W1: Introduction to neuroimaging
Topic 1: The physics of neuroimaging
Neuroimaging techniques produce bio-markers.
Technological development of two medical imaging modalities (i.e., MRI & PET) was sparked basic ideas of physics.
Main protagonists of early 20th century theoretical physics include Niels Bohr, Maurice de Broglie, Carl David Anderson & Paul Dirac
Albert Einstein = father of modern physics
Special relativity = scientific theory that describes the relationship between space and time, and how they are affected by the motion of objects.
Nothing can move faster than the speed of light :. all is relative, including time.
Profound nature of special relativity meant that physical models of entities/particles had to be changed.
Bohr’s hydrogen model
De Brogile postulated that an electron (charged particle) could stay in orbit around an opposite charge nucleus (i.e., proton) thanks to standing wave orbits.
Standing wave orbits are the three-dimensional wave-like patterns that electrons form around the nucleus of an atom.
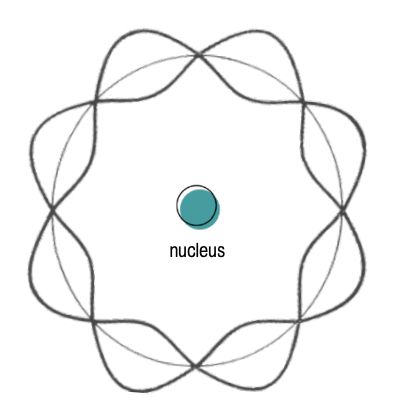
However, De Brogile’s model did not account for relativity.
Paul Dirac described the quantum wave functions that added relativistic effects to De Brogile’s model .
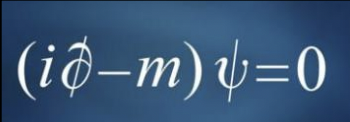
Paul Dirac’s (referred to by friends as ‘the strangest man) personality aligned with what would today be considered autistic spectrum disorder due to his fixation on mathematics and lack of interest in human interaction.
Dirac’s equation made 2 startling conditions
Charged particles (e.g., protons) ‘spin’ :. rotate around their own axis
This ‘spin’ property means that charged particles generate magnetic moment, meaning that this magnetic field had a certain strength and direction
Magnetic moment of water protons = basic principle behind MRI.
Water protons have a magnetic moment that generally is directed randomly, resulting in null magnetization. However, switching on a strong magnetic field → spins to align in the direction of the magnetic field at a rotating speed dependent on the intensity of that field.
⚠ Main components of MRI machine:
Strong magnetic filed
Gradient coils
= magnetic fields that change linearly along the X, Y and Z axes so that each point in the field of view has a slightly different magnetization, hence a different spinning frequency.
Radio frequency coil
Emit excitation pulse send spins into a different state so that the net magnetization resulting from all the spins will form an angle (90° or 180°) with the direction of the magnetic field.
Radio frequency detector
Radio frequency signals are emitted by protons
Each spin in a different location will send a signal with a very specific radio frequency.
Sometimes, the same coil can work at both excitation and detection.
Once the pulse is switched off, the water protons will go back to their initial state, creating a magnetic decay. The rate of decay of magnetization depends on the tissue water protons are in. Collecting magnetic decays at different frequencies (i.e, different locations), computer programs generate maps of magnetic relaxations, MRI images.
MRI produce detailed images thanks to higher resolution and great signal-to-noise ratio. Imaging potential of MRI extends to an ability to reconstructing a 3D representation of brain axonal paths.
These techniques can produce the same or higher level of detail than mortem tissue dissections
Example of straightforward application of MRI: use of paramagnetic agents (e.g. gadolinium) to enable the visualisation of brain vascular branches.
Molecules other than water give out magnetic resonance.
Creatinine, choline & N-acetylaspartate produce a resonance and these can be explored using MRI radiofrequency signal to explore different molecular resonances that can be used to quantify the molecular milieu of the brain.
The discovery of the BOLD effects is one striking advance in MRI applications.
BOLD (Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent) effect depends on the paramagnetic properties of haemoglobin
Haemoglobin = protein in blood that brings oxygen to peripheral tissues
Oxygenation can :. be readily imaged thanks to changes in the paramagnetic properties of haemoglobin.
