Natural Selection, Speciation & Conservation
Evolution/Natural Selection
Evolution: Change in allele (Genes) frequency of a population’s gene pool over generations (Time).
Paving the road for Darwin…
Jean Baptiste Lamark (1800s) (Use+Disuse)
Structures can be modified within one’s life → And can be passed on to offspring (acquired traits)
Charles Darwin (1859) (Traveled around the world → studied animal/plants)
Ex: Finches on the Galapagos Islands
Adaptive Radiation: Associated with different environmental niches.
Survival + Reproduction to adaptations to different food sources
Artificial Selection: (Natural Selection)
But humans choose the traits → Ex: Selective Breeding
Humans choose the desirable trait of calm dog
Wolf → Dog over many generations
Ex:: Teosinte corn
Natural Selection: Has to be heritable
Reproduction
Survival
Beneficial Traits
Variation (within) species
Mutations (asexually + sexually)
Meiosis (Create sperm/egg)
Sexual Reproduction/Fertilization
OverProduction of offspring (Many offspring die)
Competition for resources
Ex: Water/Food/Space
Differential Survival
Successful traits = adaptations
Those with adaptations survive in that environment.
“Fitness” = Survival + Reproduction
Differential Reproduction
Those beneficial traits may be passed on to the offspring
Those genes/alleles are more prevalent to the population
Ex: Peppered Moth
Light vs. Dark allele
Ex: Antibiotic resistant bacteria
Measuring Evolution: Through allele frequency
Agents of Evolution
Through mutations : only change in the DNA that alters the protein
Gene Flow: movement of organisms into/out of an area. Allele pool will change!
Sexual selection/non-random mating
Genetic Drift: Random placement of alleles (Founder affect)
Natural Selection
Gene pool: Total # og genes/alleles in a population
Ex: A a - Cystic Fibrosis
Dominant
Recessive
Large gene pool = Large Biodiversity
Small gene pool = Low Biodiversity
Hardy Weinburg Equilibrium
Serves as a null experiment
Assumptions/no evolution occuring
No genetic drift
No gene flows
No mutation
Random mating
No natural selection
P²+2pq+q²=1
p+q=1
p²: AA Homozygous dominant
2pq: Aa Heterosygous
q²: aa Homozygous recessive
Heterozygous “advantage”:
Ex: Sickle cell anemia → carriers = immune to malaria
The sickle cell gene is more prevalent in Africa (High Malaria)
Speciation
Species: Group of individuals that can mate + produce fertile offspring
New Species: Occurs through isolation + time
Allopatric: Geographic Isolation (Species Separated physically)
Ex: Chimpanzee and Bonobo
Chimpanzee: Compete w/ the Gorilla, aggressive, male dominated
Bonobo: Don’t live with Gorilla, Calm, female dominated
Sympatric: Same Location
Ex: Behavioral Differences
Pre-Reproductive Barriers: (Pre-Zygote)
Ecological Isolation
Same location/occupy different niches
Snake (Water & Land)
Temporal Isolation (Timing)
Same location → behavioral differences
Ex: Mate @ different seasons
Behavioral
Courtship (Bird Song)
Unique Behaviors
Mechanical
Anatomy does not fit together
Gametic Isolation
Post Reproduction: (Hybrids)
Hybrid Viability: hybrids are less likely to live a long/healthy life due to incompatibility
Hybrid Fertility: Many hybrids are infertile if they have an odd # of chromosomes
Ex: 24 + 23 =47
Hybrid Breakdown: Viable the 1st generation but become less viable each generation
Abrupt speciation in plants:
Polyploidy: Extra sets of chromosomes
Cause: larger fruit/plants force with colchicine: causes chromosomes to fail at separating
Ex: Allium (onion)
Adaptive Radiation:
Increase biodiversity
Species fill certain niches
