The Circular Flow and GDP
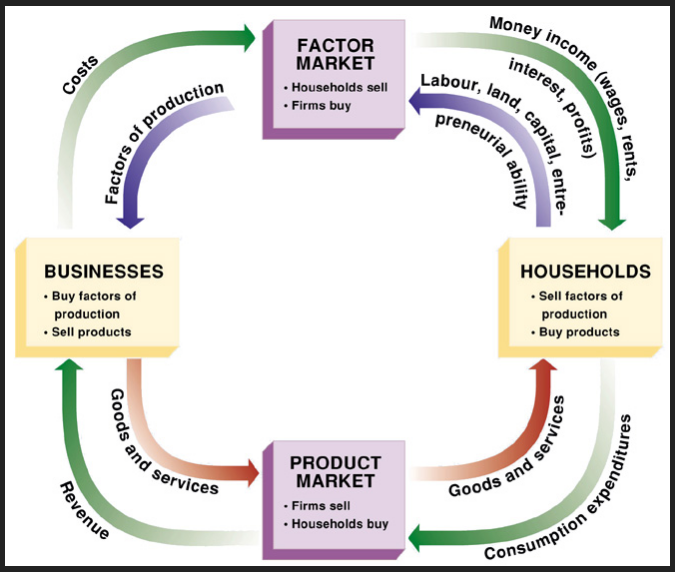
Circular Flow of Income and Expenditures
Households
Provide: Labor and other resources to firms
Receive: Income in the form of wages, rent, interest, and profits
Spend: Income on goods and services produced by firms
Firms
Produce: Goods and services using resources provided by households
Sell: These goods and services to households
Pay: Households for their resources, completing the income cycle
Expenditures and Income
The total money spent on goods and services is the same as the total money households earn
This is an important idea for understanding how a country's income is measured
Parsing GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP): the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period
market value: the total dollar value assigned to goods and services that reflects the economy’s output and helps gauge its overall growth/decline
“all” does not refer to illegal activities and goods/services that are produced and consumed within the household
More on Final and Intermediate GDP Contributions
intermediate GDP = the value of goods and services that are used as inputs in the production of other goods and services
these are not counted in GDP to avoid double-counting
final GDP = the value of goods and services that are purchased for final use, not for further production
only final goods are included in GDP to give an accurate measure of economic output
Investment and Consumption
Investment: refers to spending by businesses on capital goods that will be used for future production, such as machinery and buildings
Consumption: the spending by households on goods and services for their own use, which constitutes a significant portion of GDP
Income and Expenditure Views of GDP
Both approaches should theoretically yield the same GDP figure, as they are two sides of the same economic coin.
Income Approach to GDP
how much is earned as income on resources used to make stuff
Wages: Payments to workers
Rent: Income from land or property
Interest: Earnings from capital investments
Profits: Returns to business owners
Y = w + i + r + p
The sum of these incomes equals the total value of goods and services produced, as every dollar earned is a dollar spent in the economy
Expenditure Approach to GDP
how much is spent on stuff
Consumption (C): Household spending on goods and services
Investment (I): Spending on business capital, residential construction, and inventories
Government Spending (G): Government expenditures on goods and services
Net Exports (NX): Exports minus imports.
The formula is: GDP = C + I + G + (X - M)
Value Added Approach to Calculating GDP
no matter how much u measure gdp, u should get to the same value
value added should get u to the same value as the market value of the final goods and services produced in a given time period
Components of GDP
Y is GDP
Y = firms + households + govt + (foreign purchases (exports) - foreign products (imports))
Y = I + C + G + NX
I represents investment, C denotes consumer spending, G is government expenditure, NX refers to net exports