:. BOLD effect can be used to visualize brain functional activity when a subject performs a task in MRI scanner
2nd prediction from Dirac’s equation:
Proposed a solution of same mass as the electron but opposite charge: positron
Positron = element of antimatter
Carl Anderson is credited for enabling the visualisation of a positron via an experiement measuring cosmic radiation using gas chamber
A positron is generated by a nuclear reaction by proton-rich nuclei.
It survives after expulsion from the nucleus until it finds a slow-moving electron and it annihilates, emitting two gamma photons.
Gamma photons have a lot more energy than X-rays that instead are generated by electrons.
Electron-positron annihilation is the only known reaction in by which mass is completely converted into energy.
:. Positrons & positron-emitting atoms = great energy containers
Positron emitting isotopes (e.g., O15, C11, F18) can be produced by local cyclotrons & attached to any substrate (drug, sugar, etc.) & injected into humans.
In PET scans, radioisotope can be visualized by a ring of detectors that stop gamma radiation.
:. allowing to visualize biodistribution of almost any substance and measure its kinetics across tissues, obtaining very valuable functional information in vivo.
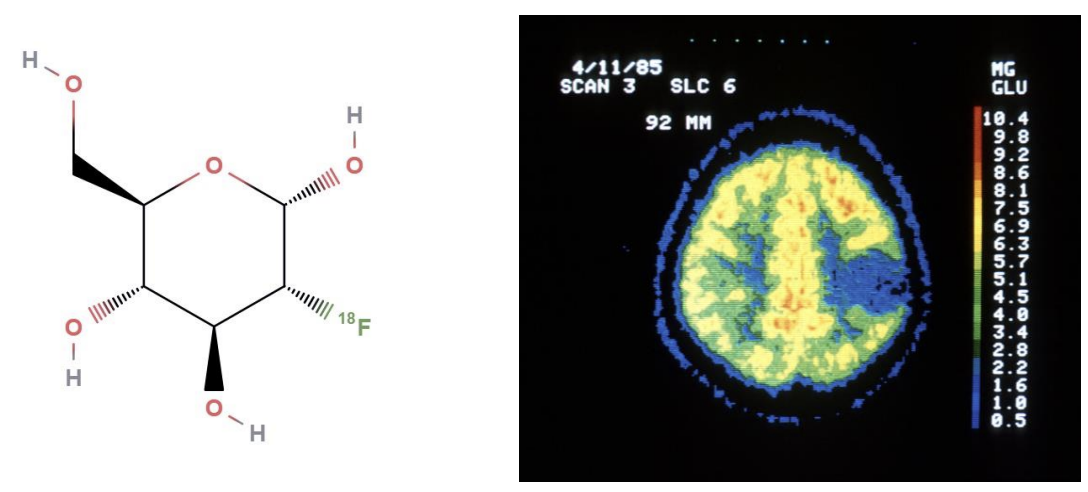
The brain is the only organ with a glucidic-only metabolism.
Topic 2: Imaging biomakers: general principles & applications in brain research
The definition of '‘biomarker (biological marker)'' is constantly evolving. Today, the definition of biomarker is rather general: “ any biological characteristic that can be objectively measured ” (Jain, 2010).
This particular definition does not outline the purpose of the measure.
Two important recurring elements in defining a biomarker: biological target + quantitative measurement for said target.
Together, these elements become informative for a particular biological process, creating a biomarker.
:. Biomarker = any biological characteristic that is biologically informative & can be objectively measured.
Can be simple (e.g. body temperature) or complex (e.g. genetic test)
Can be classified based on how invasive (or non-invasive) they are
Certain biomarkers require access to body tissue via biopsy for diagnosis or staging of a certain diseases (e.g., cancer, hepatitis)
Other biomarkers require access to body fluid (i.e., blood, urine or saliva) to investigate presence of infections.
Non-invasive means include imaging biomarkers, which can be used to look for internal trauma.
Each biomarker is optimized to investigate a particular biological function, :. right biomarker depends on the question of interest
Biomarkers can evolve over time.
