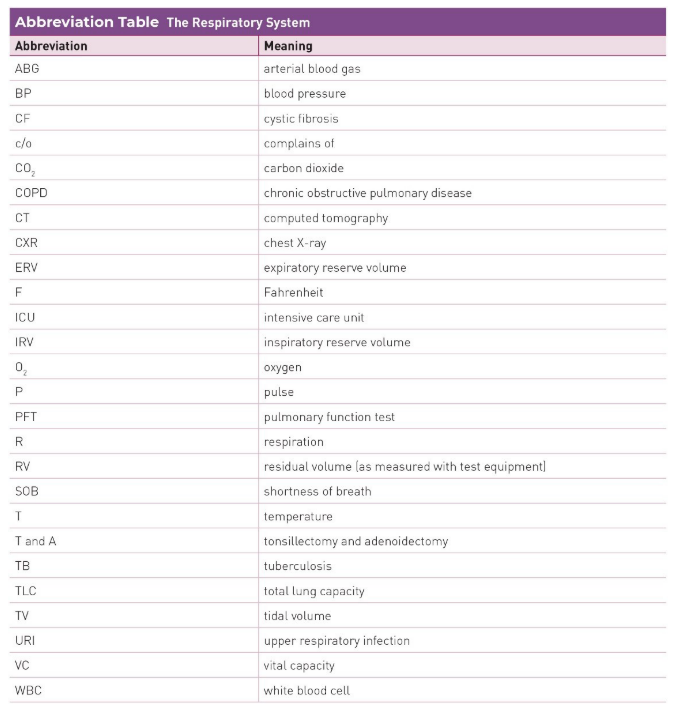
Respiratory System
Word Parts
bronch/o: bronchus
bronchi/o: bronchus
laryng/o: larynx
nas/o: nose
rhin/o: nose
-oxia: oxygen
or/o: mouth, opening
pharyng/o: pharynx
-phonia: voice
phren/o: diaphragm
pleur/o: rib, side, pleura
-pnea: breathing
pneum/o: air, lungs
pneumon/o: air, lungs
pulmon/o: lung
sinus/o: sinus cavity
thorac/o: thorax, chest
thorac/i: thorax, chest
thoracic/o: thorax, chest
trache/o: trachea
Structure & Functions
Respiratory System
Allows us to inhale oxygen
Oxygen: gas needed by our cells
Exhale carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide: gaseous metabolic waste that needs to be eliminated
Gas Exchange:
External Respiration: air brought into lungs; oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange in bloodstream at capillaries surrounding alveoli
Internal Respiration: oxygen and carbon dioxide move between the bloodstream and the body’s cells
Upper Respiratory Tract
Paranasal sinuses
Nasal cavity
Nose
Pharynx
Lower Respiratory Tract
Larynx
Lungs
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Alveoli
Nose
Air enters nose through opening called nostrils
Lines with small hairs that trap particles and prevent them from entering respiratory tract
Air passes into nasal cavity
Nasal septum divides nose into left and right halves
Here, air is warmed and moistened
Mucus: clear, sticky secretion, coats lining of nasal cavity to filter out particles
Paranasal sinuses: air-filled cavities in bones of face connected to nasal cavity
Included frontal, ethmoidal, maxillary, sphenoidal
Pharynx (throat)
Divided into three sections: nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
Tonsils (lymphatic tissue)
Aid in filtering bacteria
Three pairs:
Pharyngel tonsils (adenoids); nasopharynx
Palatine tonsils; oropharynx
Lingual tonsils; base of posterior tongue
Larynx
Also known as voice box
Organ that produces sound
Located between pharynx and trachea
Made up of cartilages and elastic membranes
Air enters larynx through a slit-like opening called glottis
Flap of cartilage (epiglottis) protects glottis during swallowing to prevent food or liquids from entering respiratory tract
As air flows over vocal cords, they vibrate to produce sound
Trachea
Known as windpipe
Cartilaginous tube that conducts air from larynx to bronchial tree
Bronchial tree consists of air-passage tubes that lead from trachea to the lungs
Bronchi
Two major airways: left bronchus and right bronchus
Air passes through bronchi; subdivide into smaller branches called bronchioles
Flow of air terminates in bronchial tree in tiny air sacs called alveoli
Alveoli: structures where gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs
Lungs
Paired, spongy organs of breathing located in thoracic cavity
Enclosed in pleura → membrane composed of two layers called parietal pleura and visceral pleura
Right Lung
Slightly larger than left
Three lobes: superior lobe, middle lobe, lower lobe
Left Lungs
Two lobes: superior lobe and inferior love
Each cone-shaped lung has an upper apex and lower base, which rests on diaphragm
Diaphragm
Sheet of muscle that separates thoracic cavity (houses the lungs) from lower abdominal cavity
