AP Pre-Calc (2025)
Unit 1
1.1 Change in Tandem
Domain is all the x values of a function
Range is all y values of a function
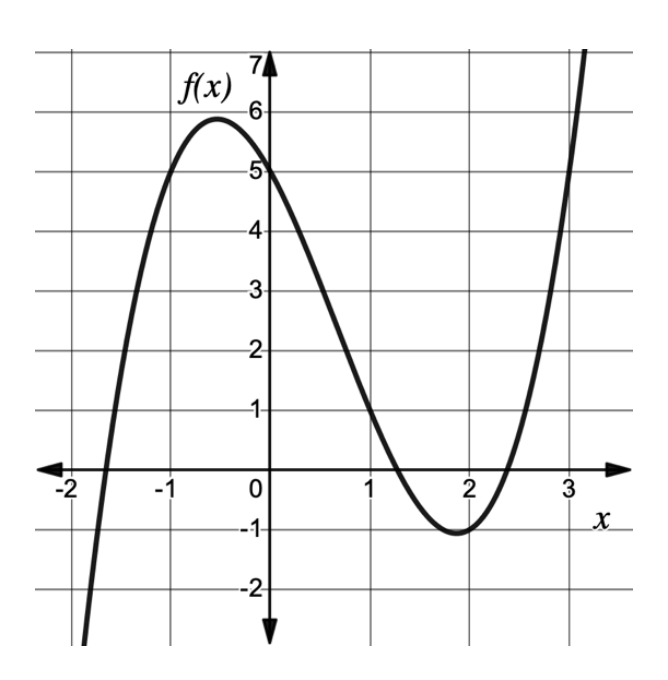
This function is increasing on the intervals x < -0.5 and x > 2
This function is decreasing on the interval -0.5 < x < 2
The function is positive on the intervals -1.5 < x < 1.2 and x > 2.2
The function is negative on the intervals x < -1.5 and 1.2 < x < 2.2
1.2 Rates of Change
Rate of change is the slope of a function
Found by (y1 - y2)/(x1-x2) on a linear function
1.3 Rates of Change in Linear and Quadratic Functions
The average rate of change for a linear function will always be constant
The rate of change of the rate of change should be zero
insert image here.
Average ROC is NOT constant over a quadratic function. The rate of change of the rate of change should be constant.
Increasing ROC | Decreasing ROC | |
Positive ROC | Function is increasing Concave up | Function is decreasing Concave up |
Negative ROC | Function is increasing Concave down | Function is decreasing Concave down |
1.4 Polynomial Functions and Rates of change
axn+bxn-1+…+c
axn = Leading term
n = Degree
a = Leading coefficient
Even degree | Odd degree | |
Positive leading coefficient | As x → ∞, f(x) → ∞ As x → -∞, f(x) → ∞ | As x → ∞, f(x) → ∞ As x → -∞, f(x) → -∞ |
Negative leading coefficient | As x → ∞, f(x) → -∞ As x → -∞, f(x) → -∞ | As x → ∞, f(x) → -∞ As x → -∞, f(x) → ∞ |
Absolute or global minimum/maximum: The highest or lowest point on the entire graph
Relative or local minimum/maximum: The highest or lowest point within an interval or the point of inflection
1.5 Polynomial Functions and Complex Zeros
If f(a) = 0, then a is a zero of the function f(x)
Factor to find zeros
f(x) = (x² - 2x - 3)
f(x) = (x - 2)(x - 1)
x ≠ 2, 1
2 and 1 are the zeros of the function f(x)
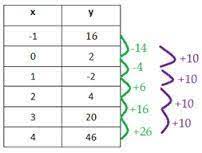
The green line is the first difference in the above function, where the purple line is the second difference. All of the differences in the second difference is even, which means the function is to the second degree.
Even functions are reflected across the y axis. This means f(-x) = f(x). The first degree must be even.
Odd functions are reflected about the origin. This means f(x) = -f(x). The first degree must be odd.
1.6 Polynomial Functions and End Behavior
Even degree | Odd degree | |
Positive leading coefficient | Limx→-∞ f(x) → ∞ Lim x→∞ f(x) → ∞ | As x → ∞, f(x) → ∞ As x → -∞, f(x) → -∞ |
Negative leading coefficient | Limx → ∞, f(x) → -∞ Limx → -∞, f(x) → -∞ | As x → ∞, f(x) → -∞ As x → -∞, f(x) → |
Same thing as 1.4, however it is a different format.
1.7 Rational Functions and End Behavior
End behavior of a rational function is the ratio of two polynomials
The denominator cannot equal 0, because then the equation does not exist.
To find domain: look at the denominator.
