WIP - Network+
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
Network+ Exam Foundations
● Network+ (N10-008)
o CompTIA Network+ is a vendor neutral networking certification that is trusted around the world. It validates the essential knowledge and skills needed to confidently design, configure, manage, and troubleshoot any wired and wireless devices. CompTIA Network+ certified individuals are in-demand worldwide. (CompTIA.org)
● Exam Description
o CompTIA Network+ covers the configuration, troubleshooting, configuring, and managing networks
▪ Network documentation
▪ Network standards
▪ Network security
▪ Cloud technologies
▪ Virtualization
● Five Domains
o 24% - Networking Fundamentals
o 19% - Network Implementations
o 16% - Network Operations
o 19% - Network Security
o 22% - Network Troubleshooting
● Exam Details
o Up to 90 questions in 90 minutes
▪ Multiple-choice
▪ Performance-based/Simulations
o Requires a 720 out of 900
o Recommended Experience:
- 1 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ CompTIA A+ Certification
▪ 9 months of networking experience
o Released: September 15 2021
● Are You Ready?
o Take practice exams
o Did you score at least 85% or higher?
o If you need more practice, take additional practice exams to hone your skills before attempting the exam
● What kind of jobs can I get?
o Help Desk Technician
o Network Support Specialist
o Network Administrator
o Network Field Technician
o Network Engineer
o Network Analyst
- 2 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
Networks Basics
Objectives 1.2 and 2.1
● OBJ 1.2: Explain the characteristics of network topologies and network types
● OBJ 2.1: Compare and contrast various devices, their features, and heir appropriate placement on the network
● Overview of Networks
o Computer Networks
▪ What comes to mind?
▪ Is it limited to computers?
▪ Is it limited to Ethernet, WiFi, or fiber?
o Purpose of Networks
▪ To make connections between machines
▪ Converged networks combine multiple types of traffic like data, video, and voice
▪ We expect 99.999% availability (The 5 9’s)
● Only 5 minutes downtime per year
o Network Traffic Examples
▪ File sharing
▪ Video chatting
▪ Surfing the Web
▪ Social Media
▪ Streaming Video
▪ Messaging
- 3 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ VoIP
● Network Components
o Client
▪ Device end-user accesses the network with
▪ Workstation, laptop, tablet, smartphone, television, server, or other terminal devices
▪ Can be any device that connects to the network
o Server
▪ Provides resources to the rest of the network
▪ Different servers provide different functions, such as an E-mail server, Web server, File server, Chat server, and Print server
▪ Can be a dedicated server hardware/software or can be a device that is acting like a server for a particular function
o Hub
▪ Older technology to connect networked devices, such as clients and servers
▪ Can be interconnected to provide more ports, but leads to increased network errors
▪ Receives information in one port and rebroadcasts it out all the other ports
o Wireless Access Point (WAP)
▪ Device that allows wireless devices to connect into a wired network
▪ Commonly used in home, small business, and even some large enterprise networks
▪ Acts as a wireless hub
- 4 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Switch
▪ Connects networked devices such as clients and servers (like a hub) ▪ Switches learn what devices are on which switch ports
▪ Switches only forward traffic received from a port to the destination port based on the device’s MAC address
▪ Provides more security and efficiently uses available bandwidth
o Router
▪ Connect two different networks together
▪ Intelligently forwards traffic to and from a network based on its logical address
▪ Most modern routers use Internet Protocol (IP) address to determine routing of traffic
o Media
▪ Connect two devices or a device to a port
▪ Made from copper cable, fiber optic cable, or radio frequency waves (WiFi)
▪ Each type has strengths and limitations, such as its available bandwidth, capacity, distance that can be covered, and cost to install and maintain
o Wide Area Network (WAN) Link
▪ Physically connects networks together
▪ Numerous WAN links are available: leased lines, DSL, Cable, Fiber Optic, Satellite, Cellular, Microwave, …
▪ Connects internal network to external networks, such as a SOHO network to Internet
- 5 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Network Resources
o Client/Server Model
▪ Uses dedicated server to provide access to files, scanners, printers, and other resources
▪ Administration and backup are easier since
resources are located on a few key servers
o Benefits of Client/Server 
▪ Centralized administration
▪ Easier management
▪ Better scalability
o Drawbacks of Client/Server
▪ Higher cost
▪ Requires dedicated resources
▪ Requires network operating system
o Peer-to-Peer Model
▪ Peers (PCs) share resources (files/printers) 
with each other directly
▪ Administration and backup are more difficult
since resources are located on a many PCs
which adds to the administrative burden
o Benefits of Peer-to-Peer
▪ Lower cost
▪ No dedicated resources required
▪ No specialized operating system required
o Drawbacks of Peer-to-Peer
▪ Decentralized management
- 6 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Inefficient for large networks 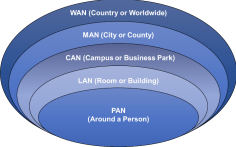
▪ Poor scalability
● Network Geography
o Personal Area Network (PAN)
▪ Smallest type of wired or
wireless network
▪ Covers the least amount
of area (few meters)
▪ Examples:
● Bluetooth cellphone to car
● USB hard drive to laptop
● Firewire video camera to computer
o Local Area Network (LAN)
▪ Connects components in a limited distance
▪ Each segment is limited to short distances, such as 100 meters with CAT 5 cabling
▪ Consists of Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) or WiFi networks (IEEE 802.11)
● Internal wired or wireless networks
o Campus Area Network (CAN)
▪ Connects building-centric LANs across a university, industrial park, or business park
▪ Covers many square miles and buildings
▪ Examples:
● College campus
● Business Parks
● Military bases
- 7 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
▪ Connects scattered locations across a city
▪ Larger than a CAN, but smaller than a WAN
▪ Covers up to a 25-mile radius in larger cities
▪ Examples:
● City departments like the police department
● Community college with campuses spread across a county
o Wide Area Network (WAN)
▪ Connects geographically disparate internal networks
▪ Consists of leased lines or Virtual Private Networks tunneled over the Internet
▪ Covers distances around the country or around the world
▪ Examples:
● The Internet (largest WAN)
● Connecting two private corporate networks from New York to
Seattle
● Wired Network Topology
o Defining Network Topology
▪ Physical Topology
● How devices are physically connected by media
▪ Logical Topology
● How the actual traffic flows in the network
o Bus Topology
▪ Uses a cable running through area that required network connectivity 
▪ Each device “taps” into the cable using either a T connector or vampire tap
▪ Old technology, not commonly used anymore
- 8 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Devices on cable form single collision domain
o Ring Topology
▪ Uses a cable running in a circular loop 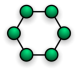
▪ Each device connects to the ring, but data travels in a singular direction ▪ FDDI (Fiber networks) used two counter-rotating rings for redundancy
▪ On token ring networks, devices wait for a turn to communicate on ring by passing a token
o Star Topology 
▪ Most popular physical LAN topology
▪ Devices connect to a single point
▪ Commonly used with Ethernet cabling, but wireless or fiber is also used
▪ If the central device fails, the entire network fails
o Hub-and-Spoke Topology
▪ Used for connecting multiple sites
