Chapter 12 - Synovial Fluid
Physiology
It is a viscous liquid found in the cavities of the movable joints (diarthroses) or synovial joints.
- The bones in the synovial joints are lined with smooth articular cartilage and separated by a cavity containing the synovial fluid.
- The joint is enclosed in a fibrous joint capsule lined by the synovial membrane.
- The synovial membrane contains specialized cells called synoviocytes that secrete a mucopolysaccharide containing hyaluronic acid and a small amount of protein (approximately one fourth of the plasma concentration) into the fluid.
- The polymerization of hyaluronic acid contributes to the noticeable viscosity to the synovial fluid.
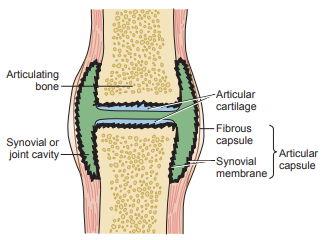
It is formed as a nonselective ultrafiltrate (excluding high molecular weight proteins) of plasma across the synovial membrane.
- The majority of the chemical constituents have concentrations similar to plasma values.
It reduces friction and lubricates in the joints, provides nutrients to the vascular-deficient articular cartilage and lessens the shock of joint compression.
Specimen Collection and Handling
- It is collected by needle aspiration called arthrocentesis.
- Normal synovial fluid does not clot; however, fluid from a diseased joint may contain fibrinogen and will clot.
- To prevent clotting, syringes are moistened with heparin anticoagulants.
- Powdered anticoagulants should not be used because they may produce artifacts that interfere with crystal analysis.
- Specimens are distributed into the following:
- a sterile heparinized tube for Gram stain and culture
- a heparin or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) tube for cell counts
- a nonanticoagulated tube for other tests
- The nonanticoagulated tube for other tests must be centrifuged and separated to prevent cellular elements from interfering with chemical and serologic analyses.
- a sodium fluoride tube for glucose analysis
- All testing should be done as soon as possible to prevent cellular lysis and possible changes in crystals.
Color and Clarity
| Color | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|
| colorless to pale yellow | normal |
| deeper yellow | noninflammatory and inflammatory effusions |
| greenish tinge | bacterial infection |
| w/ blood | hemorrhagic arthritis or traumatic aspiration |
| turbid | WBCs, synovial cell debris or fibrin |
| milky | crystals |
Viscosity
- The simplest method to measure viscosity is to observe the ability of the fluid to form a string from the tip of a syringe.
- A string that measures 4 to 6 cm is considered normal.
- If it is too viscous, it may need to be pretreated by adding a pinch of hyaluronidase to 0.5 mL of fluid or one drop of 0.05% hyaluronidase in phosphate buffer per milliliter of fluid and incubating at 37°C for 5 minutes to be able to perform other tests such as cell count.
- To measure the amount of hyaluronate polymerization, a Ropes or mucin clot test is performed.
- When added to a solution of 2% to 5% acetic acid, normal synovial fluid forms a solid clot surrounded by clear fluid.
- As the ability of the hyaluronate to polymerize decreases, the clot becomes less firm, and the surrounding fluid increases in turbidity.
- The mucin clot test is reported in terms of good (solid clot), fair (soft clot), low (friable clot), and poor (no clot).
- The mucin clot test is not routinely performed as little diagnostic information is obtained; however, it can be used to identify questionable specimens.
Cell Counts
- Cells are counted using the Neubauer counting chamber without any dilution unless the specimen is turbid or bloody.
- Traditional WBC diluting fluid cannot be used because the acetic acid forms mucin clots, so hypotonic saline (0.3%) or saline that contains saponin is a suitable diluent.
- Normal saline can be used, sometimes with methylene blue added to differentiate RBCs and WBCs.
- WBC counts less than 200 cells/L are considered normal; however, variations depend on the type of disease, the pathogenicity of the agent and antibiotic administered.
Differential Count
- Differential counts should be performed on cytocentrifuged preparations or on thinly smeared slides.