Major muscle used in breathing
When diaphragm contracts, inhalation occurs
When diaphragm relaxes, exhalation occurs
Diseases
Airways need to remain patent (open) in order for proper air exchange to take place
Reflex to cough or sneeze when pathway becomes blocked; may produce sputum or hemoptysis
Abnormal breath sounds are indication of respiratory disease
Rales: also known as crackles; high-pitched popping sounds usually originating in smaller airways, fluid
Rhonchi: low-pitched sounds that come from larger airways
Wheezing or whistling sounds: may indicate excessive secretions or partially obstructed narrow airways, heard on exhalation
Stridor: high-pitched squaking sound that occurs when one breaths in; sign of respiratory obstruction in the upper airway, larynx, trachea, or epiglottis
Eupnea: normal breathing; should be regular and effortless
Abnormalities:
Tachypnea
Bradypnea
Apnea
Dyspnea
Orthopnea
Cheyne-Stokes
Kussmaul breathing
Infectious disorders
Infectious rhinitis: virus strain; common cold
Sinusitis: inflammation of any sinus mucous membrane
Croup: also called laryngotracheobronchitis
Epiglottitis: inflammation of epiglottis
Influenza (flu): acute infectious respiratory disease caused by influenza viruses
Pneumonia: inflammation of the lung parenchyma; bacteria or virus
Laryngitis: inflammatino of larynx mucous membrane
Pertussis: whooping cough
Tuberculosis (TB): infectious disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis
Obstructive lung disease
Impair flow through bronchial tree
Asthma: lung disease characterized by reversible inflammation and constriction
Cystic fibrosis (CF): genetic disorder in which lungs become clogged with excessive amounts of abnormally thick mucus
Chronic obstructure pulmonary disease (COPD): umbrella term that includes both emphysema and chronic bronchitis
Emphysema: alveoli enlarged and inefficient, leading to shortness of breath (SOB)
Chronic bronchitis: inflammation of mucous membrane of bronchi
Expansion disorders
Atelectasis: collapsed lungs
Pneumothorax: accumulation of air in pleural cavity
Diagnostic Tests, Treatments, and Surgical Procedures
Noninvasive procedures and tests
Chest X-rays (CXRs)
Lung scans
Pulse oximetry
Computed tomography scans (CT)
Arterial blood gases
Invasive procedures
Thoracentesis (pleural tap): insertion of needle into pleural cavity to withdraw fluid
Bronchoscopy: examination of trachea and bronchial tree through a viewing instrument called bronchoscope
Conducted by respiratory therapist
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs): to assess breathing
Spirometer: instrument used for measuring air capacity of the lungs
Medications:
Antihistamines: drugs used to treat acute allergic reactions
Decongestants: used to treat congestion
Practice and Practitioners
Pulmonologist: physician who specializes in pulmonology, which is the study of the lungs and related structures
Otolaryngologists: and otorhinolaryngologists: diagnose and treat disorders of ears, nose, and throat
Respiratory therapists: allied healhcare professionals who specialize in airway management, mechanical ventilation (breathing), and blood acid-base balance