▪ Similar to Star but with WAN links instead of LAN connections
▪ Not redundant, if central office (hub) fails, the whole network can fail o Full-Mesh Topology
▪ Most redundant topology ![]()
▪ Every node connects to every other node
▪ Optimal routing is always available
▪ Very expensive to maintain and operate ![]()
▪ Number of Connections
▪ x= n(n - 1) / 2
- 9 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Partial-Mesh Topology
▪ Hybrid of the full-mesh and the hub-and-spoke topologies ![]()
▪ Provides optimal routes between some sites, while avoiding the expense of connecting every site
▪ Must consider network traffic patterns to design it effectively
● Wireless Network Topology
o Infrastructure Mode
▪ Most common type of wireless network
▪ Requires centralized management
▪ Uses a wireless access point as a centralized point like a star topology
▪ Supports wireless security controls
o Ad Hoc Mode
▪ Decentralized wireless network
▪ No routers or access points are required
▪ Forwarding decisions for data on the network are made dynamically ▪ Allows creation/joining of networks “on-the-fly”
▪ Creates P2P connections
o Wireless Mesh Topology
▪ Interconnection of different types of nodes or devices
▪ Consists of clients, routers, and gateways
▪ Utilizes different radio frequencies to extend and expand access
▪ Reliable and redundant connections
- 10 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Internet of Things (IoT)
o Internet of Things (IoT) Technologies
▪ 802.11
● Operates as infrastructure or ad hoc
▪ Bluetooth
● Low energy use variant of Bluetooth which allows for a mesh
network
▪ RFID
● Uses electromagnetic fields to read data stored in embedded tags
▪ NFC
● Enables two electronic devices to communicate within a 4 cm
range
▪ Infrared (IR)
● Operates with line of sight
▪ Z-Wave
● Provides short-range, low-latency data transfer at rates and power
consumption lower than Wi-Fi
● Used primarily for home automation
▪ Ant+
● Collection and transfer of sensor data
● Used with remote control systems (tire pressure, TVs, lights)
- 11 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
OSI Model
Objective 1.1 and 5.3
● OBJ 1.1: Compare and contrast the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model layers and encapsulation concepts
● OBJ 5.3: Given a scenario, use the appropriate network software tools and commands
● OSI Model Overview
o OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection)
▪ Developed in 1977 by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) ▪ Called the OSI model or OSI stack
▪ Consists of 7 layers
▪ Useful in troubleshooting networks
▪ Serves as a reference model in networks
o Purpose of Reference Model
▪ Categorize functions of the network into particular layer(s)
▪ Compare technologies across different manufacturers
▪ By understanding its functions, you can understand how best
to communicate with that device
- 12 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o OSI Model Layers
![]()
![]()
o Data Types in the OSI Model
![]()
![]() - 13 -
- 13 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Layer 1 (Physical)
o Physical Layer (Layer 1)
▪ Transmission of bits across the network
▪ Physical and electrical characteristics
▪ Characteristics:
● How bits are represented on the medium
● Wiring standards for connectors and jacks
● Physical topology
● Synchronizing bits
● Bandwidth usage
● Multiplexing strategy
o How are bits represented on the medium?
▪ Electrical voltage (copper wiring) or light (fiber optics) represent 1’s and 0’s (bits)
▪ Current State
● If 0 volts, then 0 is represented
● If +/- 5 volts, then 1 is represented
▪ Transition Modulation
● If it changed during the clock cycle, then a 1 is represented,
otherwise, a 0
o How are the cables wired?
▪ TIA/EIA-568-B is standard wiring for RJ-45 cables and ports
▪ Crossover cables use T-568A and T-568B
▪ Straight-thru cables typically use T-568B on both ends, but could use T-568A on both
o How are the cables connected?
▪ Layer 1 devices view networks from a physical topology perspective
▪ Includes:
● Bus
- 14 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Ring
● Star
● Hub-and-Spoke
● Full Mesh
● Partial Mesh
o How is communication synchronized?
▪ Asynchronous
● Uses start bits and stop bits to indicate when transmissions occur
from sender to receiver
▪ Synchronous
● Uses a reference clock to coordinate the transmissions by both
sender and receiver
o How is bandwidth utilized?
▪ Broadband
● Divides bandwidth into
separate channels
● Example:
o Cable TV
▪ Baseband
● Uses all available frequency on a medium (cable) to transmit data
and uses a reference clock to coordinate the transmissions by
both sender and receiver
● Example:
o Ethernet
o How can we get more out of a limited network?
▪ Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM)
● Each session takes turns, using time slots, to share the medium
between all users
- 15 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Statistical Time-Division Multiplexing (StatTDM)
● More efficient version of TDM, it dynamically allocates time slots
on an as-needed basis instead of statically assigning
▪ Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM)
● Medium is divided into various channels based on frequencies and
each session is transmitted over a different channel
o Broadband
o Examples at Layer 1
▪ Cables
● Ethernet
● Fiber optic
▪ Radio frequencies
● Wi-Fi
● Bluetooth
▪ Infrastructure devices
● Hubs
● Wireless Access Points
● Media Converters
● Layer 2 (Data Link)
o Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
▪ Packages data into frames and transmitting those frames on the network, performing error detection/correction, and uniquely identifying network devices with an address (MAC), and flow control
● MAC
● Physical addressing
● Logical topology
● Method of Transmission
● Link Layer Control (LLC)
o Connection services
o Synchronizing transmissions
- 16 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Media Access Control (MAC)
▪ Physical addressing
● Uses 48-bit address assigned to a network interface card (NIC) by
manufacturer
● First 24-bits is the vendor code
● Second 24-bits is a unique value
▪ Logical topology
● Layer 2 devices view networks logically
● Ring, bus, star, mesh, hub-and-spoke, ...
▪ Method of transmission
● Many devices are interconnected
● Determines whose turn it is to transmit to prevent interference
with other devices
o Logical Link Control (LLC)
▪ Provides connection services
▪ Acknowledgement of receipt of a message
▪ Flow control
● Limits amount of data sender can send at one time to keep
receiver from becoming overwhelmed
▪ Error control
● Allows receiver to let sender know when an expected data frame
wasn’t received or was corrupted by using a checksum
o How is communication synchronized?
▪ Isochronous
● Network devices use a common reference clock source and create
time slots for transmission
● Less overhead than synchronous or asynchronous
▪ Synchronous
● Network devices agree on clocking method to indicate beginning
and end of frames
- 17 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Uses control characters or separate timing channel
▪ Asynchronous
● Network devices reference their own
internal clocks and use start/stop bits
o Examples at Layer 2
▪ Network Interface Cards (NIC)
▪ Bridges
▪ Switches
● Layer 3 (Network)
o Network Layer (Layer 3)
▪ Forwards traffic (routing) with logical address
● Example: IP Address (IPv4 or IPv6)
▪ Logical addressing
▪ Switching
▪ Route discovery and selection
▪ Connection services
▪ Bandwidth usage
▪ Multiplexing strategy
o Logical Address
▪ Numerous routed protocols were used for logical addressing over the years:
● AppleTalk
● Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX)
● Internet Protocol (IP)
▪ Only Internet Protocol (IP) remains dominant
● IP v4
● IP v6
- 18 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o How should data be forwarded or routed?