- Specimens should be incubated with hyaluronidase prior to slide preparation.
| Cell/Inclusion | Description | Clinical Significance | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|
| neutrophils | polymorphonuclear leukocyte | bacterial sepsis, crystal-induced inflammation | 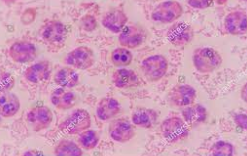 |
| lymphocyte | mononuclear leukocyte | nonseptic inflammation | 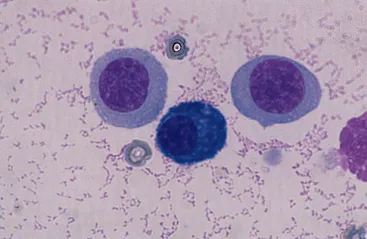 |
| macrophage (monocyte) | large mononuclear leukocyte, may be vacuolated | normal, viral infection | 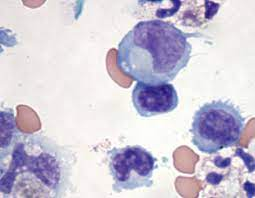 |
| synovial lining cell | similar to macrophage but may be multinucleated, resembles a mesothelial cell | normal | 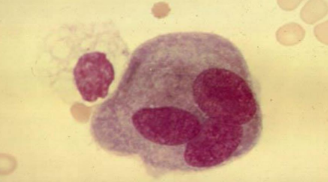 |
| lupus erythematosus (LE) cell | contains ingested round body | lupus erythematosus | 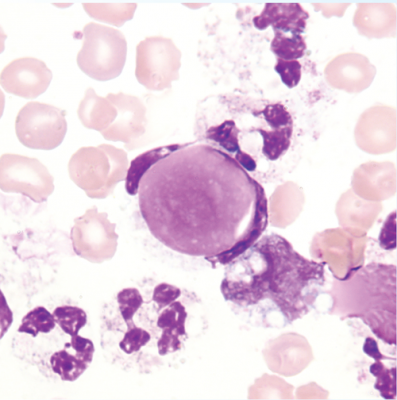 |
| Reiter cell | vacuolated macrophage with ingested neutrophils | Reiter syndrome, nonspecific inflammation | 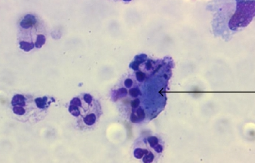 |
