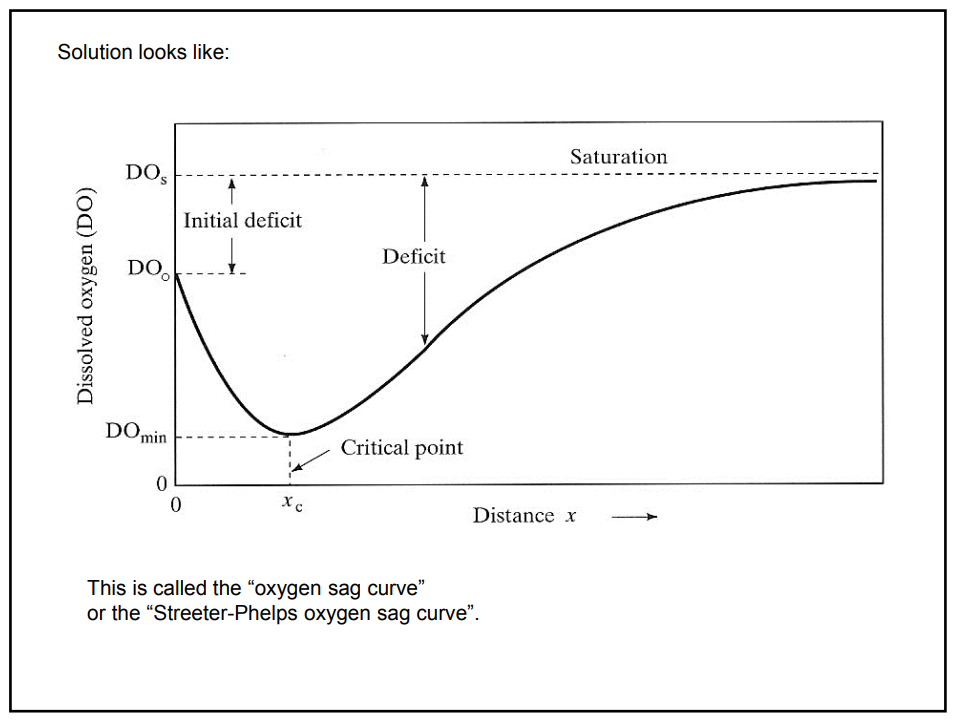
D.O
Dissolved Oxygen
Oxygen Sag Curve
Species Diversity
Higher species diversity is better
Biological Oxygen Demand
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a measure of the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by aerobic biological organisms to break down organic material in water over a specific time period. High BOD levels indicate high organic pollution, leading to oxygen depletion and harming aquatic life.
Excessive nutrients enter water.
Algal bloom occurs due to nutrient abundance.
Algae die, sink, and decompose.
Decomposition depletes oxygen.
Low oxygen levels harm aquatic life.
Water Pollution
Water Pollution Sources are Classified as:
Point source pollution: enters from a single source
Example: CWA - need a permit
Non-point source pollution: Not from a single source
Example: Runoff, sediment
Wastewater
Water from human use such as factories, sinks, etc
Artificial Eutrophication
Caused by excessive nutrient inputs from human activities like agricultural runoff or sewage discharge, leading to accelerated growth of algae and aquatic plant species.
Thermal Pollution
Warm water is bad for water pollution because it decreases oxygen solubility, leading to lower oxygen levels in water bodies. This can harm aquatic life and disrupt ecosystems.
Ocean Pollution
Oil spills
Plastic waste
Groundwater Pollution
Heavy metals such as lead, arsenic, and mercury harm humans
Effects of Water Pollution
Water pollution can harm aquatic life, disrupt ecosystems, contaminate drinking water, and lead to human health issues. It can also impact industries like fishing and tourism.
Water pollution can cause immediate damage to an ecosystem, but the effects can be long-term and far-reaching as well
Biomagnification = build up through the food chain
Levels at the bottom of the food chain (in producers) may not be harmful
Levels at the top of the food chain can be toxic
Endocrine disrupters (PCBs, PBBs, BPA) in plastics and solvents can disrupt hormone systems and also can be PDPs.
Eutrophication
Causes
Excess nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) from…
Fertilizers
Sewage
Manure
Effects
Decrease in dissolved oxygen in the H2O
Decrease/death of aquatic organisms
Reduced H2O clarity for photosynthesis by aquatic plants
Algae toxins
How it works
Excessive nutrients enter water.
