1. Transportation and Assignment Problems
Terminology:

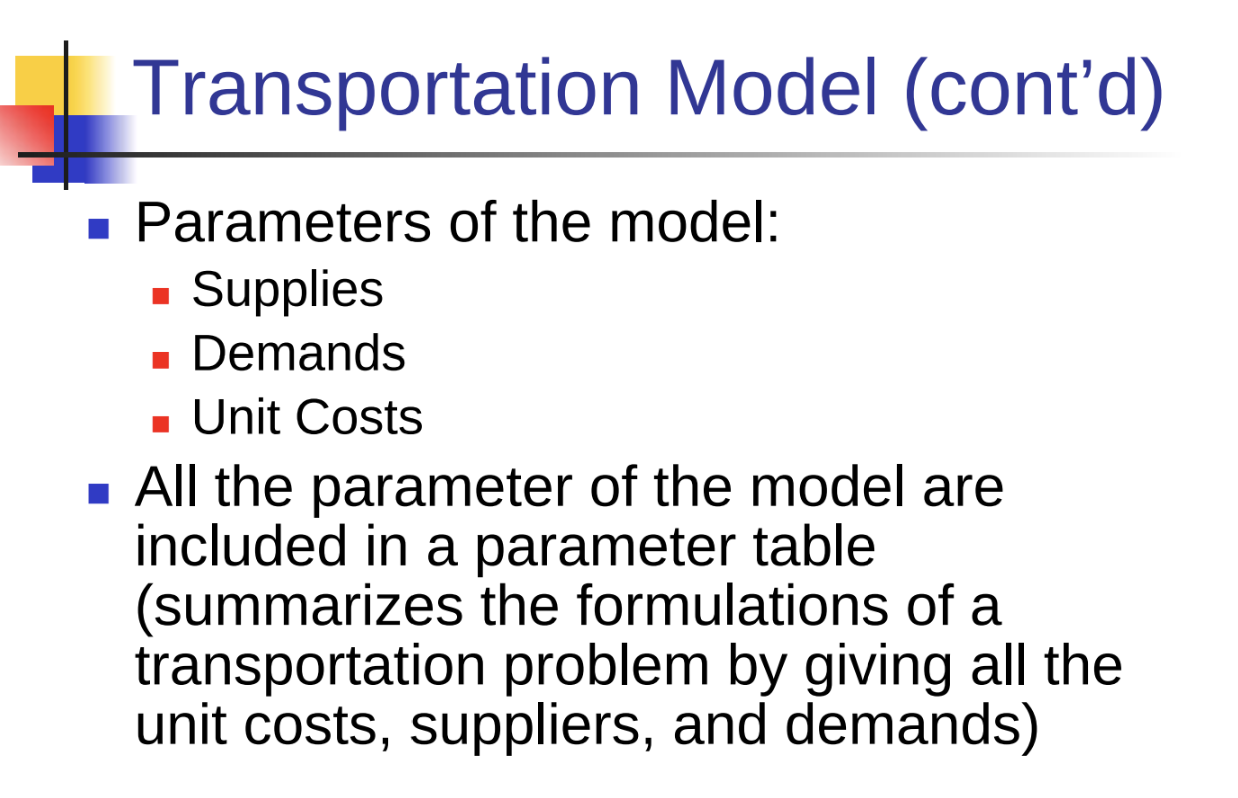
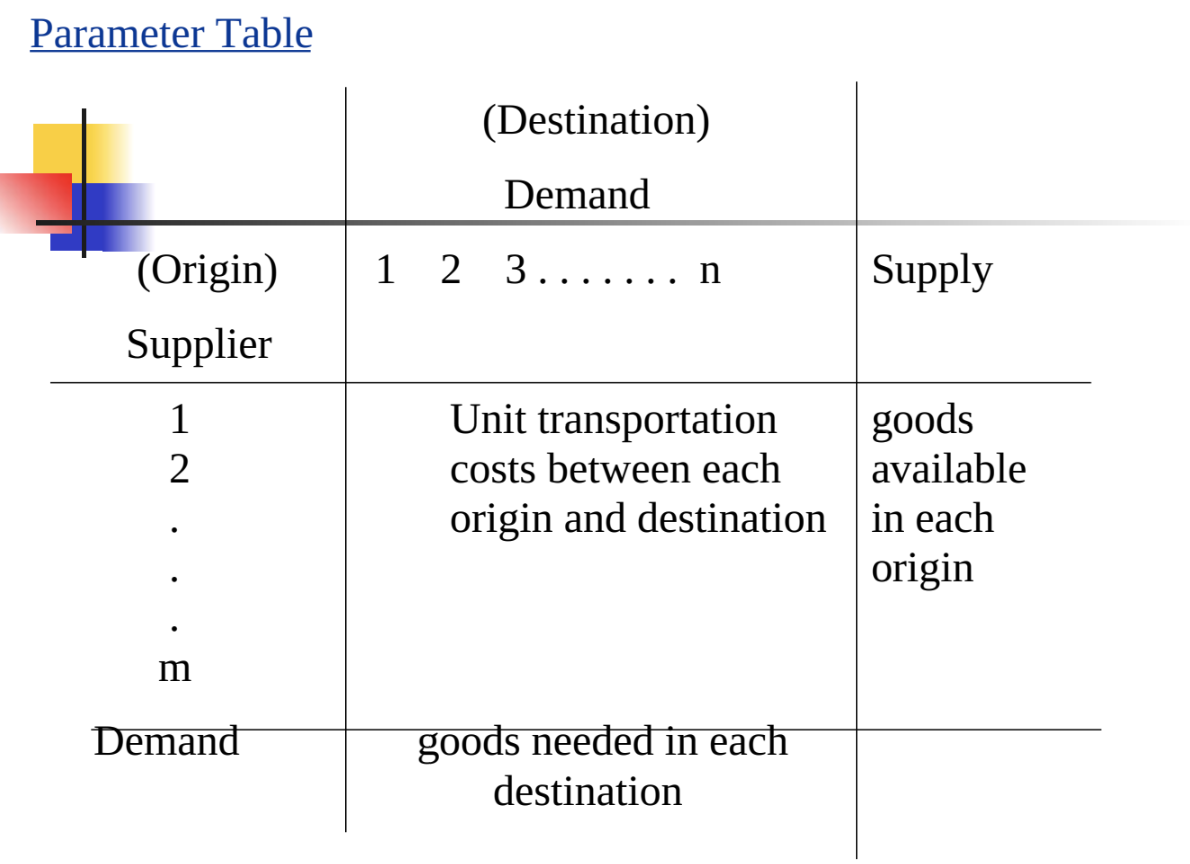
EXAMPLE 1:

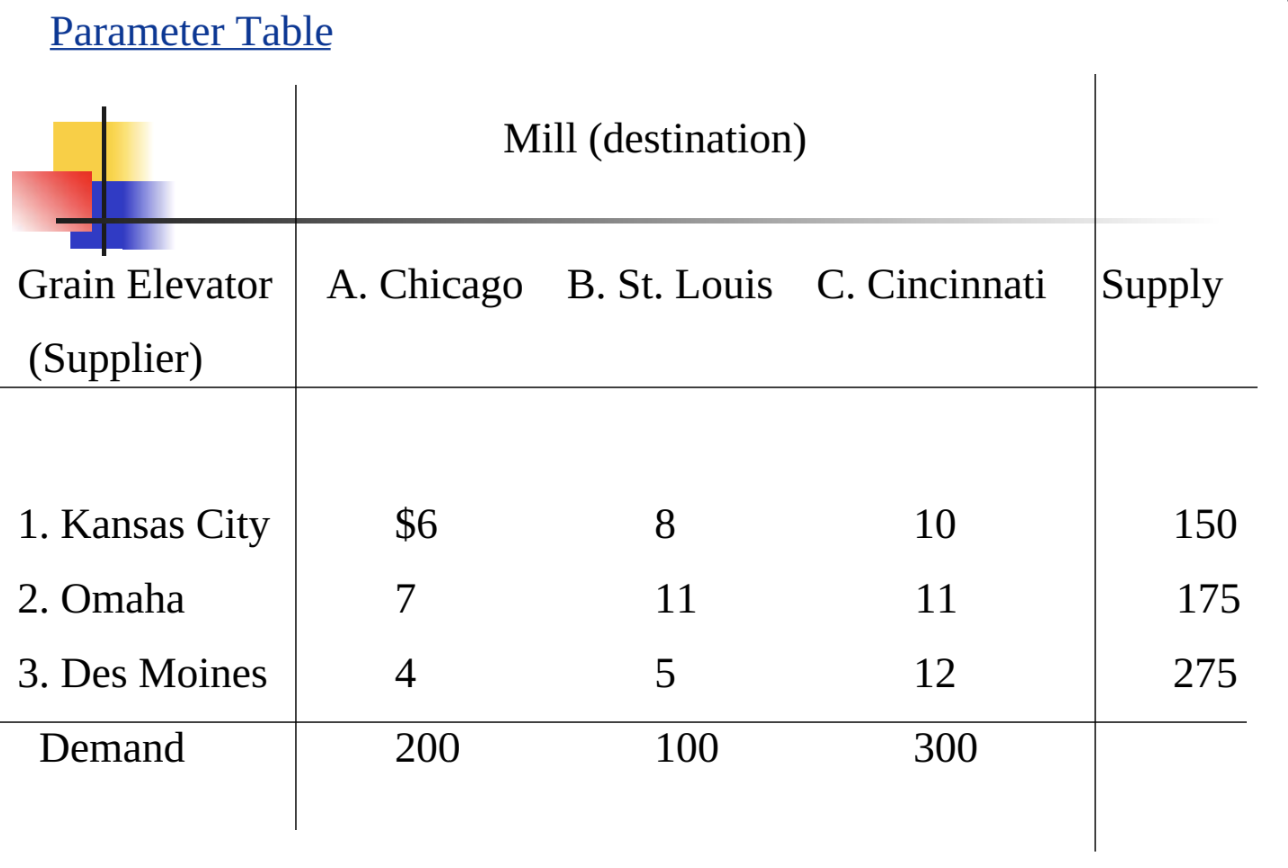