▪ Packet switching (known as routing)
● Data is divided into packets and forwarded
▪ Circuit switching
● Dedicated communication link is established between two devices
▪ Message switching
● Data is divided into messages, similar to packet switching, except
these messages may be stored then forwarded
o Route Discovery and Selection
▪ Routers maintain a routing table to understand how to forward a packet based on destination IP address
▪ Manually configured as a static route or dynamically through a routing protocol
● RIP
● OSPF
● EIGRP
o Connection Services
▪ Layer 3 augment Layer 2 to improve reliability
▪ Flow control
● Prevents sender from sending data faster than receiver can get it
▪ Packet reordering
● Allows packets to be sent over multiple links and across multiple
routes for faster service
o Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
▪ Used to send error messages and operational information about an IP destination
▪ Not regularly used by end-user applications
▪ Used in troubleshooting (ping and traceroute)
- 19 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Examples at Layer 3
▪ Routers
▪ Multilayer switches
▪ IPv4 protocol
▪ IPv6 protocol
▪ Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
● Layer 4 (Transport)
o Transport Layer (Layer 4)
▪ Dividing line between upper and lower layers of the OSI model
▪ Data is sent as segments
▪ TCP/UDP
▪ Windowing
▪ Buffering
o TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
▪ Connection-oriented protocol
▪ Reliable transport of segments
● If segment is dropped, protocol detects it and resends segment
▪ Acknowledgements received for successful communications
▪ Used for all network data that needs to be assured to get to its
destination
o UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
▪ Connectionless protocol
▪ Unreliable transport of segments
● If dropped, sender is unaware
- 20 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ No retransmission
▪ Good for audio/video streaming
▪ Lower overhead for increased performance
o TCP vs UDP
![]()
o Windowing
▪ Allows the clients to adjust the amount of data sent in each segment
▪ Continually adjusts to send more or less data per segment transmitted ● Adjusts lower as number of retransmissions occur
● Adjusts upwards as retransmissions are eliminated
o Buffering
▪ Devices, such as routers, allocate memory to store segments if bandwidth isn’t readily available
▪ When available, it transmits the contents of the buffer
▪ If the buffer overflows, segments will be dropped
o Examples at Layer 4
▪ TCP
▪ UDP
- 21 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ WAN Accelerators
▪ Load Balancers
▪ Firewalls
● Layer 5 (Session)
o Session Layer (Layer 5)
▪ Think of a session as a conversation that must be kept separate from others to prevent intermingling of the data
▪ Setting up sessions
▪ Maintaining sessions
▪ Tearing down sessions
o Setting up a Session
▪ Check user credentials
▪ Assign numbers to session to identify them
▪ Negotiate services needed for session
▪ Negotiate who begins sending data
o Maintaining a Session
▪ Transfer the data
▪ Reestablish a disconnected session
▪ Acknowledging receipt of data
o Tearing Down a Session
▪ Due to mutual agreement
● After the transfer is done
▪ Due to other party disconnecting
o Examples at Layer 5
- 22 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ H.323
● Used to setup, maintain, and tear down a voice/video connection
▪ NetBIOS
● Used by computers to share files over a network
● Layer 6 (Presentation)
o Presentation Layer (Layer 6)
▪ Responsible for formatting the data exchanged and securing that data with proper encryption
▪ Functions
▪ Data formatting
▪ Encryption
o Data Formatting
▪ Formats data for proper compatibility between devices
● ASCII
● GIF
● JPG
▪ Ensures data is readable by receiving system
▪ Provides proper data structures
▪ Negotiates data transfer syntax for the Application Layer (Layer 7)
o Encryption
▪ Used to scramble the data in transit to keep it secure from prying eyes ▪ Provides confidentiality of data
▪ Example:
● TLS to secure data between your PC and website
o Examples at Layer 6
▪ HTML, XML, PHP, JavaScript, …
- 23 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ ASCII, EBCDIC, UNICODE, …
▪ GIF, JPG, TIF, SVG, PNG, …
▪ MPG, MOV, …
▪ TLS, SSL, …
● Layer 7 (Application)
o Application Layer (Layer 7)
▪ Provides application-level services
● Not Microsoft Word or Notepad
▪ Layer where the users communicate with the computer
▪ Functions:
● Application services
● Service advertisement
o Application Services
▪ Application services unite communicating components from more than one network application
▪ Examples:
● File transfers and file sharing
● Remote access
● Network management activities
● Client/server processes
o Service Advertisement
▪ Some applications send out announcements
▪ States the services they offer on the network
▪ Some centrally register with the Active Directory server instead
▪ Example:
● Printers
- 24 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● File servers
o Examples at Layer 7
▪ E-mail (POP3, IMAP, SMTP)
▪ Web Browsing (HTTP, HTTPS)
▪ Domain Name Service (DNS)
▪ File Transfer Protocol (FTP, FTPS)
▪ Remote Access (TELNET, SSH)
▪ Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
● Encapsulation
o The process of putting headers (and sometimes trailers) around some data
● Decapsulation
o Action of removing the encapsulation that was applied
o If we move down the OSI layers from 7 to 1, we encapsulate data
o If we move upward from layers 1 to 7, we decapsulate data
o A protocol data unit is a single unit of information transmitted within a computer network
▪ Layer 1 - bits
▪ Layer 2 - frames
▪ Layer 3 - packets
▪ Layer 4 - segments if TCP or datagrams if UDP
o SYN (or synchronization) flag
▪ The most well-known flag in TCP communications because it is used to synchronize the connection during the three-way handshake
o ACK (or acknowledgement) flag
▪ Used during the three-way handshake, but it is also used to acknowledge the successful receipt of packets
- 25 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o FIN (or finished) packet
▪ Used to tear down the virtual connections created using the three-way handshake and the SYN flag
▪ The FIN flag always appears when the last packets are exchanged
between a client and server and the host is ready to shutdown the
connection
o RST (or reset) flag
▪ Used when a client or server receives a packet that it was not expecting during the current connection
o PSH (or PUSH) flag
▪ Used to ensure that the data is given priority and is processed at the sending or receiving ends
o URG (or urgent) flag
▪ It is like the Push flag and identifies incoming data as “urgent”
▪ The main difference is PSH is used by a sender to indicate data with a higher priority level where URG is sent to tell the recipient to process it immediately and ignore anything else in queue
● Source and Destination ports
o are just like the ones used in UDP, they dictate where the
data is coming from and where it is going to
● Length
o Used to indicate how many bytes the UDP packet is,
including its header and its data
● Checksum
o Not a mandatory field, but it can be used to provide some
validation that the UDP data being sent was received with
some level of integrity
o MAC address
▪ A physical address that is used to identify a network card on the local area network
- 26 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Allows the source to find the destination by using this type of addressing o EtherType field
▪ Used to indicate which protocol is encapsulated in the payload of the frame
▪ As data moves from layer 7 to layer 1, that data is encapsulated
● At layer 4, we add our source and destination ports
● At layer 3, we add our source and destination IP addresses
● At layer 2, we add our source and destination MAC addresses
▪ Once we get to layer 1, we are simply transmitting our layer 2 frames as a series of 1’s and 0’s over the medium