| rheumatoid arthritis cell (ragocyte) | neutrophil with dark cytoplasmic granules containing immune complexes | rheumatoid arthritis, immunologic inflammation |  |
| cartilage cells | large, multinucleated cells | osteoarthritis | 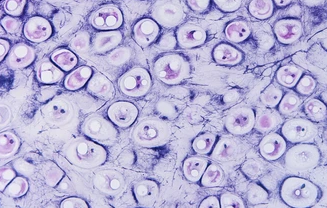 |
| rice bodies | macroscopically resemble polished rice, microscopically show collagen and fibrin | tuberculosis, septic and rheumatoid arthritis | 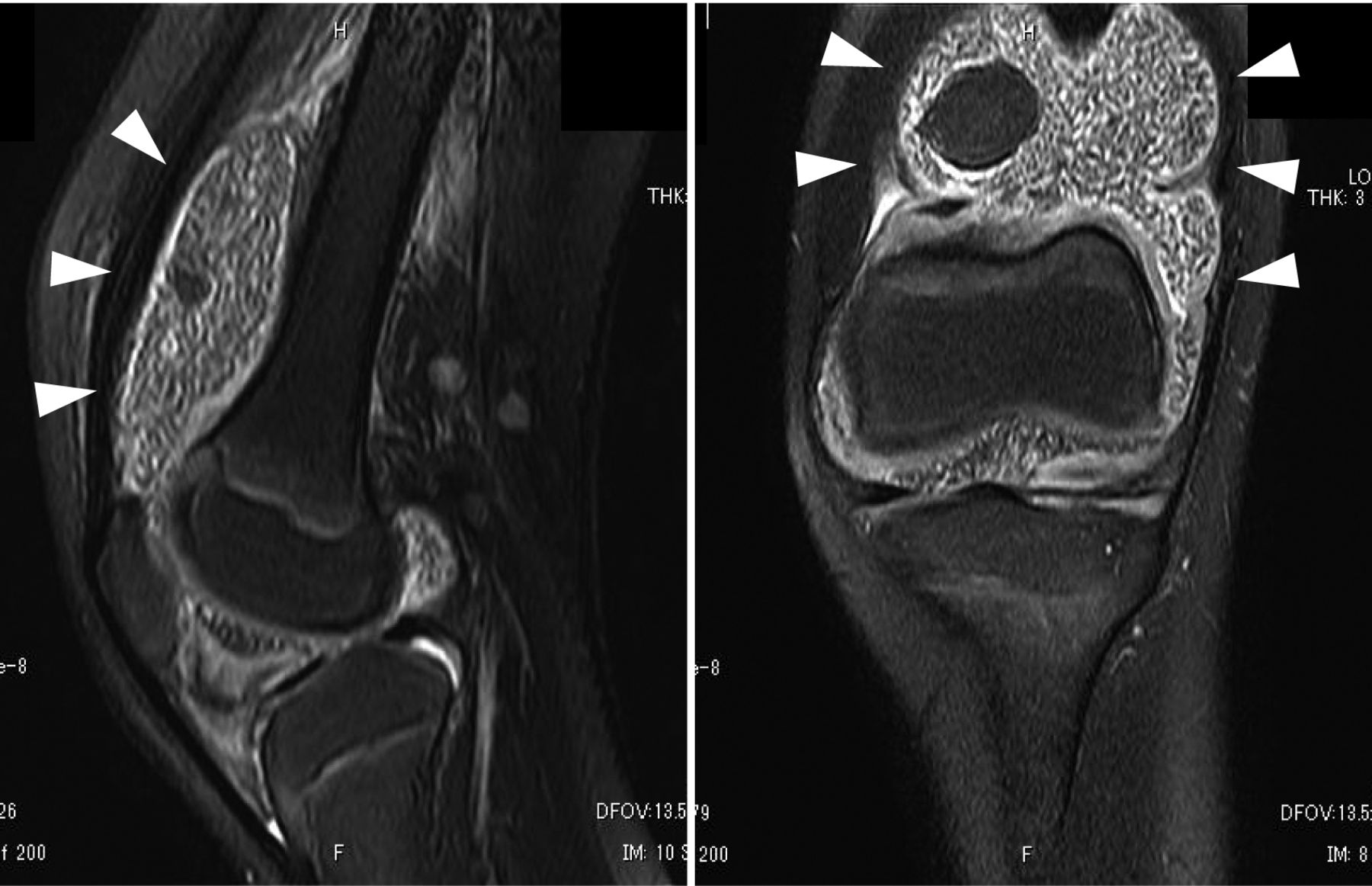 |
| fat droplets | refractile intracellular and extracellular globules, stained with Sudan dyes | traumatic injury, chronic inflammation | 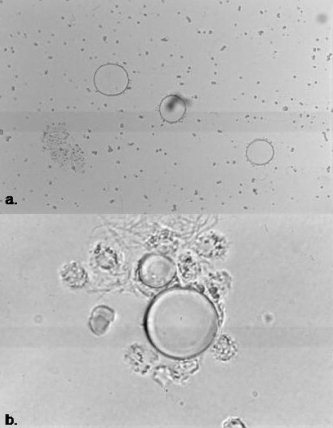 |
| hemosiderin | inclusions within clusters of synovial cells | pigmented villonodular synovitis |  |
Crystal Identification
- Examination should be performed soon after collection to ensure that crystals are not affected by changes in temperature and pH.
- Fluid must be examined prior to WBC disintegration as some crystals are found intracellularly.