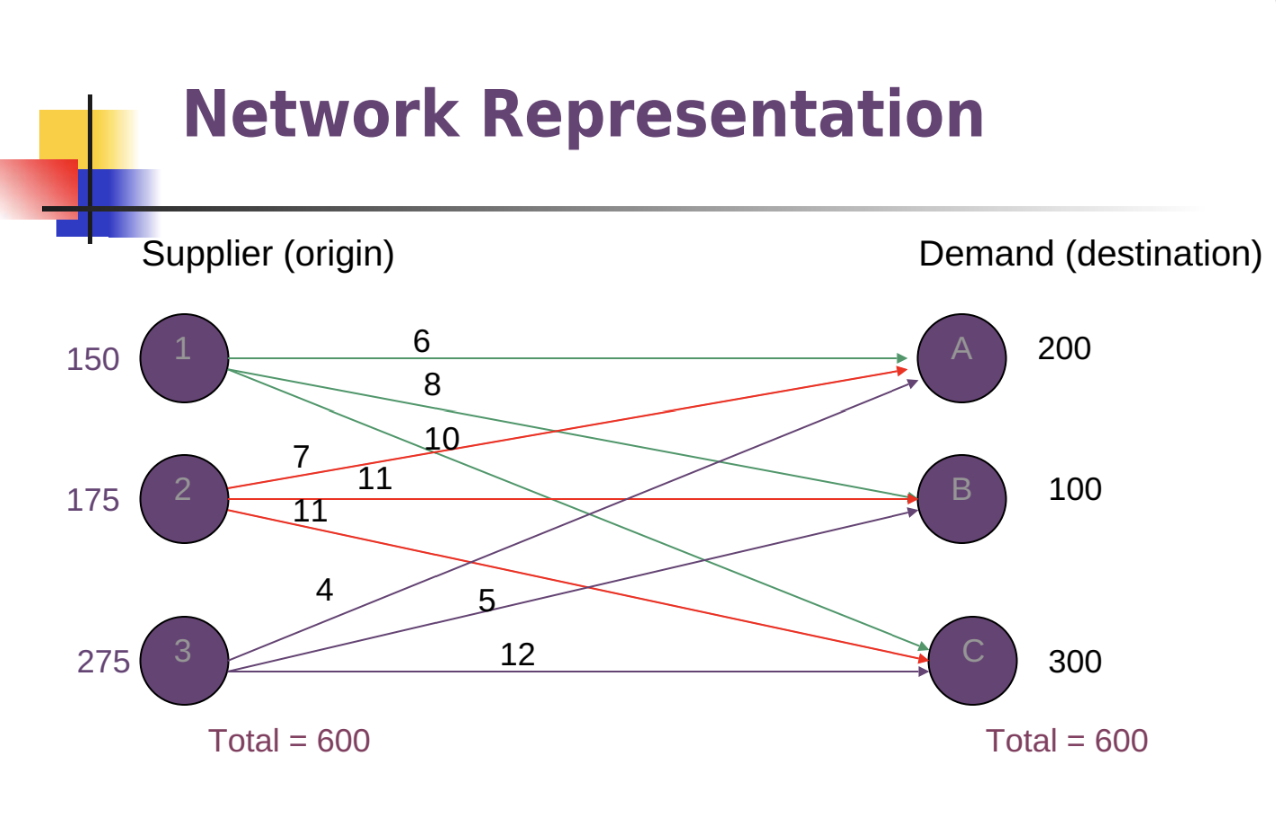
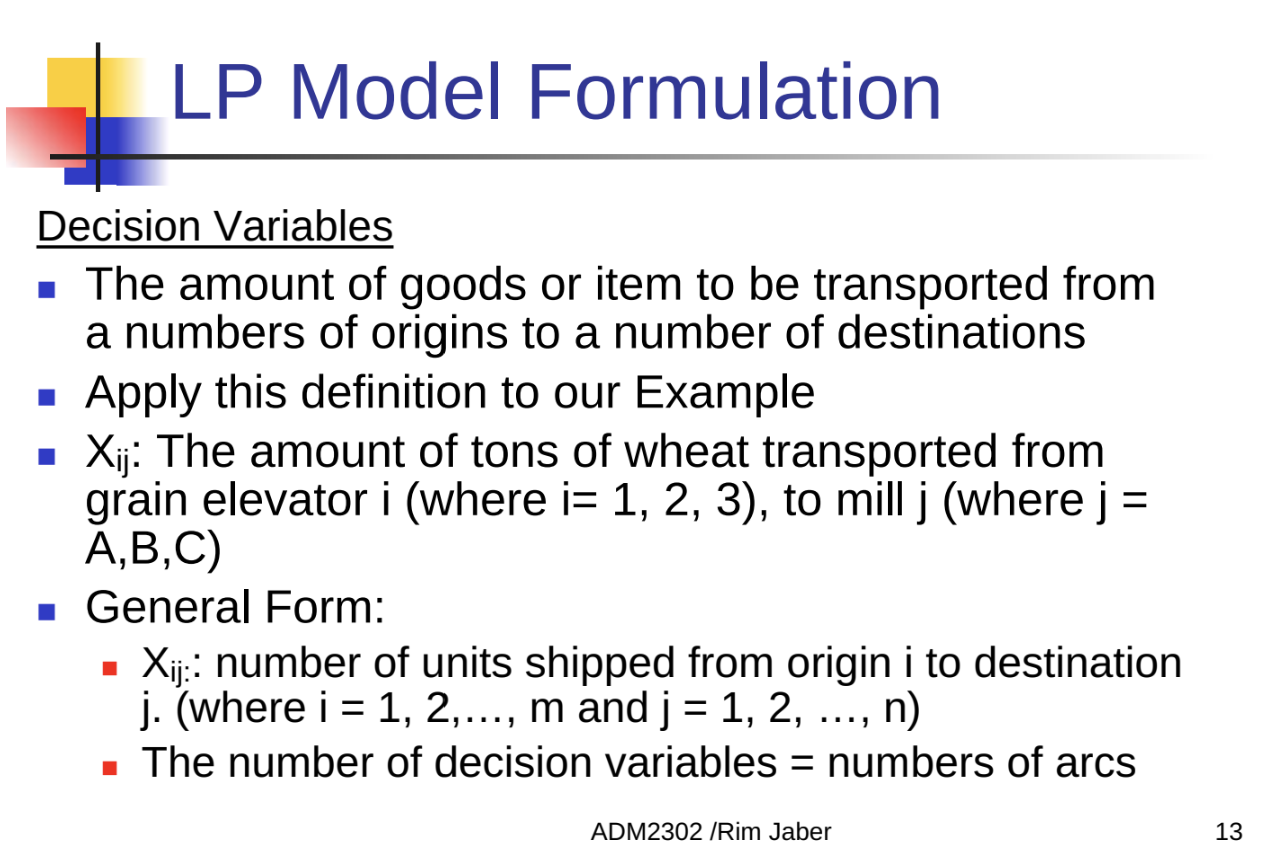
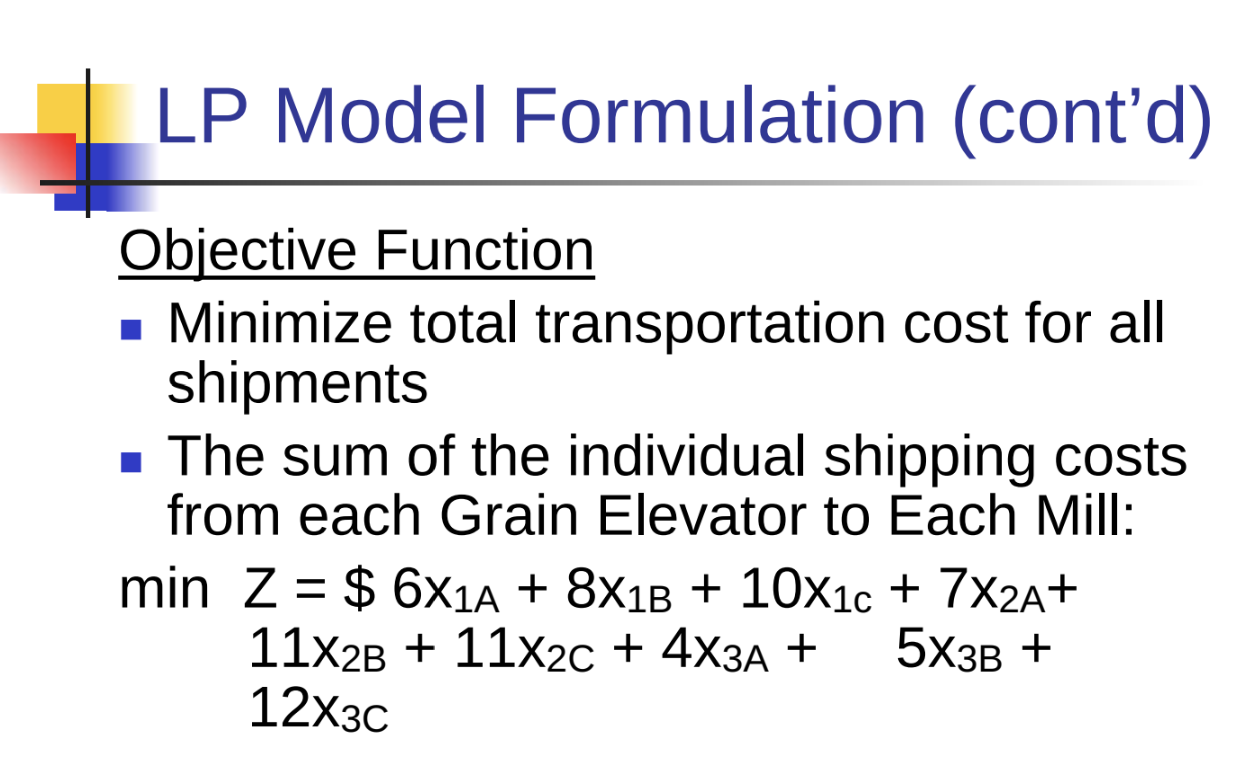
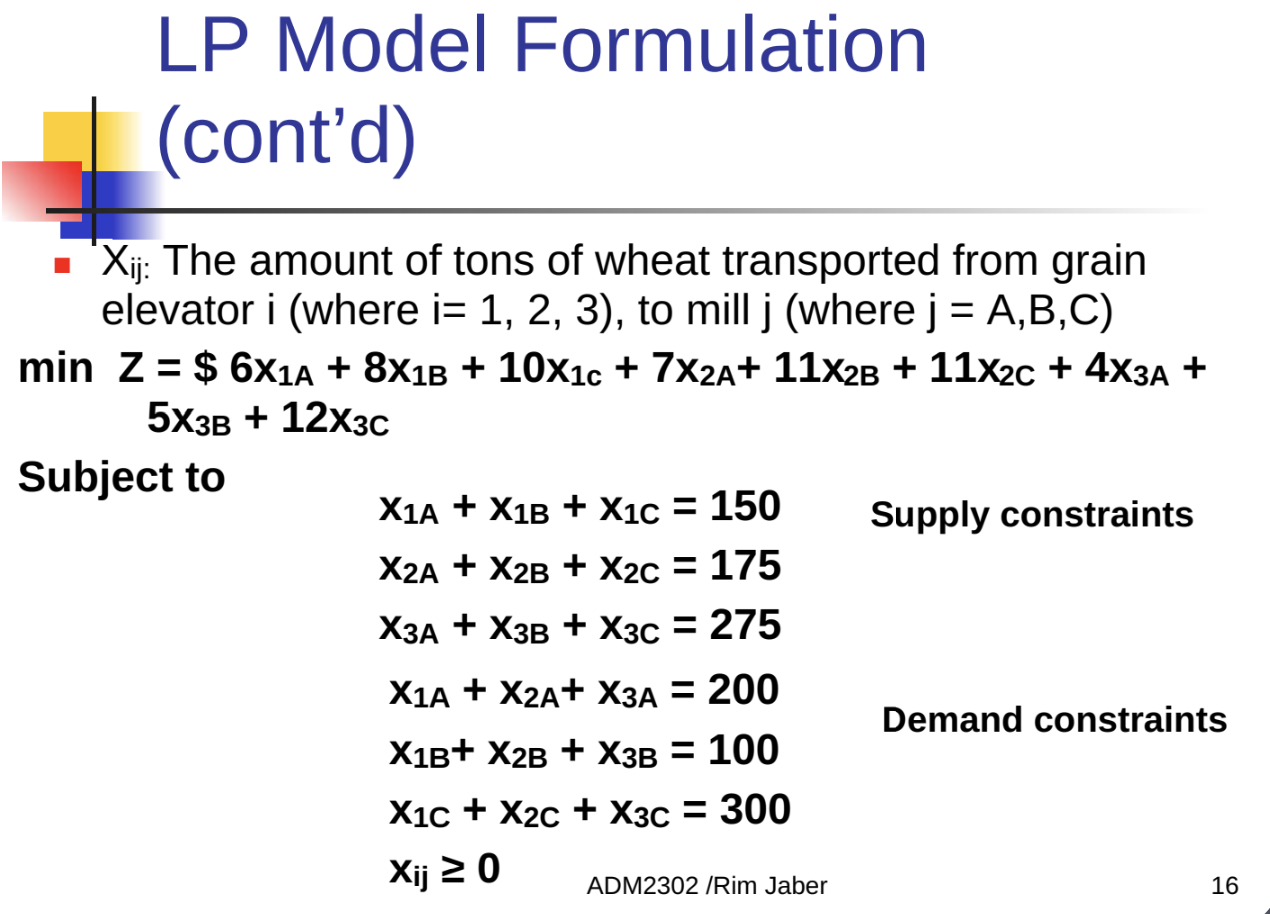
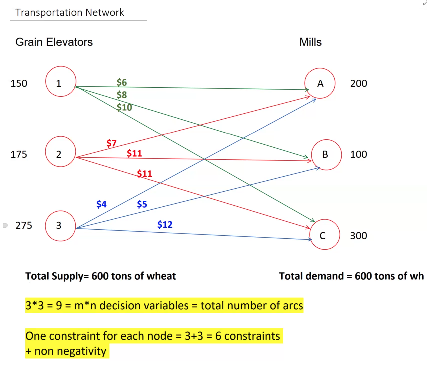