E.g., diagnosis tests of diabetes mellitus (disease marked by excess of sugar in urine) initially limited to availability of ants until Thomas Willis (1660) detected excess of glucose in urine by literally tasting them.
Today, blood and urine tests are standard practice for diagnosis of hyperglycaemia.
Biomarkers can also be classified depending of their area of application
Those designed for the pharmacological industry are used to test and develop new treatments or as surrogate endpoints in clinical trials.
Biomarkers designed for clinic use include tools and technologies for understanding prediction, cause, diagnosis, progression and regression of a disease
In clinical research, biomarkers are categorized into 2 groups:
Biomarkers of risk (antecedent biomarkers) | Biomarkers of disease |
Measures the risk of developing a certain disease | Used in presence of a disease or a condition |
Used before the disease sets in | Includes screening tests, diagnostic tests and prognostic tests. |
Includes any measurement of exposure to environmental risk factors or genetic susceptibility tests | ⚠ Disease ≠ on/off status; ✅ progression of causal cascades |
Limitations: ① Presence of a risk factor does not guarantee the development of a certain disease & ② some risk factors are difficult to measure (e.g., stress) | Some biomarkers can monitor this cascade, while others only indirectly reflect their results |


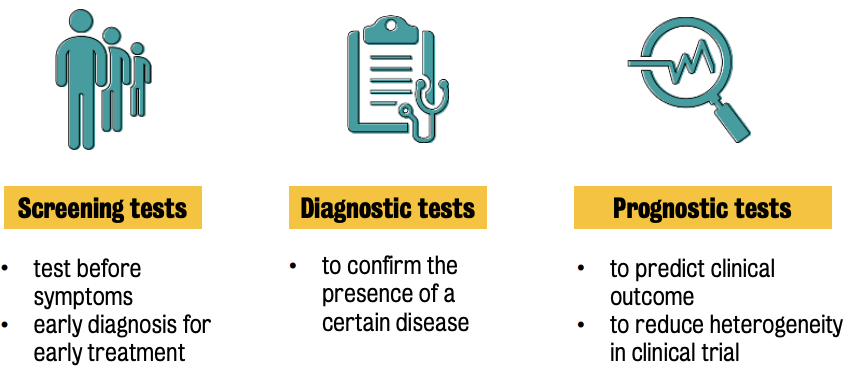
Imaging biomarker = biomarkers that use imaging as measurement probe
Allow non-invasive access to in vivo functional and structural biological characteristics.
Functional imaging modalities ++ appealing than structural ones b/c they = better predictive of pathological mechanism behind brain disease
Imaging biomarkers in AD
AD = most common form of cognitive decline in Western world
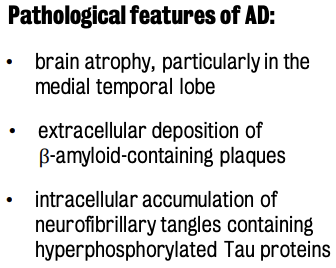
Structural MRI biomarkers are mainly used to detect the presence of atrophy across the whole brain or in some particular brain regions as hippocampus or the brain cortex.
Functional MRI (magnetic resonance spectroscopy) are used to measure connectivity loss of neuronal decline at different stages of the disease.
Molecular imaging (esp. PET) is used to investigate alteration of glucose metabolism or beta-amyloid accumulation.
⭐️ Why not use all biomarkers together?
Different biomarkers inform about different aspects of the disease & these do not necessarily occur at the same time.