Nutrients promote algae growth.
Algae bloom blocks sunlight.
Plants die due to lack of sunlight.
Decomposition depletes oxygen.
Oxygen depletion harms aquatic life.
Sewer Treatment
Primary Treatment
Removal of sticks and rocks which are removed by screens. Chemicals can be added to make them clump
Secondary Treatment
Bacteria perform aerobic decomposition to break down organic matter
Tertiary Treatment
Disinfection through chlorine, UV, and ozone reduces final pollutants left after primary and secondary treatment.
Solid Waste
Categories
Municipal (homes and businesses)
Manufacturing
Mining waste
Agricultural waste
Disposal
Landfill
Incineration
Burning trash for energy saves space but also produces air pollution
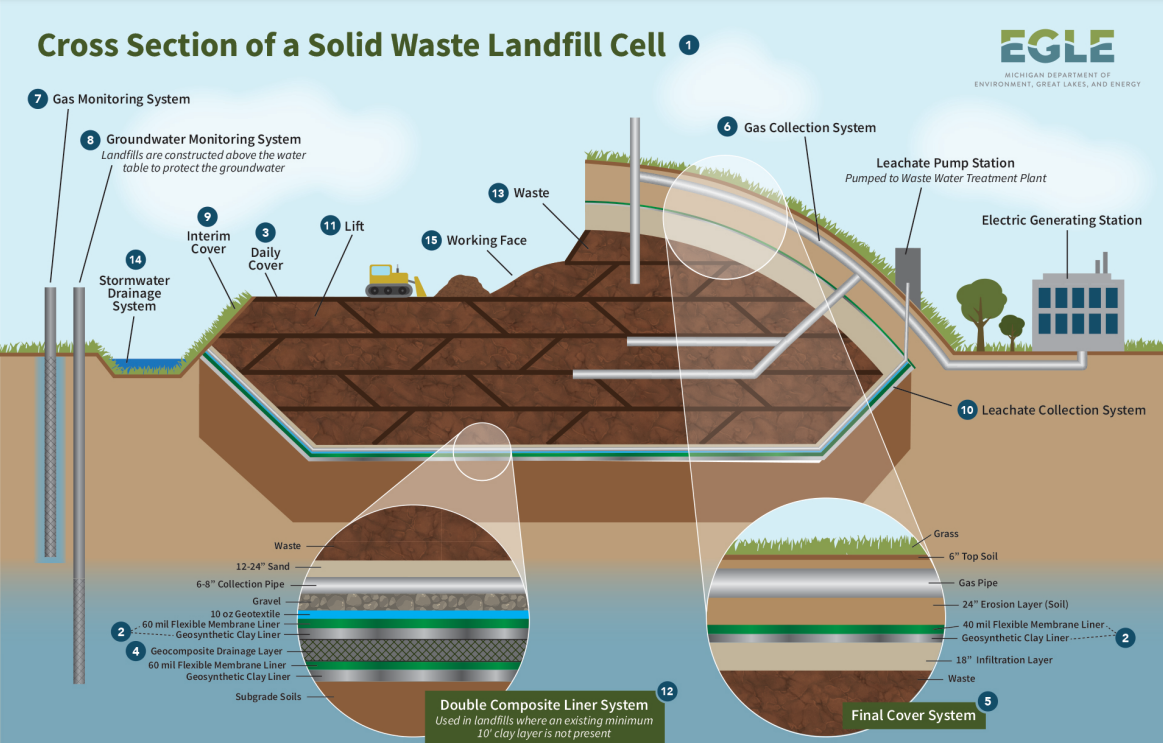
Solid Waste in Action
Solid Waste Management Terms:
Groundwater Monitoring: Monitoring water quality to prevent contamination.
Methane Collection: Capturing methane gas from waste for energy.
Solid Cap: Covering waste to prevent water infiltration.
Open Cell: Waste disposal area without liners.
Leachate: Liquid formed by water passing through waste.
Leachate Collection: System to collect and treat leachate.
Closed Cell: Waste disposal area with liners.
HDPE Liner: High-density polyethylene liner to contain waste.
Gravel: Used for drainage in waste disposal areas.
Clay: Natural material used for sealing waste containment areas.