▪ Once that host is found, it will keep decapsulating the information all the way up to layer 7, where its application can read and understand the
underlying data
- 27 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
TCP/IP Model
Objectives 1.1, 1.5 and 5.3
● OBJ 1.1: Compare and contrast the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model layers and encapsulation concepts
● OBJ 1.5: Explain common ports and protocols, their application, and encrypted alternatives
● OBJ 5.3: Given a scenario, use the appropriate network software tools and commands
● TCP/IP Model
o TCP/IP Model
▪ Also known as TCP/IP stack or the DoD Model
▪ Alternative to the OSI Model
▪ More relevant model for network designers since it’s based on TCP/IP
▪ Only a 4-layer model
o OSI Model to TCP/IP Model
![]()
o Network Interface (Layer 1)
▪ Physical and electrical characteristics
- 28 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Describes how to transmit bits across the network (1’s and 0’s)
▪ Determines how interface uses network medium
▪ Coaxial, Optical fiber, or Twisted-pair copper cabling
▪ Examples:
● Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, RS-232
o Internet (Layer 2)
▪ Packages data into IP datagrams
● Contains source and destination IPs
● Forwards datagrams between hosts across the networks
▪ Routes IP datagrams across networks
▪ Connectivity occurs externally
▪ Examples:
● IP, ICMP, ARP, RARP
o Transport (Layer 3)
▪ Provides communication session management between hosts
▪ Defines level of service and status of connection used for transport
▪ Examples:
● TCP
● UDP
● RTP
o Application (Layer 4)
▪ Defines TCP/IP application protocols
▪ Defines how programs interface with the transport layer service
▪ Layer with which the user interacts
▪ Examples:
- 29 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● HTTP, TELNET, FTP, SNMP, DNS, SMTP, SSL, TLS, …
● Data Transfer Over Networks
o Ports
▪ Port numbers can be 0 to 65,535
▪ “Well-known” & Reserved Ports
● Ports 0 to 1023
▪ Ephemeral Ports
● Short-lived transport port that is automatically selected from a
predefined range
● Ports 1024 to 65,535
- 30 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Data Transfer
![]()
o IPv4 Packets
▪ Source Address
● IP of sender
▪ Destination Address
● IP of receiver
▪ IP Flags
● Allows packet fragmentation
▪ Protocol
● Is this packet using TCP or UDP?
o Overhead of TCP and UDP
![]()
● Ports and Protocols
o File Transfer Protocol FTP (Port 20, 21)
- 31 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Transfers computer files between a client and server on a computer network
▪ Unsecure method
▪ Data transferred in the clear
o Secure Shell SSH (Port 22)
▪ Cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network
▪ Best known for remote login to computer systems by users
o SSH File Transfer Protocol SFTP (Port 22)
▪ Provides file access, file transfer, and file management over any
reliable data stream
o Telnet (Port 23)
▪ Provides bidirectional interactive text-oriented communication facility using a virtual terminal connection
▪ Like SSH, but insecure
o Simple Mail Transfer Protocol SMTP (Port 25)
▪ Internet standard for sending electronic mail
▪ RFC 821 was defined originally in 1982
▪ RFC 5321 developed in 2008 (current version)
o Domain Name Service DNS (Port 53)
▪ Hierarchical decentralized naming system for computers, services, or other resources connected to the Internet or a private network
▪ Converts domain names to IP addresses
o Dynamic Host Control DHCP (Port 67, 68)
▪ DHCP server dynamically assigns an IP address and other network configuration parameters to a client
- 32 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Enables computers to request IP addresses and networking parameters automatically?
▪ Reduces burden on network administrators
o Trivial File Transfer TFTP (Port 69)
▪ Transmits files in both directions of a client-server application
▪ Used for booting an operating system from a local area network file server
▪ Doesn’t provide user authentication or directory visibility
▪ Essentially a stripped-down version of FTP
o Hyper Text Transfer HTTP (Port 80)
▪ Foundation of data communication for WWW
▪ Designed for distributed, collaborative, and hypermedia presentation across many devices
o Post Office Protocol v3 POP3 (Port 110)
▪ Used by local e-mail clients to retrieve e-mail from a remote server over TCP/IP connection
o Network Time Protocol NTP (Port 123)
▪ Provides clock synchronization between computer systems over
packet-switched, variable-latency data networks
▪ Created in 1985, one of the oldest Internet protocols in current use o NetBIOS (Port 139)
▪ Network Basic Input/Output System
▪ Provides services allowing applications on separate computers to
communicate over a local area network for file and printer sharing
o Internet Message Access Protocol IMAP (Port 143)
▪ Provides e-mail clients to retrieve e-mail messages from a mail server over a TCP/IP connection
- 33 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Allows the end user to view and manipulate the messages as if they’re stored locally
o Simple Network Management SNMP (Port 161)
▪ Provides collection and organization of information about managed devices on IP networks
▪ Can modify that information to change device behavior, commonly used in network devices
o Lightweight Directory Access LDAP (Port 389)
▪ Open, vendor-neutral, industry standard for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services
▪ LDAP and Active Directory use this port
o HTTP Secure HTTPS (Port 443)
▪ Foundation of ecommerce on WWW
▪ Designed for adding security to the insecure HTTP protocol
o Server Message Block SMB (Port 445)
▪ Provides shared access to files, printers, and miscellaneous
communications between devices on a network
o System Logging Protocol Syslog (Port 514)
▪ Used to send logging data back to a centralized server
o Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Transport Layer Security SMTP TLS (Port 587) ▪ Secure and encrypted way to send emails
o LDAP Secure LDAPS (Port 636)
▪ Open, vendor-neutral, industry standard for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services
Provides secure directory services
o Internet Message Access Protocol over SSL IMAP over SSL (Port 993) ▪ Secure and encrypted way to receive emails
- 34 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Post Office Protocol Version 3 over SSL POP3 over SSL (Port 995)
▪ Secure and encrypted way to receive emails
o Structured Query Language Server Protocol SQL (Port 1433)
▪ Used for communication from a client to the database engine
o SQLnet Protocol (Port 1521)
▪ Used for communication from a client to an Oracle database
o MySQL (Port 3306)
▪ Used for communication from a client to the MySQL database engine o Remote Desktop Protocol RDP (Port 3389)
▪ Proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft
▪ Provides a user with a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a network connection
▪ User employs RDP client software for this purpose and the other
computer must run RDP server software
o Session Initiation Protocol SIP (Port 5060, 5061)
▪ Provides signaling and controlling multimedia communication sessions in applications
▪ Used for Internet telephony for voice and video calls, VOIP, and instant messaging
- 35 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Ports to Remember
![]() ● IP Protocol Types
● IP Protocol Types
o Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
▪ A transport protocol that operates at layer 4 of the OSI model
▪ Used on top of the Internet Protocol for the reliable packet transmission
▪ Operates by conducting a three-way handshake between a client and a
server, and then establishing the connection
▪ TCP is considered a connection-oriented method of communication
o User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
▪ A lightweight data transport protocol that also works on top of IP
