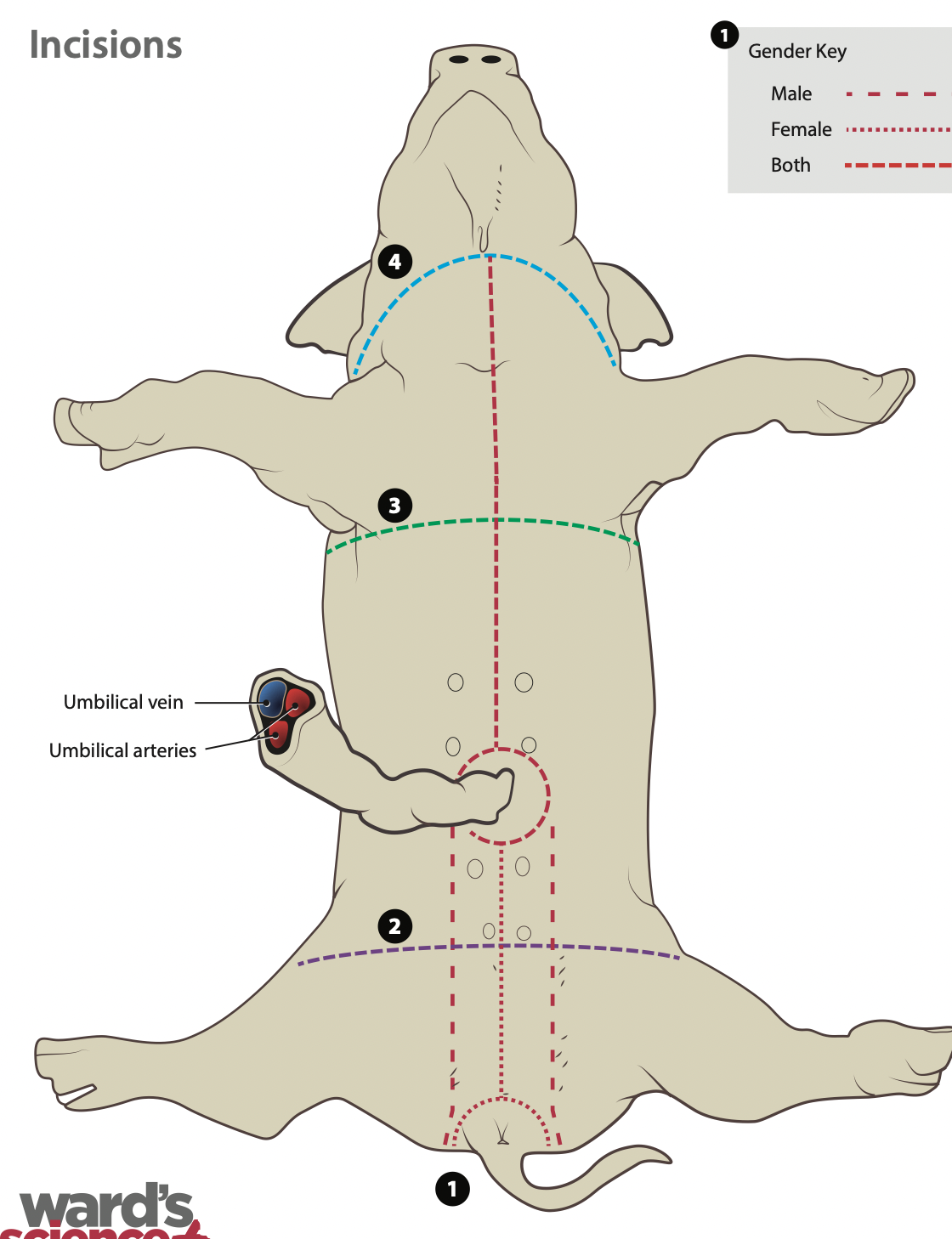
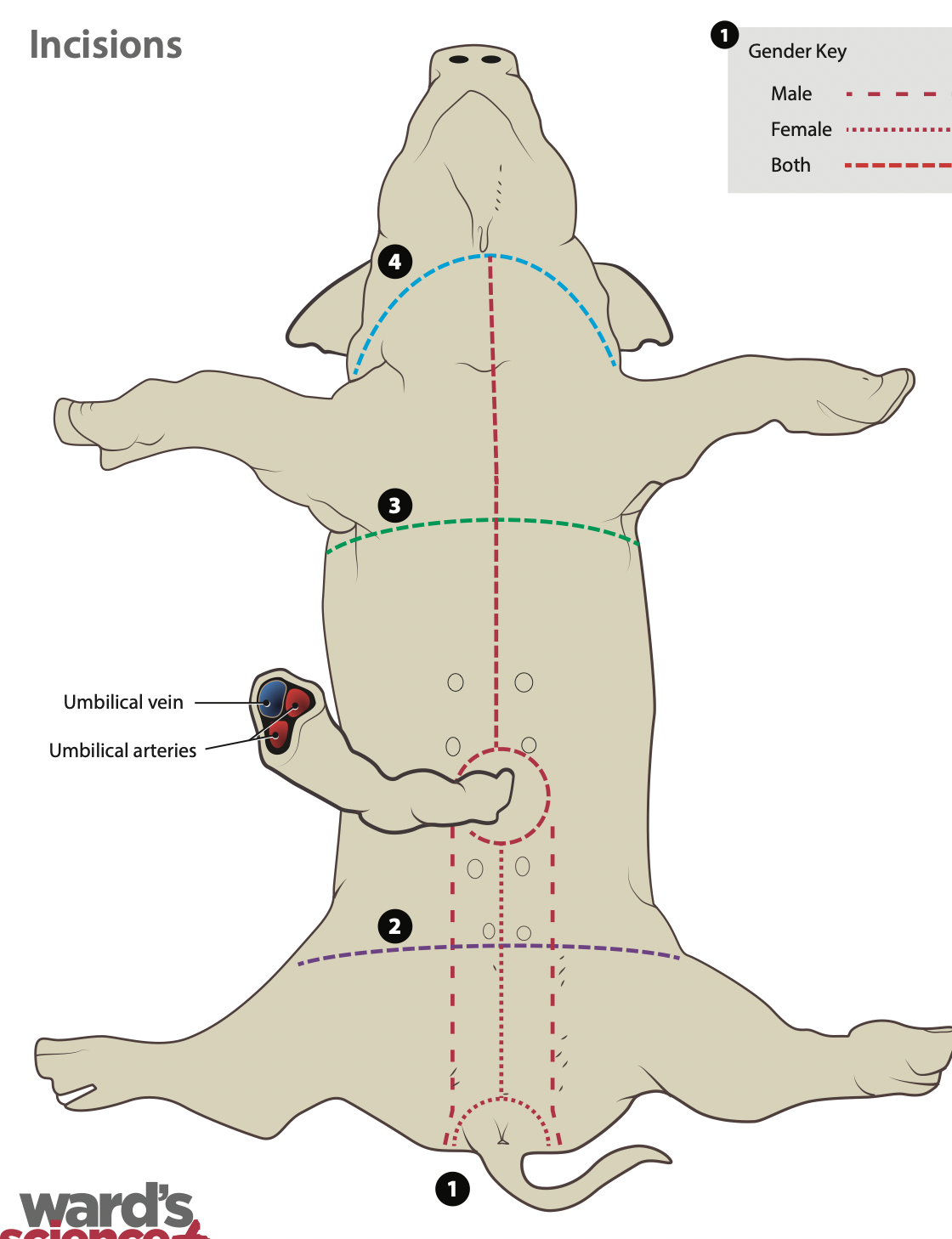
Pig dissection - Bell ringer
Photo Location Definition |
 Umbilical vein: The umbilical vein carries oxygen and nutrient from the mothers arterial blood to the fetus |