Selective Pressures:
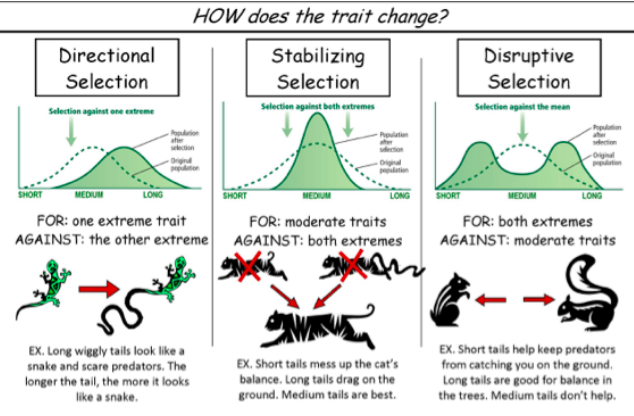
Stabilizing: Middle phenotype is favored
Disruptive: Both extremes are favored/rare/lead to new species
Rate of Evolution:
Gradualism (Slower)
Punctuated (Faster)
Evidence of Natural Selection
Fossil Records: Imprints in sedimentary rocks
Change over time
Relative dating: older organisms are @ the bottom
Radioactive dating: Knowing the age of the rock or fossil = the age of organism
C^14 dating
K-40 dating (cells), ½ life of 1.26 billion
Artificial selection: Selective Breeding
Humans select for desirable traits/phenotypes = increase allele frequency
Ex: Modern Corn (Natural selection)
Antibiotic Resistance: Bacteria with the resistant (Mutation) trait live (are not killed by antibiotics
Survive (other die)
Reproduce…
Homologous traits anatomy: Similar bone structure/anatomy (May have a different use)
From a common ancestor
Ex: Pentadactyl Limb (5)
Analogous traits anatomy:
Not related
Have the same function
Convergent Evolution
Evolve to fit a similar niche
Ex: Dolphin & Shark: Swim
Anatomy Vestigial Structure
No longer used…the presences
Show common ancestry
Ex: Whale hip (= used to walk)
Embryology: DNA, Amino Acids, Proteins
More similar = more related
Biodiversity/Conservation
Types:
Ecosystem: Habitats, communities, processes (Species interactions)
Species: # of species (types) + amount of species
Genetic: amount of diverse alleles (traits)
Low diversity: Risk of extinction (cannot adapt to change)
Ex: FL Panthers, Cheetahs
Species Diversity:
Richness: total # of species
Evenness: amount of each species
Dominance: What species is most abundant
Change in Biodiversity: There is more species now than ever before, due to fossil evidence
Mass Extinction: There have been 5 major mass extinctions…on the verge of 6?
Extinction: Permanently disappear cannot adapt to there environment
6th? Extinction:
= increased extinction rate (Present day)
Habitat decline = species decline
50% of the coral reefs are going extinct
1/6 species are at risk of extinction
Keystone species extinction: can cause domino effect
Causes of Biodiversity: habitat destruction
Fragmentation
Deforestation
Urbanization
Farming
Monoculture crops (soil nutrients)
loss of biodiversity
Ex: Dipterocarp (Tree: Deforestation)
Ex: Red wolf in NC
Edge Effect: Increase CO_2, runoff, Infection Disease
Pollution: Air, Water, acid Precipitation (Lead to disease)
Overhunting
Invasive Species: Non-native species that is introduced
No natural predators
Ex: Kudzu vines: Brought to America from Japan grows out of control/on top of other species…out competes the native species
Ex: Cane Toad
Overfishing: Decrease in Biodiversity
Problem: It is worldwide
Dilution Hypothesis
Loss of biodiversity
Reduces genetic diversity = increase risk to disease
Any introduction of disease can decrease biodiversity
Rodents are resilient to disease
Human Population: Lead cause of Biodiversity loss
Monitor Diversity:
Keystone species:
Species that will affect other species in the ecosystem
others rely on it
A cascade effect on the ecosystem
Ex: Beaver → Create Dams + Rivers
Conservation:
Prevention
Improvement
Use natural resources
global + economic awareness
In-Situ conservation: “On-Site”
Recover species
Ex: Nature reserves/regulations: limit human impact
Ex-Situ conservation: “Off-site”
Ex:
Captive Breeding
Seed Banks
Botanical Gardens
Sustainable Harvesting:
Max Sustainable # of species
(How many animal can be hunted without harming the population)
EDGE of Existence:
Evolutionary distinct + Globally endangered
Protects organisms on the verge of extinction