▪ Can detect if its packets are corrupted when they are received by a client
using a checksum, but there is no connection and no sequencing to the
UDP segments
- 36 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Great for some applications, like streaming audio and video, but it
definitely does NOT provide reliable delivery of the data
o Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
▪ A network level protocol that is used to communicate information about network connectivity issues back to the sender
▪ ICMP is used a lot by network technicians during troubleshooting, but it is also used by attackers to conduct ping scans and network mapping
o Generic Routing Encapsulation protocol (GRE)
▪ A tunneling protocol that was developed by Cisco to encapsulate a wide variety of network layer protocols inside a virtual point-to-point or
point-to-multipoint link over an Internet Protocol network
▪ Important to set a smaller maximum transmission unit or MTU size on the tunnel
▪ It does not provide any encryption
o Internet Protocol Security protocol (IPsec)
▪ Set of secure communication protocols at the network or packet
processing layer that is used to protect data flows between peers
● Authentication Header (AH)
o A protocol within IPSec that provides integrity and
authentication
● Encapsulating security payload (ESP)
o Provides encryption and integrity for the data packets sent
over IPsec
o Backwards-compatible with most IP routers including
those that were not designed to work with IPsec initially
- 37 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
Media and Cabling Distribution
Objectives 1.3 and 5.2
● OBJ 1.3: Summarize the types of cables and connectors and explain which is the appropriate type for a solution
● OBJ 5.2: Given a scenario, troubleshoot common cable connectivity issues and select the appropriate tools
● Media
o Material used to transmit data over the network
● Copper Media
o Types of Media
▪ Three categories:
● Copper
● Fiber optic
● Wireless
▪ Each category is divided into subcategories
▪ Each has different specifications and uses
o Coaxial Cable (Coax)
▪ Inner
● Insulated conductor or center wire passes data
▪ Outer
● Braided metal shield used to help shield and protect the data
transmission
● Provides EMI resistance due to shielding
- 38 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Coaxial Cables
▪ RG-6
● Commonly used by local cable companies to connect individual
homes
▪ RG-59
● Typically used to carry composite video between two nearby
devices, such as from a cable box to the television
o Coaxial Connectors
▪ F-connector
● Typically used for cable TV and cable modem connections
▪ BNC
● Termed Bayonet Neill-Concelman or British Naval Connector
● Was used for 10BASE2 Ethernet networks
o Twinaxial Cable
▪ Similar to coaxial cable but uses two inner conductors to carry the data instead of just one
o Serial Cable
▪ Usually have a series of straight copper wires inside a single cable or plastic jacket
▪ DB-9 or DB-25 (RS-232)
● 9-pin or 25-pin D-subminiature
- 39 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Used for asynchronous serial communications and connecting to
an external modem
o Twisted Pair Cables
▪ Most popular physical LAN media type
▪ Eight individually insulated strands of copper wire inside each cable
▪ Each pair twisted together to reduce EMI
● Tighter twists = less EMI
▪ Types:
● Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
● Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
o Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
▪ Number of twists determines how much EMI can be blocked
● CAT 6 has more twists per inch than CAT 5
▪ UTP is cheaper than STP
▪ Media of choice in most LANs
o Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
▪ Wires are twisted in pairs and surrounded in a metallic shielding to minimize EMI
▪ Outer shielding minimizes EMI, but makes STP cost more than UTP o Twisted Pair Connectors
▪ RJ-45
● 8-pin connector in Ethernet networks
● Most Ethernet use only 4-pins
▪ RJ-11
● 6-pin connector
● Commonly only 2 or 4 pins are used
● Commonly found in telephone systems
- 40 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Registered Jack (RJ)
▪ Used to carry voice or data which specifies the standards a device needs to meet to connect to the phone or data network
o Bandwidth
▪ Theoretical measure of how much data could be transferred from a source to its destination
o Throughput
▪ Actual measure of how much data transferred from a source to its destination
o Cable Lengths
▪ Keep cable runs under 70 meters from the IDF to the office
o Straight-Through Patch Cables
▪ Contains the exact same pinout on both ends of the cable
▪ T-568B is the preferred standard for wiring a building if no pre-existing pattern is used
● Data Terminating Equipment (DTE)
- 41 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o “Endpoint” devices that connect to a piece of data
communications equipment or DCE (e.g. laptops, desktops,
servers, and routers)
● Data Communications Equipment (DCE)
o Includes things like switches, modems, hubs, and bridges
● Connecting DTE and DCE devices
o Straight-through
▪ DTE to DCE
▪ DCE to DTE
o Crossover
▪ DTE to DTE
▪ DCE to DCE
o Crossover Cables
▪ Swaps the send and receive pins on the other end of the cable when the connector and its pinout are created
o Pinouts (568A/568B)
▪ TIA/EIA-568A and TIA/EIA-568B are standard
▪ Orange and Green pairs swap
o Medium Dependent Interface Crossover (MDIX)
▪ An automated way to electronically simulate a crossover cable connector even if using a straight-through patch cable
▪ If a switch doesn't support MDIX, use a crossover cable to make them talk o Plenum and Non-Plenum Cable
▪ Plenum Cable
o A special coating put on a UTP or an STP cable that
provides a fire-retardant chemical layer to the outer
insulating jacket
o Minimizes dangerous fumes if cable on fire
o Safe for use in ceilings, walls, and raised floors
- 42 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Non-plenum Cable
● Also known as PVC
● Normal UTP/STP rated cable
● Cannot be used in raised floors, ceilings, or walls
● Fiber Media
o Fiber Optic Cables
▪ Uses light from an LED or laser to transmit information through a glass fiber
● Immune to EMI
● Uses light instead of electricity
▪ Benefits:
● Greater range (many miles)
● Greater data-carrying capacity (measured in Tbps)
▪ Types:
● Multimode Fiber (MMF)
● Single-mode Fiber (SMF)
o Single-Mode Fiber (SMF)
▪ Used for longer distances and has smaller core size which allows for only a single mode of travel for the light signal
▪ SMF’s core size is 8.3-10µ in diameter
o Multimode Fiber (MMF)
▪ Used for shorter distances and has larger core size which allows for multiple modes of travel for the light signal
▪ MMF’s core size is 50-100µ in diameter
▪ Up to 2 kms or less
- 43 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
Fiber Optic Connectors Specialized SC Connectors ![]()
![]()
o Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
▪ Combines multiple signals into one signal and sends over a single fiber optic strand using different wavelengths of the laser light source
- 44 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Transceivers
o Copper vs Fiber Optic Cables ![]()
▪ Fiber-Optic Advantages
● Higher bandwidth
● Longer distances
● Immune to EMI
● Better security
▪ Copper Advantages
● Less expensive
● Easy to install
● Inexpensive tools
o Media Converters
▪ Convert media from one format to another
▪ Layer 1 device
● Physical conversion of signal only
▪ Examples:
● Ethernet to Fiber Optic
● Fiber Optic to Ethernet
● Coaxial to Fiber
● Fiber to Coaxial
o Transceivers
▪ Device that sends (transmits) and receives data
● Bidirectional
o Devices take turns communicating
o Known as half-duplex
● Duplex
o Full duplex occurs when devices can both communicate at
the same time
o Half duplex occurs when devices can either transmit or
receive, but cannot do both at the same time