- Specimens may be first examined under low and high power using a regular light microscope with Wright stains, however this should not replace the use of polarized microscopy.
| Crystal | Shape | Significance | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|
| monosodium urate | needles, found extracellularly or within the cytoplasm of neutrophils | gout (impaired metabolism or consumption of purines, chemotherapy, impaired excretion of uric acid) | 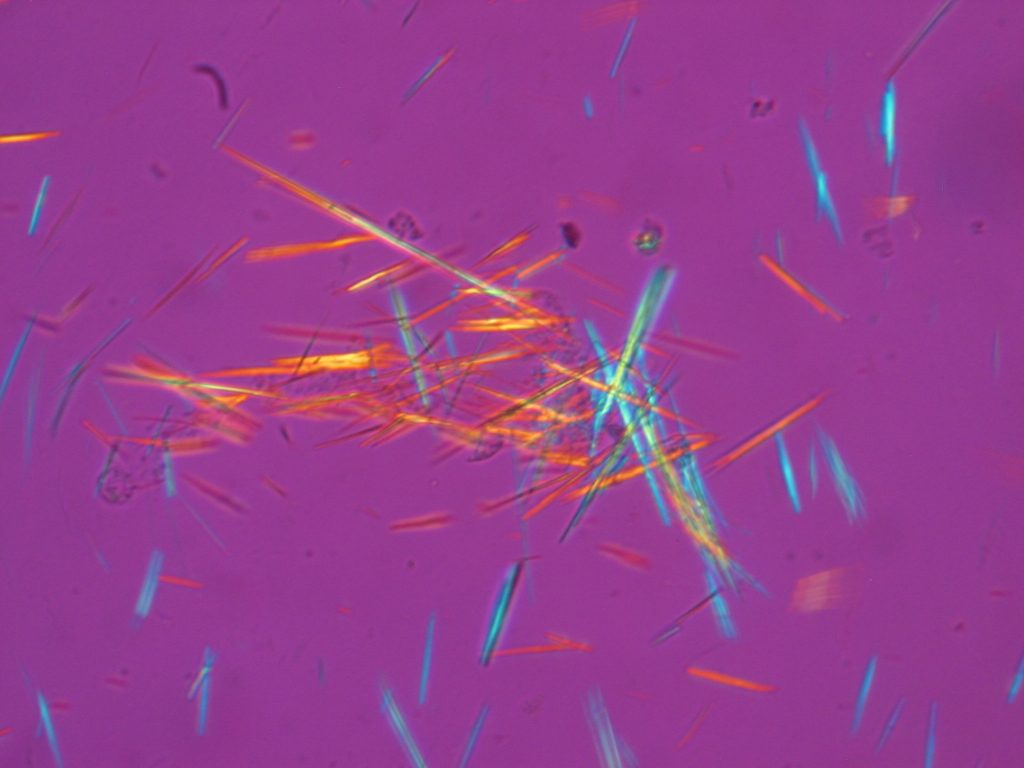 |
| calcium pyrophsphate | rhombic square or rodded, found within vacuoles of neutrophils | pseudogout (cartilage calcification from degenerative arthritis, endocrine disorders that increase serum calcium) | 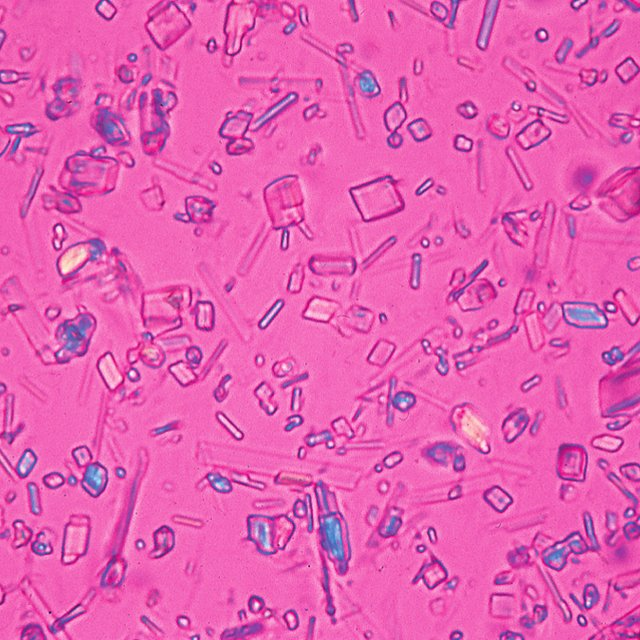 |
| cholesterol | notched, rhombic plates | chronic inflammation | 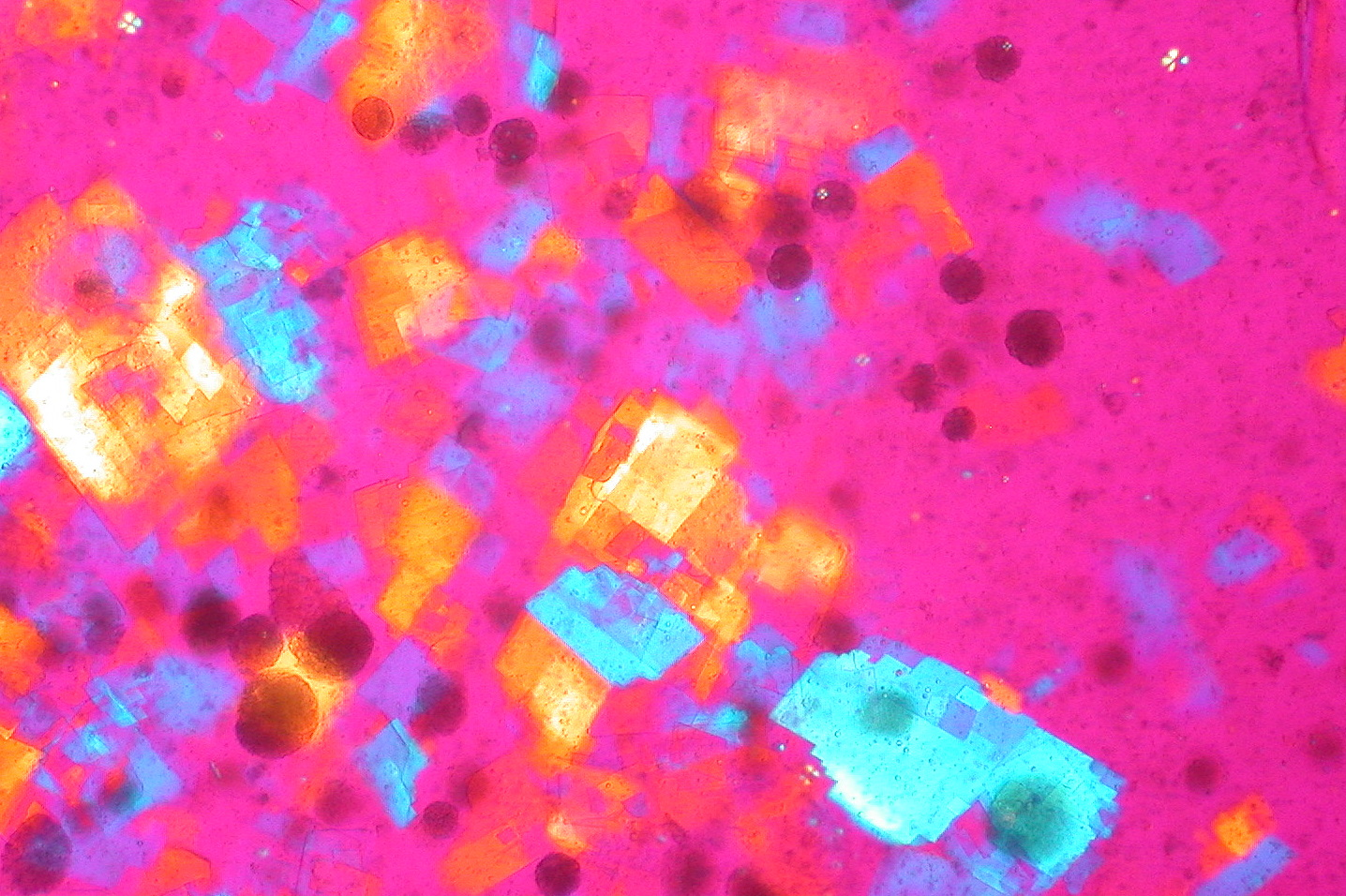 |
| corticosteroid | flat plates of varied shapes | injections | 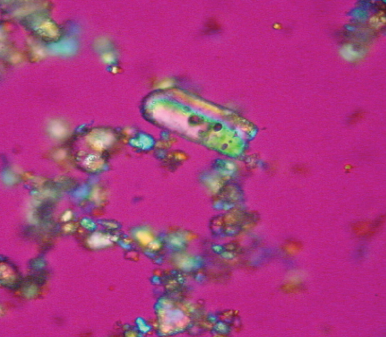 |
| calcium oxalate | envelopes | renal dialysis | 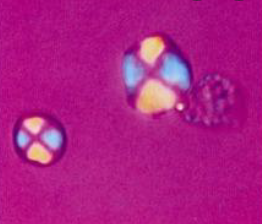 |
| hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate) | macroscopic red splotches, does not polarize | calcified cartilage degeneration, osteoarthritis | 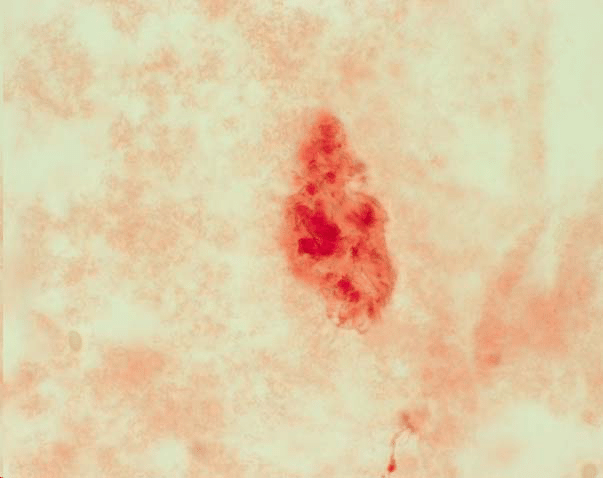 |
| microscopic thick jagged rods (in electron microscopy) | 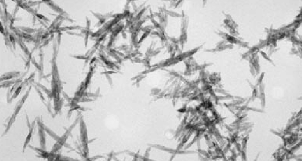 |