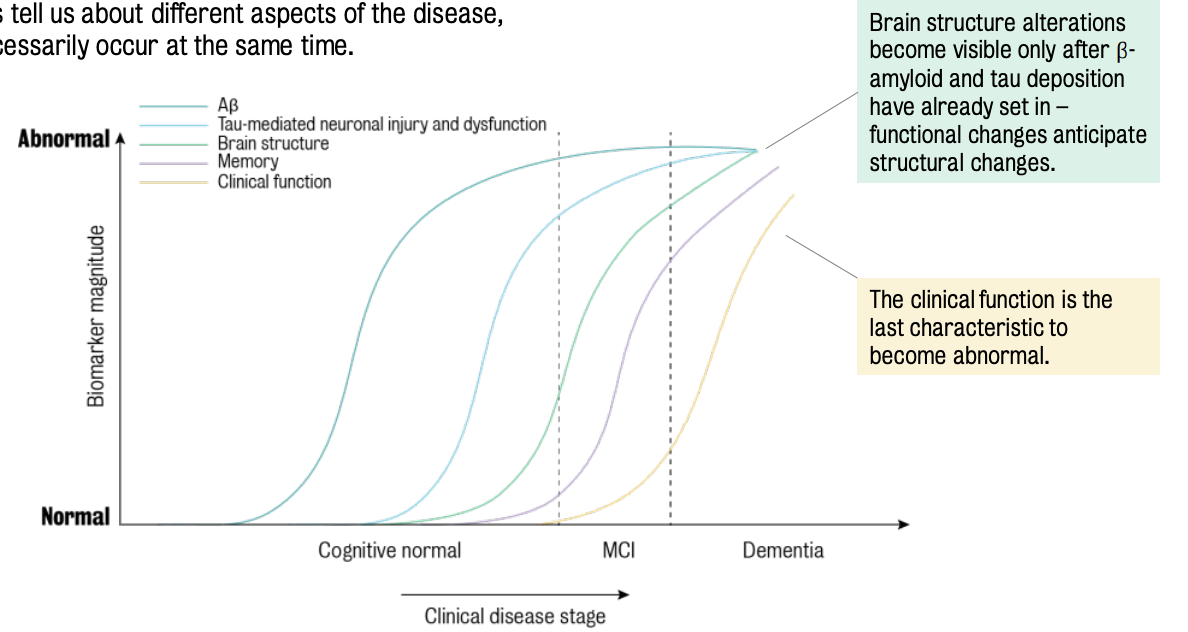
⚠ Time is crucial for AD pathology & the most appropriate imaging biomarker should be chosen according to the research questions.
In psychiatry research, the development of imaging biomarkers relies on how biological targets of the measures are defined.
However, there is a lack of understanding of the biological mechanisms to drive these conditions.
Led to the research for intermediate phenotypes → Endophenotypes = objective characteristics used to separate behavioural symptoms into more stable phenotypes with a clear genetic connection
Brain imaging offers a unique opportunity to measure in vivo pathological abnormalities at molecular and system levels.
Statistical principles used to characterize the performance of a biomarker
Certain degree of variability is observable within a distribution of measures for a particular biological feature in a homogeneous population of subjects.

Variability is unavoidable.
An ideal biomarker aims for complete separation between different conditions (e.g., healthy vs affected subjects). In reality, groups tend to overlap + distribution of measures can vary a lot from case to case & significantly differ from the typical bell shape.
A biomarker is assessed on its capacity to identify the biological process of interest.
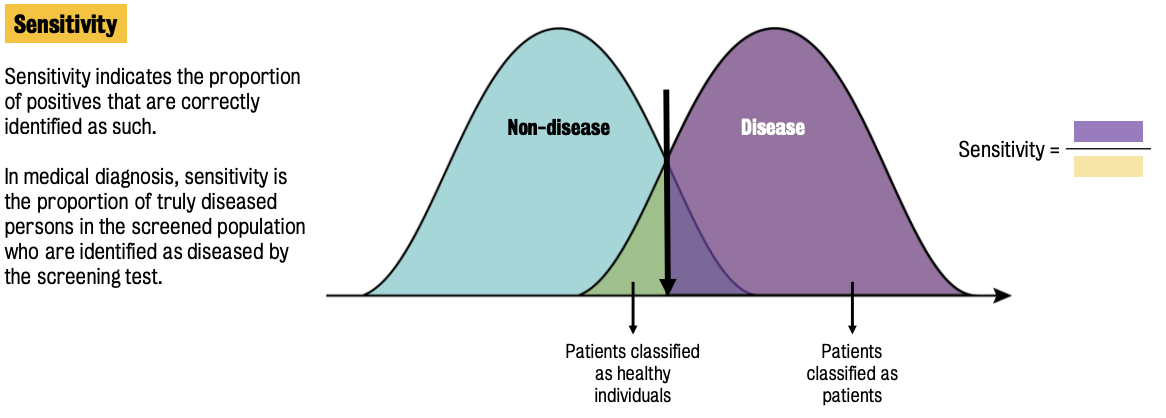
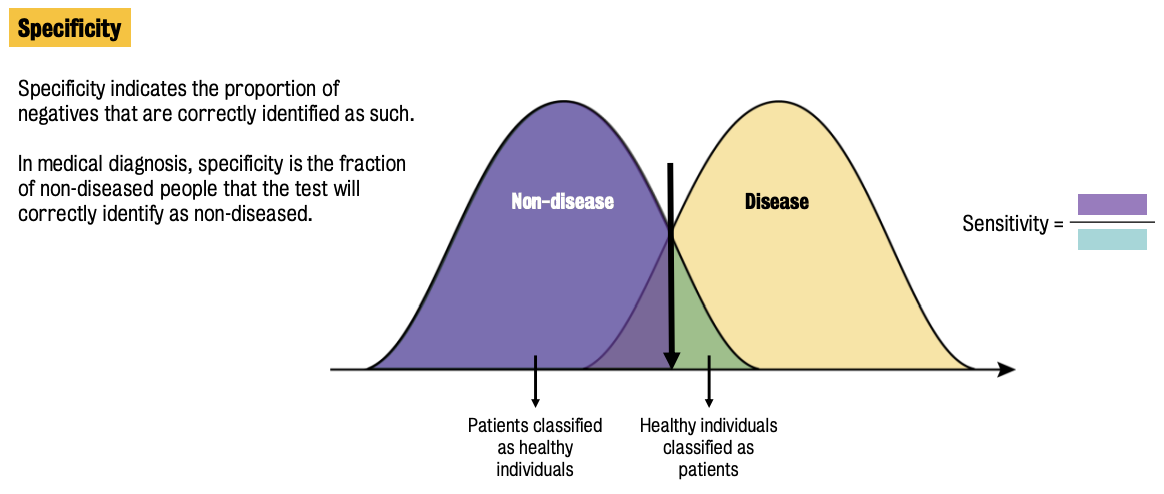