- 45 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Types of transceivers used in switches and routers
o GBIC
▪ Standard, hot-pluggable gigabit Ethernet
transceiver (copper or fiber)
o Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP)
▪ Compact, hot-pluggable optical module transceiver
▪ Support up to 4.25 Gbps ![]()
▪ Known as Mini-GBIC
o SFP+
▪ Enhanced SFP
▪ Support up to 16 Gbps
o Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable (QSFP)
▪ Compact, hot-pluggable optical module transceiver
▪ Supports up to 100 Gbps
● Cable Distribution
o An organized system to connect the network’s backbone in the main distribution frame to the intermediate distribution frames and finally to the end user’s wall jacks
o Cable Distribution System
▪ Use an organized system that is hierarchical
● Demarcation point
o The entrance facilities where you WAN connection will
enter your building
▪ Components
● Entrance facilities
● MDF
● Cross-connect facilities
● IDF
- 46 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Backbone wiring
● Telecommunications closet
● Horizontal wiring
● Patch Panels
● Work area
o Punch Down Blocks
▪ 66 block
● Used for phones and older LAN wiring
● Causes crosstalk due to proximity of cables
● Bad choice for higher-speed LAN wiring
o Do not use for CAT 5 or above
▪ 110 block
● Used for higher-speed network wiring
o Required for CAT 5 or above cabling
▪ Krone block
● A proprietary European alternative to a 110 block
▪ BIX block
● Another proprietary punch down block that comes in various sizes
● If you are going to work on a BIX block, you will need a BIX-specific
punch down tool
o Patch Panels (Copper)
▪ Device with jacks to connect wiring from the jack to a network switch in a flexible manner
▪ Has punch downs (like a 110 block) on the back side that is used to
connect wiring to wall jacks in building
▪ Front has RJ-45 jacks
o Patch Panels (Fiber)
▪ Connect fiber jacks throughout building to a single patch panel in network closet
▪ Front uses patch cables to connect different wall jacks and switch ports - 47 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Example of Cable Distribution
![]()
- 48 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
Ethernet Fundamentals
Objectives 1.3, 2.1, 2.3, 4.4, and 5.5
● OBJ 1.3: Summarize the types of cables and connectors and explain which is the appropriate type for a solution
● OBJ 2.1: Compare and contrast various devices, their features, and their appropriate placement on the network
● OBJ 2.3: Given a scenario, configure and deploy common ethernet switching features ● OBJ 4.4: Compare and contract remote access methods and security implications ● OBJ 5.5: Given a scenario, troubleshoot general networking issues
● Ethernet Fundamentals
o Ethernet Fundamentals
▪ In early computer networks, there were many different network
technologies competing for a portion of the market share
▪ Ethernet, Token Ring, Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), and others fought for dominance
▪ Currently, Ethernet is dominant for Layer 1
▪ Due to Ethernet’s popularity, it is important to understand the
fundamentals of Ethernet
o Origins of Ethernet
▪ Was first run over coax cables (10Base5, 10Base2)
▪ Ethernet has changed to using twisted pair cables
▪ 10BASE-T is Unshielded Twisted Pair
● Maximum speed: 10 Mbps
● Maximum distance: 100 meters
- 49 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o How should devices access the network?
▪ Deterministic
● Very organized and orderly
● Need an electronic token to transmit
● For example, Token Ring networks
▪ Contention-based
● Very chaotic
● Transmit (almost) whenever you want
● For example, Ethernet networks
o Carrier Sense Multiple Access/ Collision Detect (CSMA/CD)
▪ Ethernet devices transmit based on a principle called carrier sense multiple access/collision detect (CSMA/CD)
▪ Carrier sense
● Listen to the wire, verify it is not busy
▪ Multiple access
● All devices have access at any time
▪ Collision detect
● If two devices transmit at the same time, a collision occurs
● Back off, wait a random time, and try again
- 50 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Example of CSMA/CD ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
o Collision Domains
▪ Comprised of all devices on a shared Ethernet segment (everything on same cable or hub)
▪ Devices operate at half-duplex when connected to a hub (Layer 1 device)
▪ Devices must listen before they transmit to avoid collisions when
operating as CSMA/CD
- 51 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Collision Domains with Switches
▪ Ethernet switches increase scalability of the network by creating multiple collision domains
▪ Each port on a switch is a collision domain, no chance of collisions, and increases speed
▪ Switches can operate in full-duplex mode
o Speed Limitations
![]()
▪ Bandwidth is the measure of how many bits the network can transmit in 1-second (bps)
▪ Type of cable determines the bandwidth capacity of the network
o Distance Limitations
![]()
** Not an exhaustive list of cable types **
- 52 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Type of cable determines the distance limitation of the network
● Network Infrastructure Devices
o Network Infrastructure
▪ Primary devices used in our networks
▪ Devices they evolved from
o Hub
▪ Layer 1 device used to connect multiple network devices/workstations ▪ Known as multiport repeaters
▪ Three basic types of Ethernet hubs:
● Passive hub
o Repeats signal with no amplification
● Active hub
o Repeats signal with amplification
● Smart hub
o Active hub with enhanced features like SNMP
o Collision Domains
▪ Multiple network segments connected together by hubs
▪ Hubs (layer 1) were used to connect multiple network segments together
- 53 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Each LAN segment becomes a separate collision domain
o Bridges
▪ Bridges analyze source MAC addresses in frames entering the bridge and populate an internal MAC address table
▪ Makes intelligent forwarding decisions based on destination MAC address in the frames
o Switch
▪ Layer 2 device used to connect multiple network segments together ▪ Essentially a multiport bridge
▪ Switches learn MAC addresses and make forwarding decisions based on them
▪ Switches analyze source MAC addresses in frames entering the switch and populate an internal MAC address table based on them
- 54 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Layer 2 Switch
▪ Each port on a switch represents an individual collision domain
▪ All ports belong to the same broadcast domain
o Router
▪ Layer 3 device used to connect multiple networks together
▪ Make forwarding decisions based on logical network address information ● Such as using IP addresses (IPv4 or IPv6)
▪ Routers are typically more feature rich and support a broader range of interface types than multilayer switches
▪ Each port is a separate collision domain
▪ Each port is a separate broadcast domain
- 55 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Layer 3 Switch
▪ Layer 3 device used to connect multiple network segments together
▪ Can make Layer 3 routing decisions and interconnect entire networks (like a router), not just network segments (like a switch)
o Summary of Network Infrastructure
![]()
● Additional Ethernet Features
o Features to enhance network performance, redundancy, security, management, flexibility, and scalability
▪ Common switch features
● Virtual LANs (VLANs)
● Trunking
● Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- 56 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Link aggregation
● Power over Ethernet
● Port monitoring
● User authentication
o Link Aggregation (802.3ad)
▪ Congestion can occur when ports all operate at the same speed
▪ Allows for combination of multiple physical connections into a single logical connection
▪ Bandwidth available is increased and the congestion is minimized or prevented
o Power Over Ethernet (PoE 802.3af, PoE+ 802.3at)
▪ Supplies electrical power over Ethernet
