Networking Overview 1.1
Unit 1: Networking Concepts
1.1 Introduction to Networking
Definition of a Network: A network consists of two or more computer systems linked by a transmission medium that share protocols for exchanging data.
Components of a Network:
Nodes: Devices that send, receive, and forward data.
Intermediate Nodes: Responsible for forwarding functions (e.g., routers).
End Systems/Hosts: Send and receive the actual data traffic (e.g., PCs, smartphones).
Links: The communication pathways that connect nodes.
1.1.2 Types of Networks
1.2.1 Client-Server Networks
Client: A device that consumes services provided by a server.
Server: A more powerful computer making applications and resources available to clients.
Characteristics:
Centralized management of application services and resources.
Majority of nodes function as clients, with servers granting access to resources.
1.2.2 Peer-to-Peer Networks
Definition: Each host acts as both client and server.
Characteristics:
Decentralized structure where service management is distributed among nodes.
Small peer-to-peer networks are sometimes called workgroups.
1.3 Appliances, Applications, and Functions
1.3.1 Appliances
Definition: Specialized platforms designed for specific network roles. Examples include:
Switches: Forward data between devices.
Routers: Connect different networks and route data.
Firewalls: Enforce security rules.
Load Balancers and Proxies: Improve network performance.
Deployment Types:
Physical Appliances: Run on dedicated hardware.
Virtual Appliances: Run as virtual machines on a hypervisor.
1.3.2 Applications
Purpose: Services that allow networks to perform tasks like file sharing and email usage.
1.3.3 Functions
Addition of Properties: Networks can be configured for specific tasks, enhancing their functionality, including:
Virtual Private Networks (VPN): Enable secure connections over the Internet.
Quality of Service (QoS): Optimizes the network for time-sensitive applications (e.g., video, voice).
1.4 Network Types
1.4.1 Local Area Networks (LAN)
Definition: Networks confined to a single geographical location.
Examples:
Home/Residential Network: Typical internet router with connected devices.
Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) Network: Centralized server with client devices for business use.
Small and Medium-sized Enterprise (SME) Network: Structured cabling with multiple routers/switches.
Enterprise LAN: Large-scale network with extensive infrastructure and hundreds/thousands of devices.
Datacenter: Hosting only servers and storage without end-user client devices.
1.4.2 Wide Area Networks (WAN)
Definition: Networks connecting multiple local networks across larger geographical areas.
Characteristics:
Used to connect branch offices and allow remote access via the Internet.
1.5 Network Topology
1.5.1 Physical Topology
Definition: The actual layout of nodes and how they are interconnected through transmission media.
Example Types: Direct connections (e.g., single cable) or connections via switches with separate cables.
1.5.2 Logical Topology
Definition: The way data flows within the network regardless of physical connections.
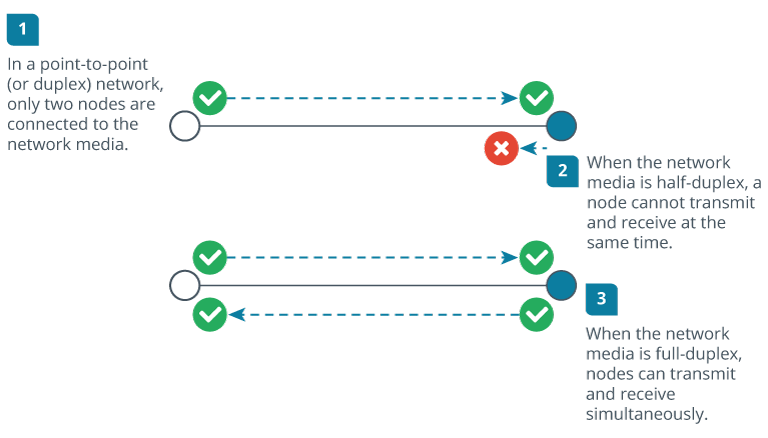
1.5.3 Point-to-Point Link
Definition: Direct link between two nodes, ensuring dedicated bandwidth.
Characteristics: Can be physical or logical, offering a 1:1 connection.
1.5.4 Star Topology
Definition: Each node connects to a central forwarding device (e.g., switch/router).
Advantages:
Easy to troubleshoot and reconfigure due to centralized monitoring.
Faults can be isolated effectively.
Hub-and-Spoke Topology: A variation often used in WANs with a central hub connecting remote sites.
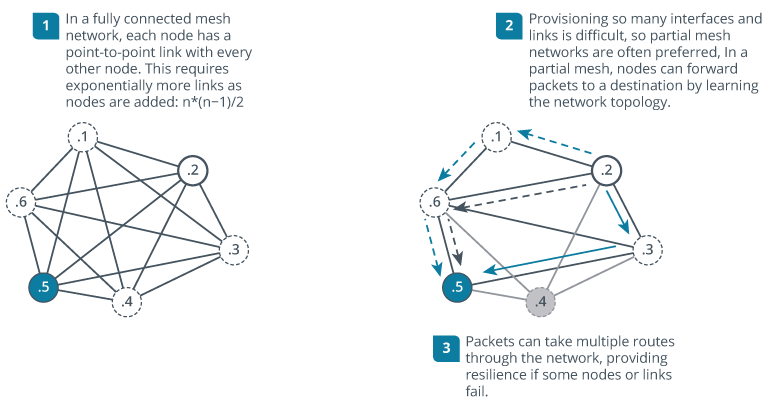
1.5.5 Mesh Topology
Definition: Each device is interconnected, typically used in larger WANs.
Full Mesh: Every device has a direct point-to-point link to every other device (impractical for large networks).
Partial Mesh: Only critical devices are interconnected, providing redundancy and fault tolerance through intermediary links.