Chemistry Test
- Synovial fluid is chemically an ultrafiltrate of plasma, chemistry test values are approximately the same as serum values.
- Simultaneous blood and synovial fluid samples should be obtained, preferably after the patient has fasted for 8 hours to allow equilibration between the two fluids.
- The most frequently requested test is the glucose determination, as markedly decreased values are indicative of inflammatory (group 2) or septic (group 3) disorders.
- Under these conditions, normal synovial fluid glucose should not be more than 10 mg/dL lower than the blood value.
- To prevent falsely decreased values caused by glycolysis, specimens should be analyzed within 1 hour or preserved with sodium fluoride.
- Because the large protein molecules are not filtered through the synovial membranes, normal synovial fluid contains less than 3 g/dL of protein (approximately one third of the serum value).
- Increased levels are found in inflammatory and hemorrhagic disorders; however, measurement of synovial fluid protein does not contribute greatly to the classification of these disorders.
- Elevated synovial fluid uric acid level may be used to confirm the diagnosis when the presence of crystals cannot be demonstrated in the fluid.
- Measurement of serum uric acid is often performed as a first evaluaton of suspected cases of gout.
- Fluid analysis for crystals is frequently still required.
Microbiologic Tests
- An infection may occur as a secondary complication of inflammation caused by trauma or through dissemination of a systemic infection.
- Bacterial infections are most frequently seen; however, fungal, tubercular, and viral infections also can occur.
- Both Gram stains and cell cultures are as organisms are often missed on Gram stain.
- Patient history and other symptoms can aid in requests for additional testing.
- Routine bacterial cultures should include an enrichment medium, such as chocolate agar.
- In addition to Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, common organisms seen are the fastidious Haemophilus species and N. gonorrhoeae.
Serologic Tests
- Serologic testing plays an important role in confirming joint disorders supplementary to serum tests.
- Rheumatoid arthritis and lupus erythematosus are diagnosed in the serology laboratory by demonstrating the presence of their particular autoantibodies in the patient’s serum and synovial fluid.
- Arthritis is a frequent complication of Lyme disease, so demonstration of antibodies to the causative agent Borrelia burgdorferi confirms it.
- The extent of inflammation can be determined through measurement of the concentration of acute phase reactants such as fibrinogen and C-reactive protein.