● Requires CAT 5 or higher copper cable
● Provides up to 15.4 watts of power to device
● PoE+ provides up to 25.5 W of power to device
▪ Two device types
● Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE)
- 57 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Powered Device (PD)
o Port Monitoring or Mirroring
▪ Helpful to analyze packet flow over network
● Connect a network sniffer to a hub and it sees all
● But, switches require port monitoring for network analyzer to see
all the traffic
▪ Port mirroring makes a copy of all traffic destined for a port and sends it to another port
o User Authentication (802.1x)
▪ For security purposes, switches can require users to authenticate
themselves before gaining access to the network
▪ Once authenticated, a key is generated and shared between the
supplicant (device wanting access) and the switch (authenticator)
- 58 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Authentication server checks the supplicant’s credentials and creates the key
▪ Key is used to encrypt the traffic coming from and being sent to the client o Management Access and Authentication
▪ To configure and manage switches, you can use two options:
● SSH
o Remote administration program that allows you to connect
to the switch over the network
● Console port
o Allows for local administration of the switch using a
separate laptop and a rollover cable (DB-9 to RJ-45)
o Out-of-band (OOB)
▪ Management involves keeping all network configuration devices on a separate network
o First-Hop Redundancy
▪ Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) uses virtual IP and MAC addresses to provide a “active router” and a “standby router”
● HSRP is a Cisco-proprietary protocol
● If Active is offline, then standby answers
o Other First-Hop Redundancy Protocols
▪ Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP)
● Cisco-proprietary protocol
▪ Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
● Open-source protocol
▪ Common Address Redundancy Protocol (CARP)
● Open-source protocol
o MAC Filtering
▪ Permits or denies traffic based on a device’s MAC address to improve security
- 59 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
![]()
![]() o Traffic Filtering
o Traffic Filtering
▪ Multilayer switches may permit or deny traffic based on IP addresses or application ports
o Quality of Service (QoS)
▪ Forwards traffic based on priority markings
● Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) (802.1D)
o Permits redundant links between switches and prevents traffic loops - 60 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Availability is measured in 9’s
▪ Five 9’s is 99.999% uptime and allows only 5 minutes down per year
o Shortest Path Bridging (SPB) is used for larger network environments instead o Without STP, MAC Address table corruption can occur
![]()
![]()
o Broadcast Storms
▪ If broadcast frame received by both switches, they can forward frames to each other
▪ Multiple copies of frame are forwarded, replicated, and forwarded again until the network is consumed with forwarding many copies of the same initial frame
o Root and Nonroot Bridges
▪ Root bridge
● Switch elected to act as a reference point for a spanning tree
● Switch with the lowest bridge ID (BID) is elected as the root bridge
- 61 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● BID is made up of a priority value and a MAC address (with the
lowest value considered root)
▪ Nonroot bridge
● All other switches in an STP topology
▪ MAC Address table corruption can occur
o Root, Designated, and Non-Designated Ports
▪ Root Port
● Every non-root bridge has a single root port
● Port closest to the root bridge in terms of cost
● If costs are equal, lowest port number is chosen
▪ Designated Port
● Every network segment has a designated port
● Port closest to the root bridge in terms of cost
● All ports on root bridge are designated ports
▪ Non-Designated Port
● Ports that block traffic to create loop-free topology
o Root and Nonroot Bridges
▪ Single root port on non-root bridge
▪ All other ports on non-root bridge are non-designated
- 62 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ All ports on root bridge are designated
o Port States
▪ Non-designated ports do not forward traffic during normal operation, but do receive bridge protocol data units (BPDUs)
▪ If a link in the topology goes down, the
non-designated port detects the failure and determines whether it needs to transition to a forwarding state
▪ To get to the forwarding state, though, it has to transition through four states
▪ Blocking
● BPDUs are received but they are not forwarded
● Used at beginning and on redundant links
▪ Listening
● Populates MAC address table
● Does not forward frames
▪ Learning
● Processes BPDUs
● Switch determines its role in the spanning tree
▪ Forwarding
● Forwards frames for operations
▪ Root and Non-designated port are blocking
- 63 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Designated ports are forwarding
o Link Costs
▪ Associated with the speed of a link
▪ Lower the link’s speed, the higher the cost
▪ Long STP is being adopted due to higher link speeds over 10 Gbps
▪ Values range from 2,000,000 for 10-Mbps Ethernet to as little as 2 for 10 Tbps
- 64 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
o VLANs
▪ Switch ports are in a single broadcast domain
▪ Allow you to break out certain ports to be in different broadcast domains
▪ Before VLANs, you had to use routers to separate departments, functions, or subnets
▪ Allow different logical networks to share the same physical hardware
▪ Provides added security and efficiency
o Before VLANs
▪ Different switches were required for each LAN for separation
o Using VLANs
▪ Same switches but switch ports can be in different VLANs
o VLAN Trunking (802.1q)
▪ Multiple VLANs transmitted over the same physical cable
▪ VLANs are each tagged with 4-byte identifier
● Tag Protocol Identifier (TPI)
● Tag Control Identifier (TCI)
▪ One VLAN is left untagged
● Called the Native VLAN
- 65 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Specialized Network Devices
o Virtual Private Network (VPN)
▪ Creates a secure VPN or virtual tunnel over an untrusted network like the Internet
o VPN Concentrator
▪ Virtual private network (VPN) creates a secure, virtual tunnel network over an untrusted network, like the Internet
▪ One of the devices that can terminate VPN tunnels is a VPN concentrator, although firewalls can also perform this function
o VPN Headend
▪ A specific type of VPN concentrator used to terminate IPSec VPN tunnels within a router or other device
o Firewalls
▪ Network security appliance at your boundary
▪ Firewalls can be software or hardware
▪ Stateful firewalls
● Allows traffic that originates from inside the network and go out
to the Internet
● Blocks traffic originated from the Internet from getting into the
network
o Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)
▪ Conducts deep packet inspection at Layer 7
▪ Detects and prevents attacks
▪ Much more powerful than basic stateless or stateful firewalls
▪ Continually connects to cloud resources for latest information on threats o Intrusion Detection or Prevention System (IDS/IPS)
▪ IDS recognizes attacks through signatures and anomalies
▪ IPS recognizes and responds
- 66 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Host or network-based devices
o Proxy Server
▪ A specialized device that makes requests to an external network on behalf of a client
o Content Engine/Caching Engine
▪ Dedicated appliance that performs the caching functions of a proxy server o Content Switch/Load Balancer
▪ Distributes incoming requests across various servers in a server farm ● Other devices you may find on your network
o VoIP Phone
▪ A hardware device that connects to your IP network to make a
connection to a call manager within your network
o Unified Communications (or Call) Manager
▪ Used to perform the call processing for hardware and software-based IP phones
