W1/L1: Finance for Marketers
Introduction
Finance plays a crucial role in marketing, helping marketers justify budgets, measure performance, and contribute to overall business strategy. Understanding financial concepts is essential for career growth in marketing.
Importance of Financial Fluency in Marketing
CEOs trust CFOs more than marketers due to the lack of financial language proficiency.
Finance is often seen as more critical in boardroom decisions.
Marketers must align their strategies with financial outcomes to gain credibility.
Key Topics
Metrics Used in Finance vs. Marketing
Marketing’s Impact on Value Creation
Linking Marketing to Financial Performance
Enhancing Cashflows (DuPont Model)
Accelerating Cashflows
Reducing Risks (Vulnerability and Volatility)
1. Metrics Used in Finance vs. Marketing
Common Metrics in Finance
Finance professionals evaluate business success based on measurable outcomes, including:
Net Profit = Total Revenue - Total Expenses
Margin % = (Net Profit / Revenue) × 100
Return on Investment (ROI) = (Net Profit / Investment) × 100
Annual Growth % = [(New Revenue - Old Revenue) / Old Revenue] × 100
Common Metrics in Marketing
Marketers focus on consumer-related success metrics such as:
Customer Satisfaction – Measures customer happiness with products/services.
Brand Awareness – The extent to which consumers recognize a brand.
Market Share = (Company’s Sales / Industry Sales) × 100
Customer Loyalty – Retention rates and repeat purchases.
Challenges in Measuring Marketing Success
Marketers focus on awareness, while finance professionals focus on tangible financial returns.
Advertising is considered a short-term expense, even though it contributes to long-term brand value.
2. The Impact of Marketing on Value Creation
Marketing activities drive value creation in multiple ways, such as enhancing brand equity, customer equity, and customer satisfaction.
Brand Equity
Strong brands can charge premium prices and maintain loyal customers.
Reduces risk and cost of capital.
Improves future cash flows.
Customer Equity
Customer equity is the total value derived from a company’s customer base.
Formula for Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
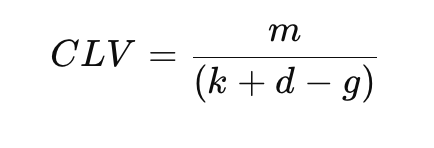
Where:
mm = annual profit per customer
kk = cost of capital
dd = defection rate (1 - retention rate)
gg = growth rate
Customer Satisfaction
Satisfied customers lead to higher retention rates.
Satisfaction is not always linear to sales; some satisfied customers may not increase spending.
Companies with dominant market share may have customers who are satisfied due to a lack of alternatives rather than genuine brand loyalty.
3. Linking Marketing to Financial Performance
Marketing actions should be aligned with financial performance through three key stages:
1. Build (Investment in Market-Based Assets)
Companies must allocate resources to create a strong market presence.
Metrics for Building Market Assets:
Advertising Spend – Budget allocation for promotional activities.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) = Marketing Spend / New Customers Acquired
Brand Awareness Growth – Percentage increase in brand recognition.
2. Leverage (Driving Market Performance)
Marketers use their existing assets to drive financial results.
Leverage Metrics:
Incremental Revenue from Existing Customers
Retention Rate = (Customers at End - New Customers) / Customers at Start
Reduced Marketing Costs – Cost savings from customer retention.
3. Assess (Evaluating Marketing's Financial Impact)
Measuring financial performance using finance and marketing KPIs.
Assessment Metrics:
Customer Level: Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Product Level: Brand Value
Firm Level: Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio = Share Price / Earnings per Share
4. Enhancing Cashflows (DuPont Model)
Enhancing cash flows means increasing profitability through effective marketing and financial strategies.
Key Drivers of Profitability
Price Premiums: Strong brands charge higher prices (e.g., Apple).
Customer Retention: Keeping customers is cheaper than acquiring new ones.
Efficient Channel Management: Optimizing distribution to reduce costs.
The DuPont Model
A breakdown of Return on Equity (ROE) using:
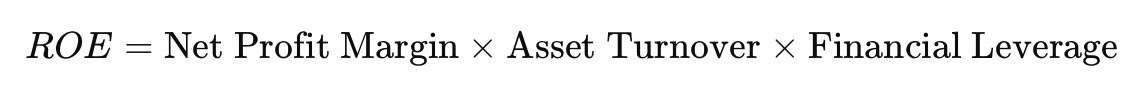
Where:
Net Profit Margin = Net Profit / Revenue
Asset Turnover = Revenue / Assets
Financial Leverage = Assets / Equity
DuPont analysis helps marketers understand how profitability, efficiency, and debt influence financial performance.
5. Accelerating Cashflows
Accelerating cash flows involves increasing the speed at which a company generates revenue.
Key Strategies
Reducing Time to Market – Faster product launches.
Reducing Time to Volume – Increasing production capacity.
Reducing Time to Penetration – Faster customer adoption.
Key Metrics
Time-to-Market – Speed from development to product launch.
Market Share Growth – Percentage increase in industry share.
Revenue Growth Rate – Change in revenue over time.
Example:
Apple launches the iPhone annually with preorders and global availability to ensure rapid market penetration.
6. Reducing Risks (Vulnerability & Volatility)
Risk reduction helps companies maintain stable cash flows.
Vulnerability
Definition: Business exposure to external disruptions (e.g., competitor actions, economic downturns).
Mitigation Strategies:
Strong brand positioning.
Diversified customer base.
Volatility
Definition: Fluctuations in revenue or market performance.
Examples: Seasonal businesses, fashion trends.
Mitigation Strategies:
Diversification: Expanding product offerings to reduce reliance on one market.
Dynamic Pricing: Adjusting prices based on demand (e.g., airline ticket prices).
Customer Loyalty Programs: Encouraging repeat purchases.
Predictive Analytics: Forecasting demand changes.
Conclusion
Marketing and finance are interconnected. Marketers must:
Align marketing metrics with financial objectives.
Justify spending with measurable ROI.
Use financial models like CLV and DuPont to support business decisions.
Focus on enhancing and accelerating cashflows while managing risks.