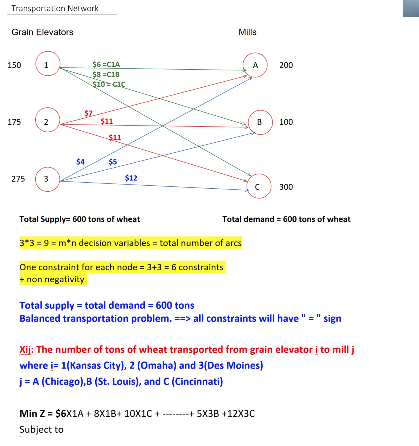
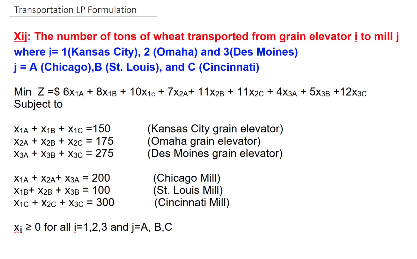
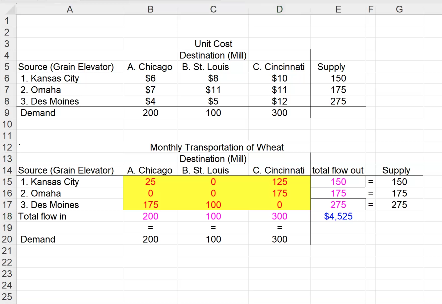

Unbalanced Transportation Problem:

Total Supply > Total Demand
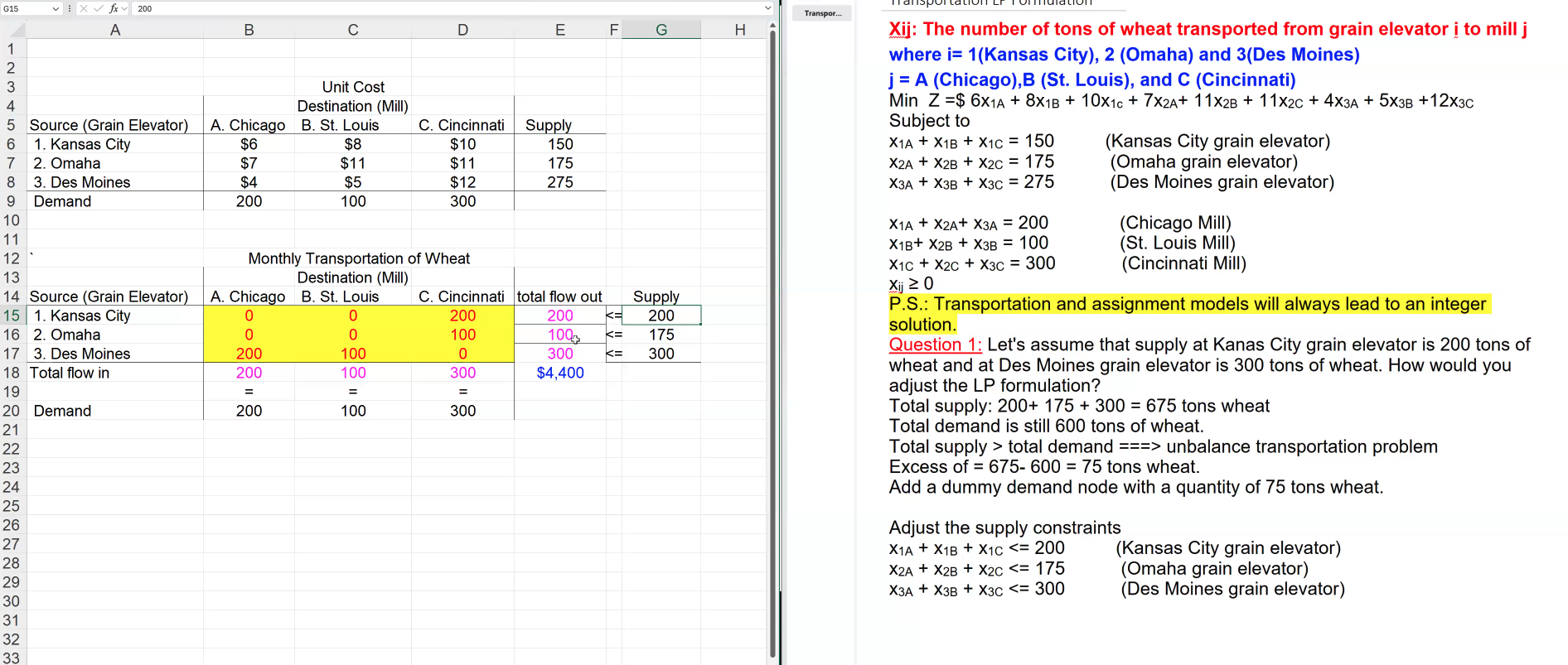
Total Demand > Total Supply
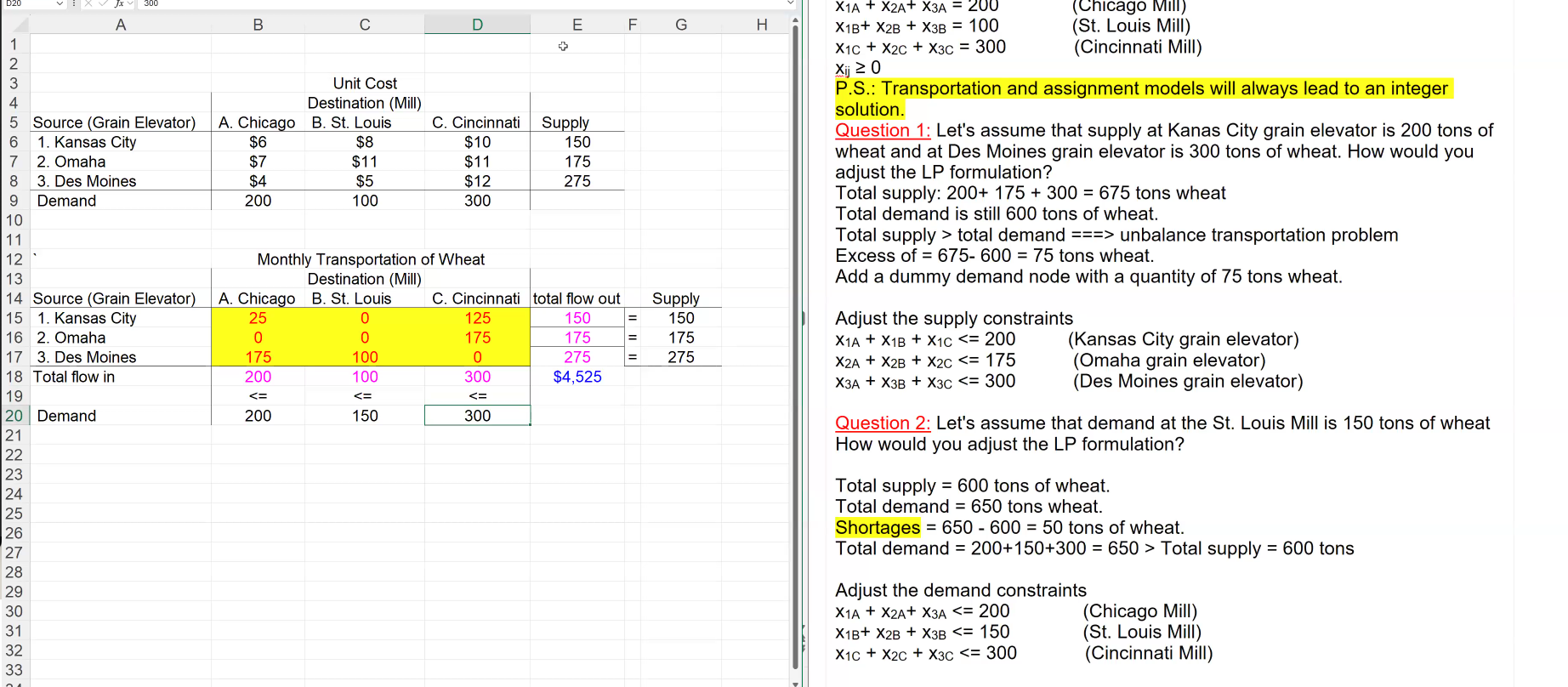

EXAMPLE 2:

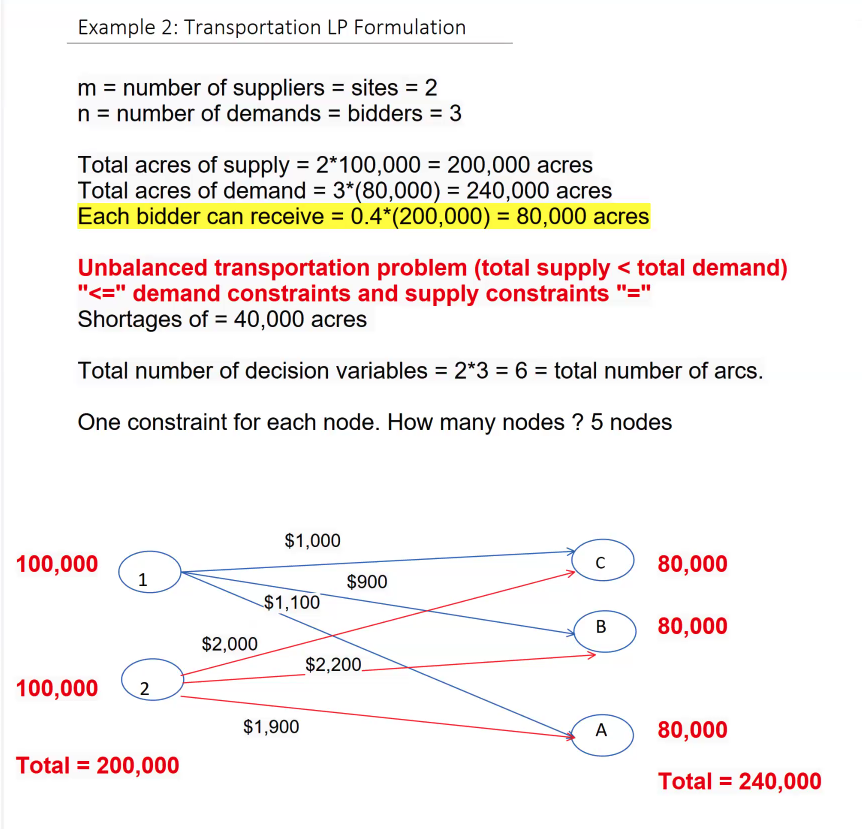
EXAMPLE 3:


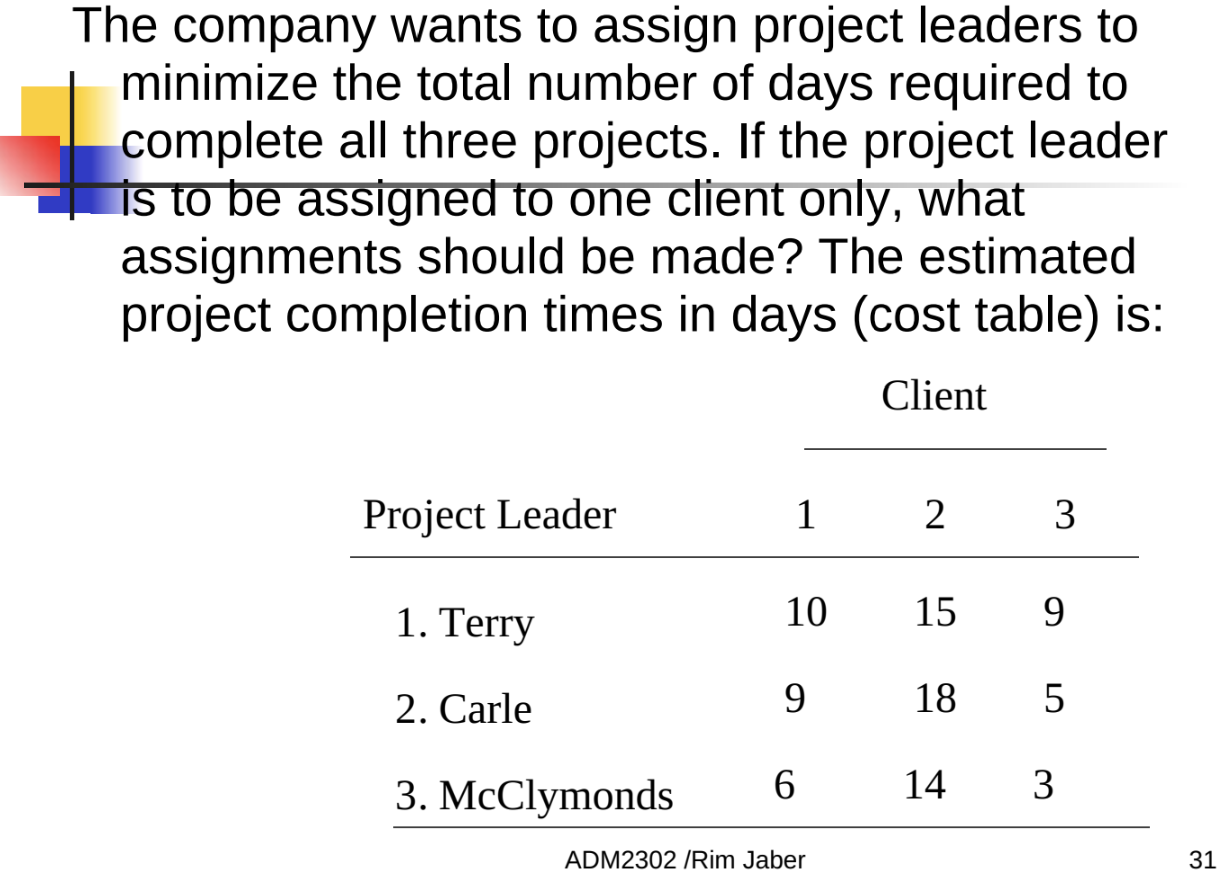
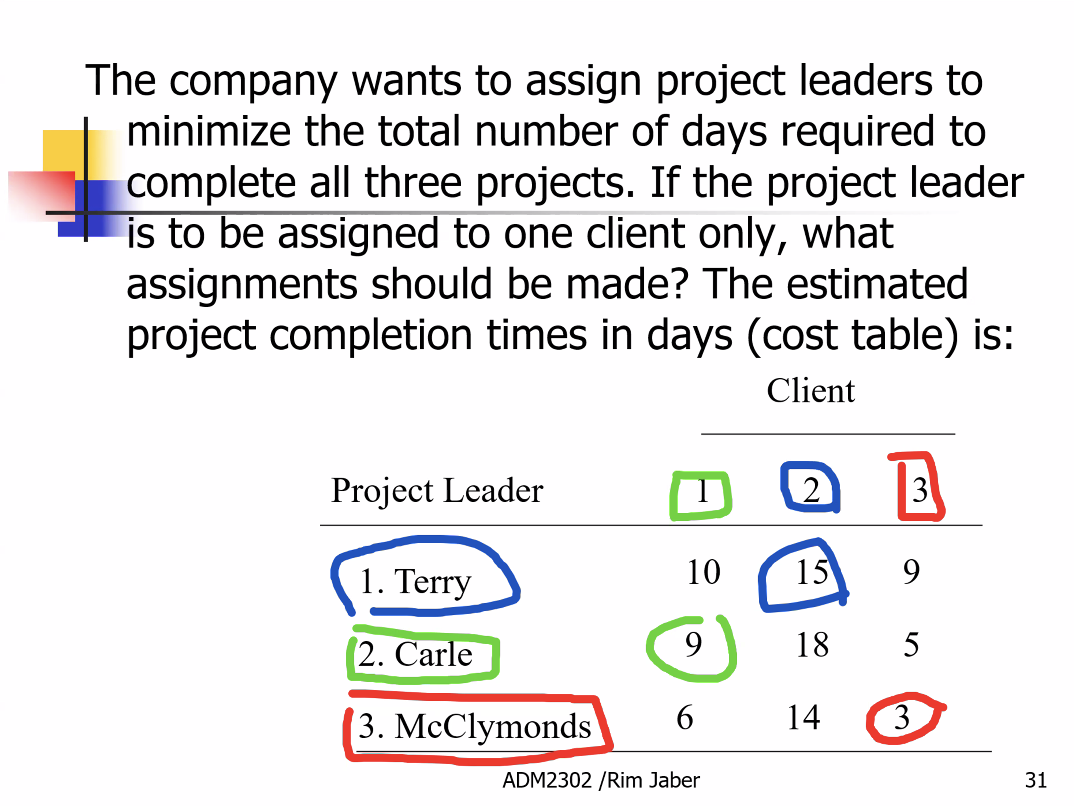
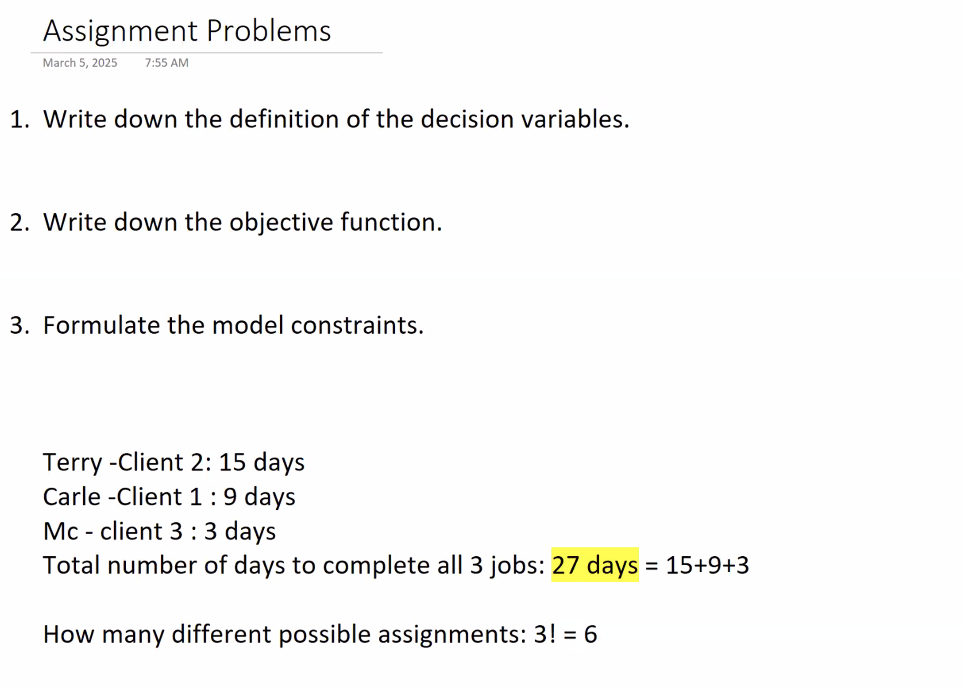
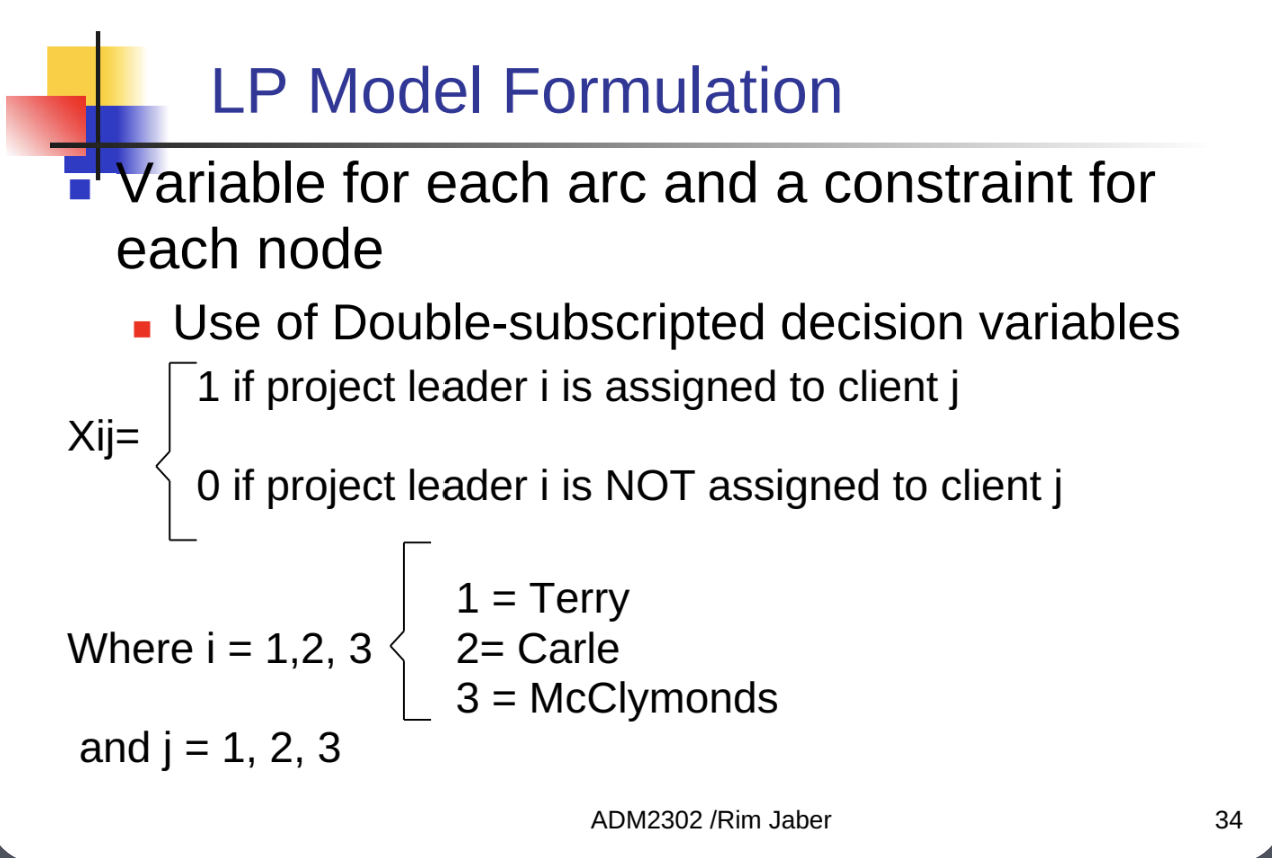
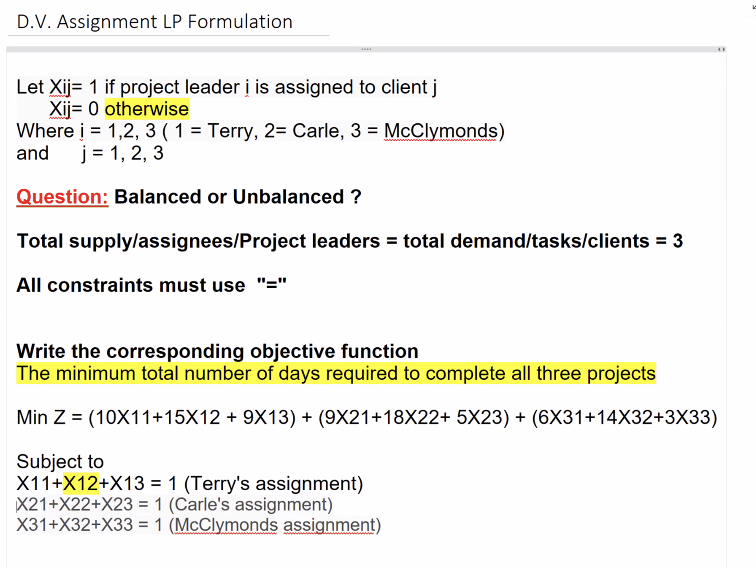