 Umbilical artery: The umbilical arteries carry deoxygenated blood and metabolic waste products away from the fetus to the placenta |
Tongue: The tongue is a manipulative, muscular structure that helps with chewing, swallowing and sensing food |
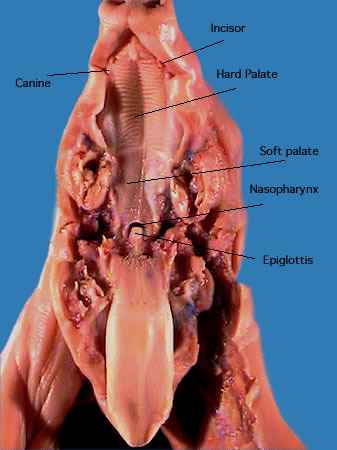 Epiglottis: The epiglottis is a fold of skin that covers the opening to the trachea during swallowing to prevent food from entering |
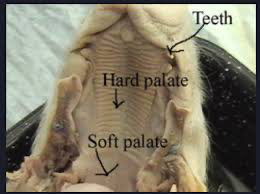 Hard palate: The hard palate is made of bone, that separate the oral cavity from the nasal cavity |
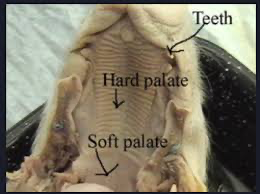 