Two main parameters used to assess biomarker performance: sensitivity & specificity
Sensitivity = ratio of truly diseased population in the screened population who are identified as diseased by the screening test.
Specificity = fraction of non-diseased people that the test will correctly identify as non-diseased.
There are ++ other parameters that can be used to assess biomarker performance
Biomarker tests need a threshold for classification purposes
Generally, the intersection of two distribution serves as the threshold
Parameters of interest include: ① true positive; ② true negatives; ③ false positives & ④ false negatives
Together, these parameters define the 'error matrix' → a full characterization of the biomarker performance
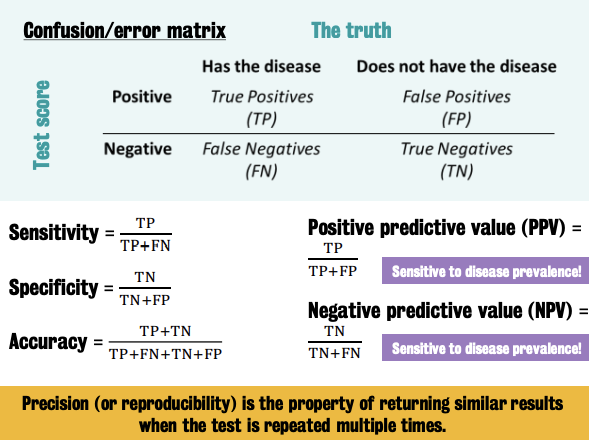
Precision (or reproducibility of a test) cannot be derived from the error matrix.
It requieres ad hoc test-retest experiments
Prevalence = proportion of disease found to be affecting a particular population.
🚫 affect sensitivity or specificity of the test, but has an important impact on the positive and negative predicted values.
By reducing prevalence of a disease, false positives become much more than the true positive cases, meaning that only a few individuals with a positive test do actually have the disease
ROC (receiver operating characteristic) curve
Summarizes the capacity of a test to separate two groups as its discrimination threshold is varied.