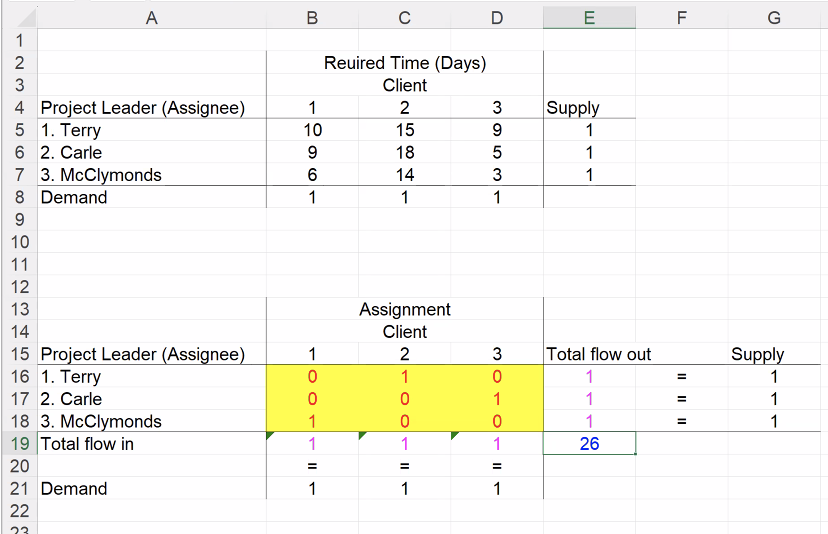
we could do more assignments for the 3 clients which is why we calculate 3!: Terry could be assigned to client 2 or client 1 or etc.