Soft palate: The soft palate rises to prevent food from going into the nasal cavity. It contains no bone |
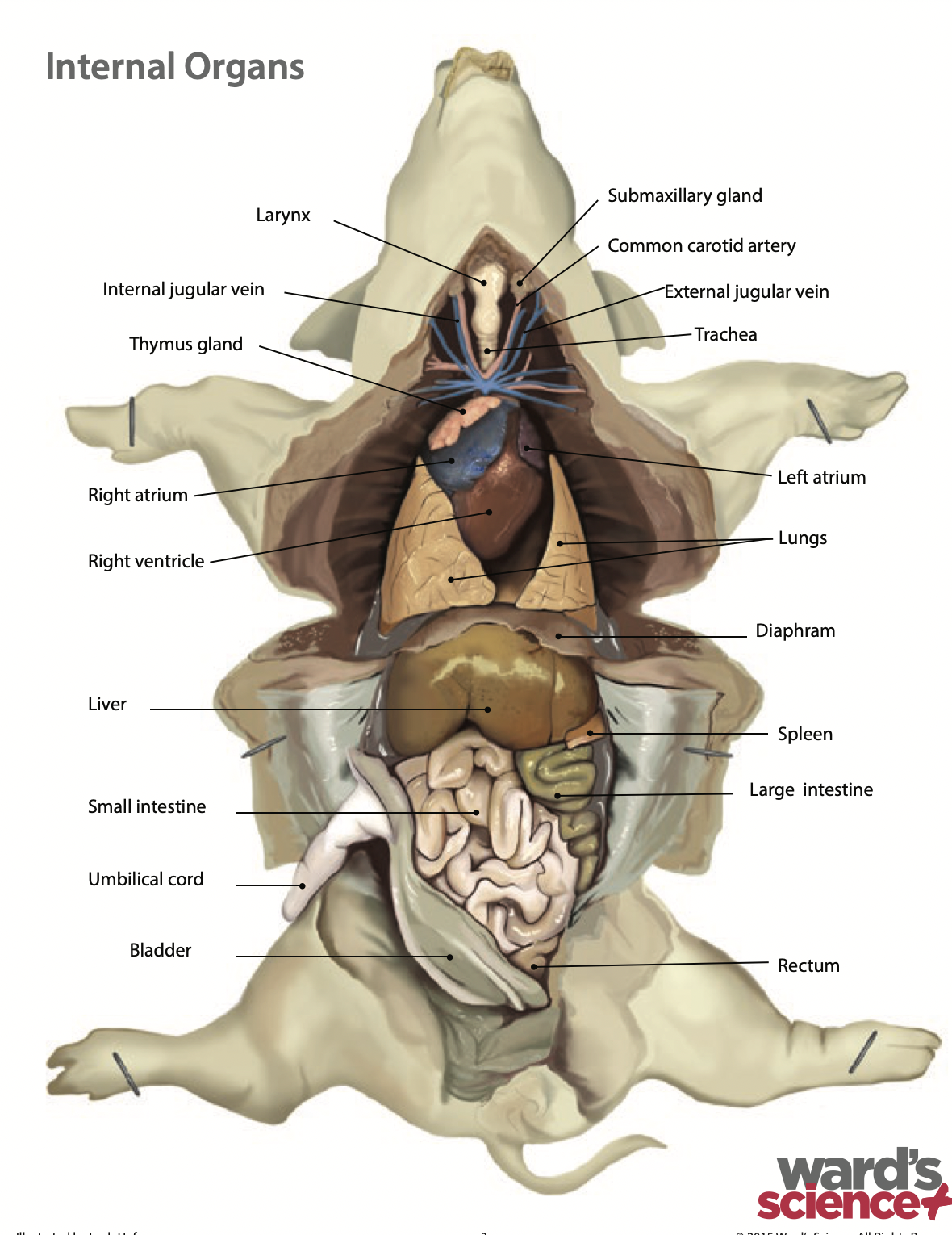 Larynx: The larynx is the voice box. It is where our vocal cords are and what air passes through before our trachea |
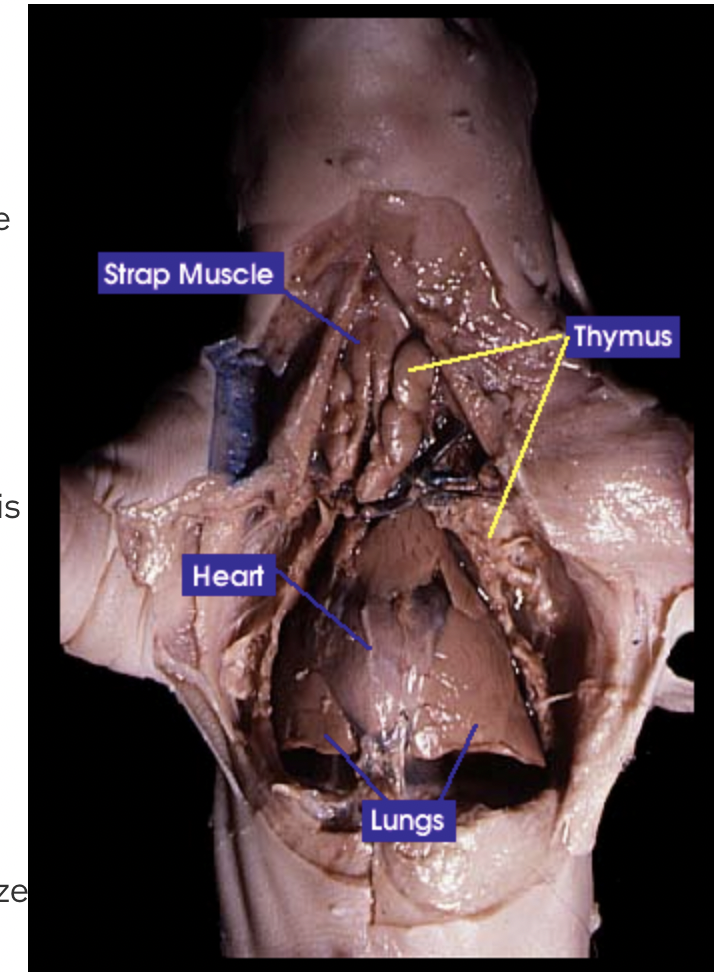