Used to compare biomarker classification performance
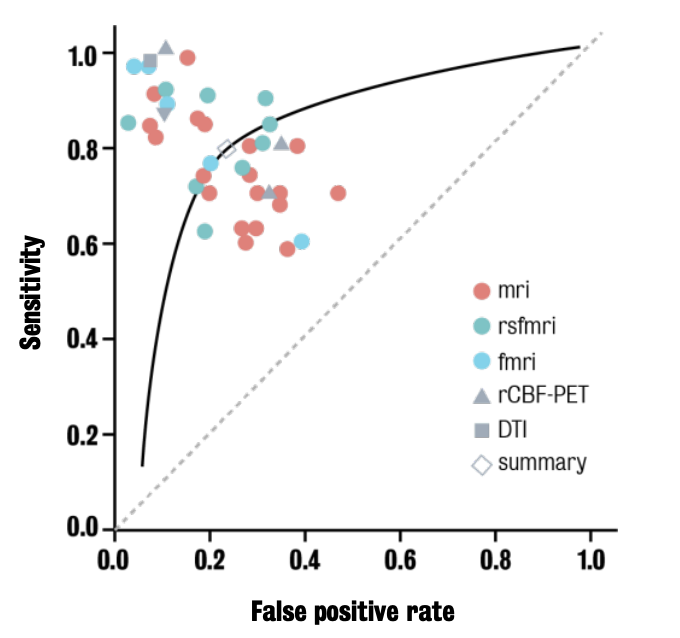
Caption: ROC curve show variability of a biomarker performance even within the same imaging modality.
The development of novel biomarkers follows a well-defined timeline that includes validation and qualification.

Need for new and performing biomarkers fuels this area of research
Use of imaging in CNS drug discovery
Goal: Understand how the search for novel drugs to treat symptoms of nervous system dysfunction is aided by the new technologies of pharmacological MRI.
Historical drug discovery
Early psychotropic drug discoveries relied on serendipity (i.e., chance).
E.g., reserpine & chlorpromazine
Reserpine stems extract from an Indian plant called rauwolfia. It was used to calm crying children & reduce high levels of blood pressure.
Chlorpromazine = prototypical compound of phenothiazines. Used to calm agitated patients & reduce distress, psychotic behaviours, delusions and hallucinations in psychotic patients
⭐️ This discovery paved the way for the development of anti-schizophrenia medication.
Interest in how these compounds worked.
Toward the end of WW2, there is a move away from serendipitous approach due to unreliability of chance drug discovery.
By 2020, drug discovery evolved to incorporate structural biology, computational biology, genomics, proteomics, and systems biology for a more systematic approach.
Post-serendipity Era
By 2010, despite billions made from tranquilizers, the rate of new drug development declined, particularly in neuroscience.
Phase 1 of clinical development assess a new drug's safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics, but many CNS drugs failed at this stage.
Pharmaceutical companies, driven by stockholder value, faced bleak prospects due to the lack of new drugs for CNS diseases
Difficulty finding new drugs for CNS disease
Modern Drug Discovery Techniques
Medicinal chemists and in vitro assay developers improved synthesis and testing, leading to high throughput screening for compounds with high affinity for specific receptors.
High throughput screening, using mechanization and robotics, greatly increased the number of assays that could be performed in a day, revolutionizing drug discovery.
The challenge remains in whole animal target validation, i.e., identifying the correct target in the genome relevant to diseases like schizophrenia.