Ex: h(x)=(f(x))/(g(x)), h(x) = x² - 4, g(x) = x² - 2x - 24
g(x) = (x - 6)(x + 4)
x ≠ 6, -4
This means that the domain is all real numbers except 6 and -4
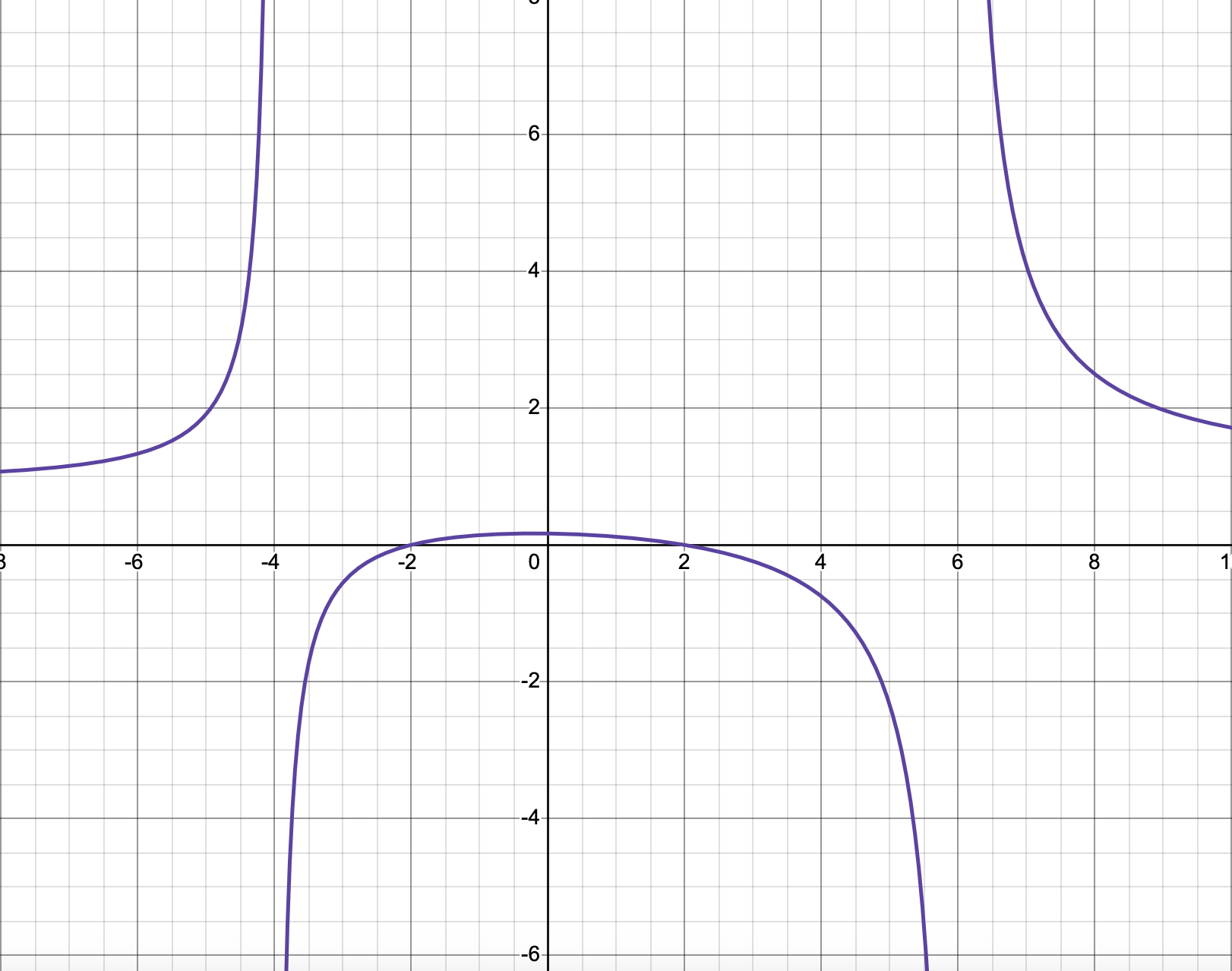
Asymptote is a number that the graph always approaches, but never reaches.
The end behavior can be found by the degrees of the equation.
If the degree of the numerator is larger than the degree of the denominator, then the end behavior is a slant asymptote. This just means that the asymptote is the leading terms quotient.
If the leading terms are 4x² and 2x, then the asymptote is y=2x.
If the numerator and denominator have equal degrees, then the asymptote is the quotient of the leading coefficients.
If the leading terms are 6x³ and 3x³, then the asymptote is (6/3), or a horizontal line at 2.
If the numerator has a smaller degree than the denominator, the asymptote is y=0.
1.8 Rational Functions and Zeros
Zeros are when a function’s y=0.
To find, factor the numerator of an equation.
(x² - x - 12)/(x - 3)
Factoring the numerator gives us (x - 4)(x + 3)
There are zeros at x = 4, x = -3
However, if the zeros were also on the denominator, then they would cancel out and have a hole, not a zero
1.9 Rational Functions and Vertical Asymptote
Vertical asymptotes are very similar to horizontal asymptotes, it is just a line at x = a that the function approaches, but never reaches.
Limx→a- r(x) = ∞
This means that as we approach a (the vertical asymptote) from the left side (the NEGATIVE side), the function approaches ∞
Limx → a+ r(x) = -∞
This means that as we approach a from the right side (the POSITIVE side), the function approaches -∞
Vertical asymptotes can be found by factoring the denominator
(x - 2)/(x - 3)(x + 4)
The vertical asymptotes are at x = -4, 3
1.10 Rational Functions and Holes
Holes are what happens when there is a real zero on a graph. It’s represented by a hollow circle in the function.
This happens when the numerator and the denominator have a common value and cancel out.
(10x + 30)/(x² + x - 6)
(10(x-3))/((x+3)(x-2))
Because both the denominator and numerator cannot = -3, x = -3 becomes a hole
Limx → -3- f(x) = -2
Limx → -3+ f(x) = -2
This means the hole is at (-3, -2)
1.11 Equivalent Equations and Binomial Theorem
Unit 2
2.1
Geometric Sequence is a series of numbers where every number is the previous, multiplied by a common ratio.
Example: 6, 12, 24, 48…
Unit 3
3.11
Cosecant: 1/sinx = cscx
Secant: 1/cosx = secx
Cotangent: 1/tanx = cotx