o Industrial Control System (ICS)
▪ Describes the different types of control systems and associated
instrumentation
o Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
▪ Acquires and transmits data from different systems to a central panel for monitoring and control
o Virtual Network Devices
▪ Major shift in the way data centers are designed, fielded, and operated
- 67 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
IP Addressing
Objectives 1.4 and 1.6
● OBJ 1.4: Given a scenario, configure a subnet and use appropriate IP addressing schemes ● OBJ 1.6: Explain the use and purpose of network services
● Internet Protocol (IP) Address
o An assigned numerical label that is used to identify Internet communicating devices on a computer network
▪ Layer 2
● Between two devices that are internal to own network or LAN
▪ Layer 3
● Between two different networks or even two different subnets
● IPv4 Addressing
o Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) Addressing
▪ Written in dotted-decimal notation
● 10.1.2.3
● 172.21.243.67
▪ Each IPv4 address is divided into 4 separate numbers and divided by dots ▪ Each of these divisions are called octets due to having 8 bits assigned
▪ 32-bits in length
o IPv4 Addressing
▪ IPv4 address is divided into network and host portions
▪ Subnet mask defines the network portion
- 68 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Network portion if a binary 1
● Host portion if binary 0
o Classes of IP Addresses
▪ Default subnet mask assigned by first octet
● Classful Masks if using default subnet mask
▪ Defines the Class of IP Address
Notice that 127 is skipped between Class A and Class B since
it is a reserved block for the loopback address (127.0.0.1)
o Routable IPs
▪ Publicly routable IP addresses are globally managed by ICANN
● Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers
o ARIN, LACNIC, AFNIC, APNIC, and RIPE NCC
▪ Public IP’s must be purchased before use through your Internet Service Provider (ISP)
o Private IPs
▪ Private IP’s can be used by anyone
▪ Not routable outside your local area network
▪ Network Address Translation (NAT) allows for routing of private IPs through a public IP
- 69 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Specialized IPs
▪ Loopback addresses (127.x.x.x range)
● Refers to the device itself and used for testing
● Most commonly used as 127.0.0.1
▪ Automatic Private IP Addresses (APIPA)
● Dynamically assigned by OS when DHCP server is unavailable and
address not assigned manually
● Range of 169.254.x.x
Special address ranges never assigned by an administrator or DHCP server
o Identifying Network and Hosts in IPv4
![]()
![]()
o Virtual IP Addresses (VIP or VIPA)
▪ An IP address that does not correlate to an actual physical network interface
- 70 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ respond to numerous IP addresses and have them resolve to your physical network interface to establish connectivity
o Subinterfaces
▪ A virtual interface that is created by dividing up one physical interface into multiple logical interfaces
● IPv4 Data Flows
o Unicast
▪ Data travels from a single source device to a single destination device ![]()
o Multicast
▪ Data travels from a single source device to multiple (but specific)
destination devices
o Broadcast
▪ Data travels from a single source device to all devices on a destination network
- 71 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
![]()
![]()
● Assigning IP Addresses
o Static
▪ Simple
▪ Time-consuming
▪ Prone to human errors
▪ Impractical for large networks
o Dynamic
▪ Quicker
▪ Easier
▪ Less confusing
▪ Simplistic for large networks
o Components of an IP Address
▪ Information assigned from static or dynamic
● IP Address
● Subnet Mask
● Default Gateway
● Server addresses
o Domain Name System (DNS)
▪ Converts domain names to IP address
o Windows Internet Name Service (WINS)
- 72 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Converts NetBIOS computer name into an IP
address
o Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) Configuration
▪ Based on the older Bootstrap Protocol ![]()
(BOOTP for short)
● Required static database of IP and
MAC to assign
▪ DHCP service assigns an IP from an
assignable pool (scope)
▪ IP Address Management is software
used to manage the IP’s being assigned
o Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP)
▪ Provides clients with
● IP
● Subnet mask
● Default gateway
● DNS server
● WINS server
● Other variables needed for VoIP
▪ Each IP is leased for a given amount of time and given back to the pool when lease expires (TTL) ![]()
o Automatic Private IP Address (APIPA)
▪ Used when device does not have a
static IP address and cannot reach a
DHCP server
▪ Allows a network device to self-assign
an IP address from the 169.254.0.0/16
network
▪ Designed to allow quick configuration of
a LAN without need for DHCP
- 73 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
▪ Non-routable but allows for network connectivity inside the local subnet o Zero Configuration (Zeroconf)
▪ Newer technology based on APIPA providing:
● Assigning link-local IP addresses
o Non-routable IP usable only on local subnet
● Resolving computer names to IP addresses without the need for
DNS server on local network
o mDNS - Multicast Domain Name Server
● Locating network services
o Provides service discovery protocols
▪ Service Location Protocol (SLP)
▪ Microsoft’s Simple Service Discovery Protocol
(SSDP)
▪ Apple’s DNS-based Service Discovery (DNS-SD)
- 74 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Computer Mathematics
o Humans count using Base-10 numbers
▪ Decimals
▪ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, …
o Computers and networks do not understand decimal numbers natively o Process numbers using Base-2 numbers
▪ Binary
▪ 0, 1, 10, 11, …
● Converting Binary to Decimal
o Use table to convert from binary to decimal
o Each number is a factor of 2
o Starting from the right and go to the left
o Populate the table with the binary digits
o Add up any columns that contain a 1
● Converting Decimal to Binary
o Use subtraction to convert decimal to binary
- 75 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
(Check Your Answer by Adding It Back Up)![]()
128 + 32 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 167
● Computer Mathematics Practice
o You must be able to convert:
o Binary Decimal ![]()
Decimal Binary
● Converting Binary to Decimal
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- 76 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
● Converting Decimal to Binary
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
● Subnetting
o Default classful subnet masks are rarely the optimal choice for a subnet size - 77 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Subnets can be modified using subnet masks to create networks that are better scoped
o Creating a subnet involves borrowing bits from the original host portion and adding them to the network portion
o Purpose of Subnets
▪ More efficient use of IP addresses than classful default
▪ Enables separation of networks for security
▪ Enables bandwidth control
o Subnet Masks
![]()
Classful subnets for Class A, B, and C in red
- 78 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Subnetting Formulas
o Classful vs Subnetted Networks![]()
![]()
o Calculating Number of Subnets
![]()
- 79 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1
CompTIA Network+ (N10-008) ![]()
Study Notes
o Calculating Number of IPs![]()
![]()
o Listing Subnets
o Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR)
▪ Instead of advertising multiple individual routes, the routes can be summarized and advertised as a single route
▪ Used to summarize contiguous networks
● Called route aggregation
![]()
- 80 -
https://www.DionTraining.com © 2022
Dion Training Solutions, LLC is a Platinum Delivery Partner for CompTIA. CompTIA ® is a registered trademark of the Computer and Computing Technology Industry Association. All rights reserved.
V1.1