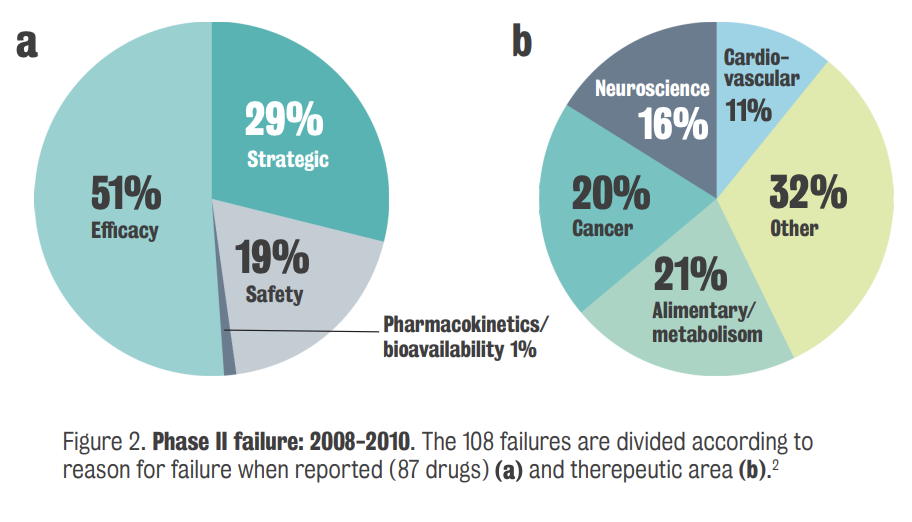
Four Pillars of Drug Development
Demonstrating the right dose for the drug's affinity to its target, especially in the brain, is crucial, often using PET.
PET can radiolabel a drug and show that it specifically interacts with the target
Showing a pharmacological consequence when the drug occupies the receptor, confirming target engagement.
Pharmacokinetics: (Branch of pharmacology focused on) ensuring that the drug reaches the target (i.e., brain) in sufficient concentrations that will exert the desired effect, factoring in how long the drug remains effective in the system.
Safety and Tolerability: Assessing the safety profile of the drug, confirming that it does not produce adverse side effects and is safe for patients to use
Cost & Proof of Concept
High cost (10 years and $1 billion) per launched drug highlights the need for better evidence of success.
A "bean counting" approach can hinder scientific exploration by prioritizing cost over comprehensive drug investigation.
‘Bean counting’ simply looks at the probability of success of a molecule.
Reverse pharmacology, identifying a drug's mechanism after it's found to work, can lead to flawed assumptions if not carefully validated.
Drug-induced models and Validation
Drug-induced models, like using NMDA antagonists to mimic schizophrenia symptoms, offer insights but require careful consideration and validation.
Invoking the same methodology in both animal models and patients strengthens validation and proof of concept
Scientists often prioritize positive results over negative ones, potentially cherry-picking data and overlooking contradictory evidence — i.e., dismissing any data that doesn’t support their hypotheses.
Improving the Probability of Preclinical Success
More focus on target identification stage, emphasizing a genetic approach, using hair follicles from patients with schizophrenia converting them into neurons
Use of techniques such as CRISPR-Cas 9, which can repair genetic errors and validate targets using patient-derived cells, but this approach is time-consuming and requires careful patient phenotyping
Ensure assays measure the same psychological construct in animal models and humans, citing the stop-signal reaction time task as a translational cognitive assay
The stop-signal reaction time, used to measure motor impulsivity, can be replicated in rats using operant tasks with lever pressing.
Focus on brain circuits relevant to the disorder, such as the hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease, and validate tasks by lesioning the hippocampus.
Imaging shows that orbital frontal cortex & areas of the brain are responsible for the difficulty going from the intra- to the extradimensional shifting
Extradimensional shifting is very disruptive to schizophrenics
Translate cognitive tasks like the Wisconsin Card Sorting Task into animal versions to assess cognitive inflexibility, focusing on extradimensional shifts
Tissue oxygen measurement in freely moving rats is equivalent to fMRI measurements, validated through electrophysiological studies .
Oxygen amperometry can be used as a surrogate for functional imaging in rats, allowing for clinical proof of concept studies at a reduced cost compared to human MRI studies .
Oxygen amperometry can detect slow oscillations and regional connectivity in the rat brain, similar to the default mode network observed in human MRI studies
AMPA potentiators can reverse the effects of alcohol and morphine in animals, providing a proof of concept for human studies .
Clozapine normalizes the inter-regional coherence response to ketamine, which is a valid approach to measuring drug responses
Despite the pharmaceutical industry's hesitation, the close alignment of these techniques with human studies makes psychiatric drug discovery a promising area.