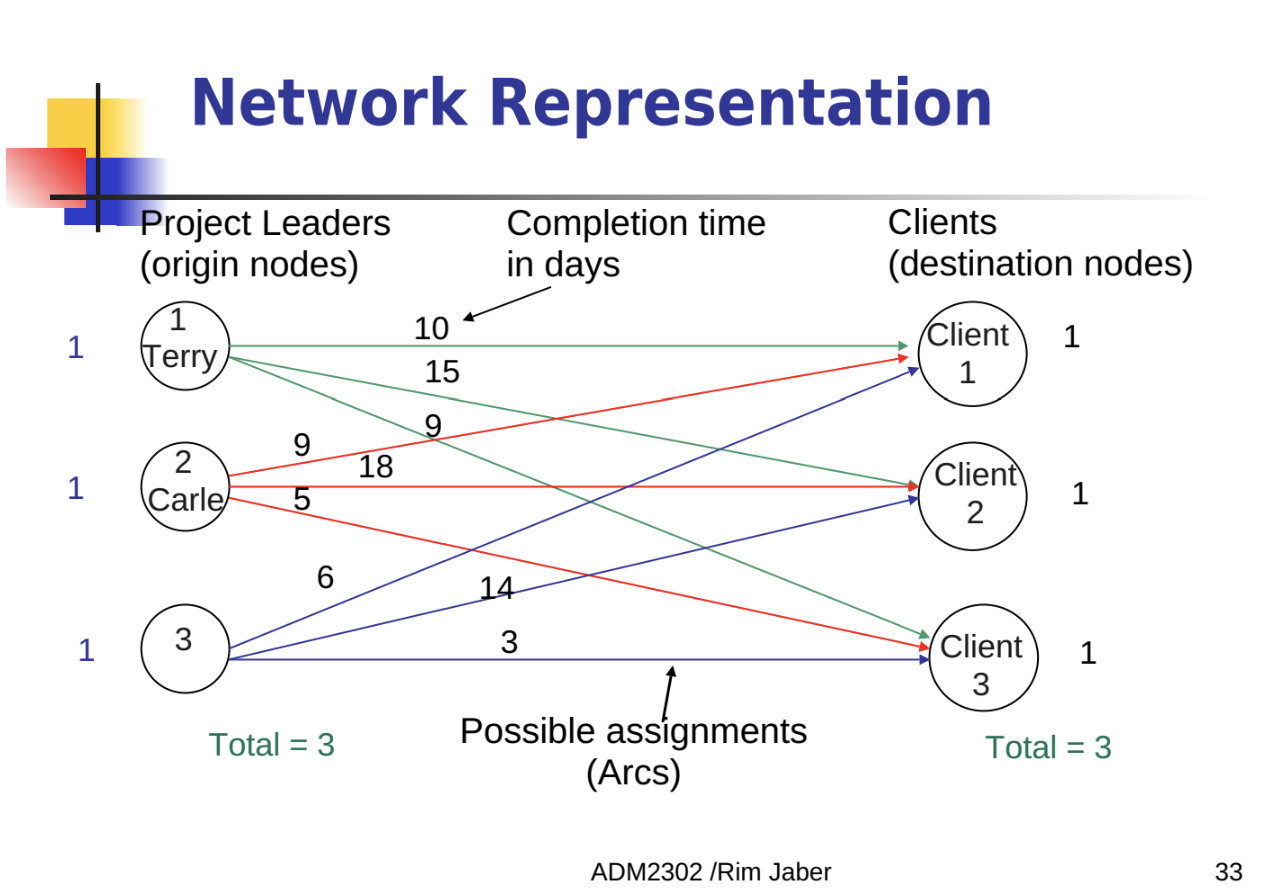
the 15 is the number of days is what it would take to complete the assignment if Terry is assigned to client 2
flow can have either a value of 0 or 1 (0=did not assign, 1=assigned)
if Terry is assigned to client 2 then the flow will be 1 for client 2
if Terry is assigned to client 2 then the flow will be 0 for client 1 and client 3