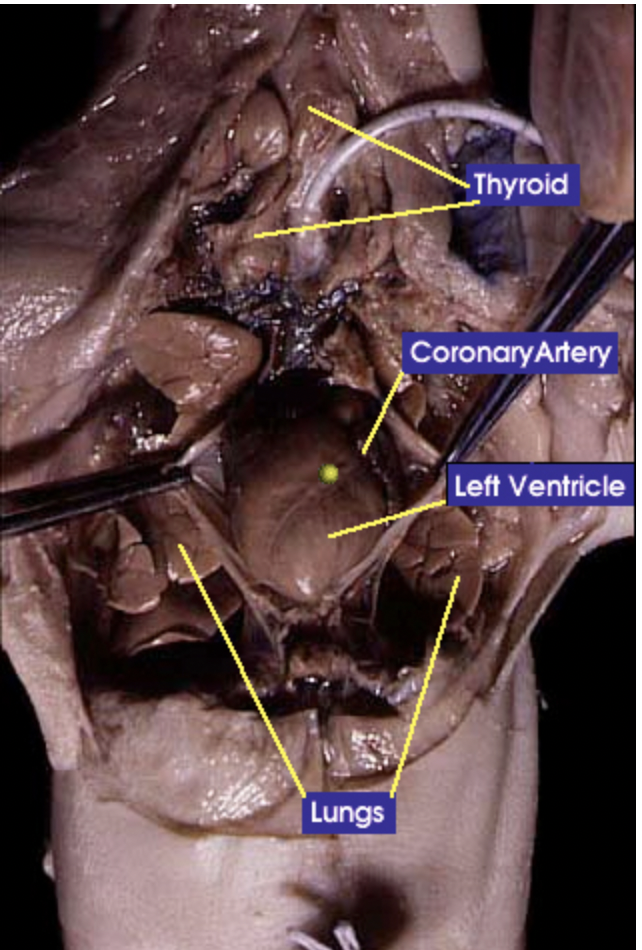 Thyroid gland: The thyroid gland controls the speed of ones metabolism |
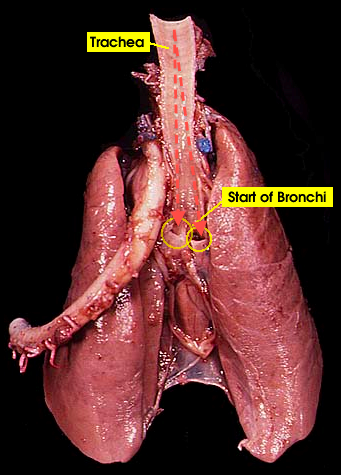 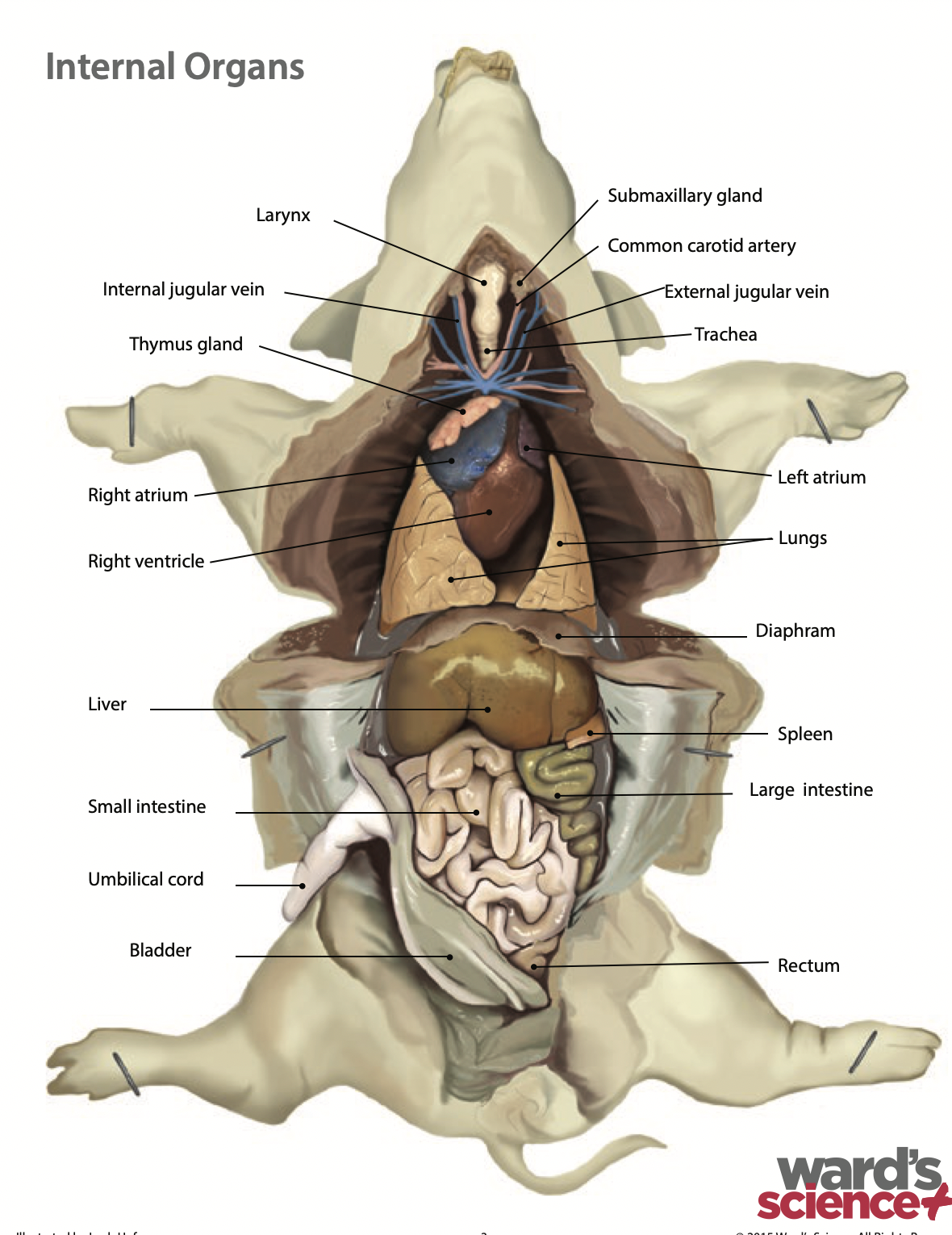 Trachea: The trachea is a windpipe that carries air into the lungs |
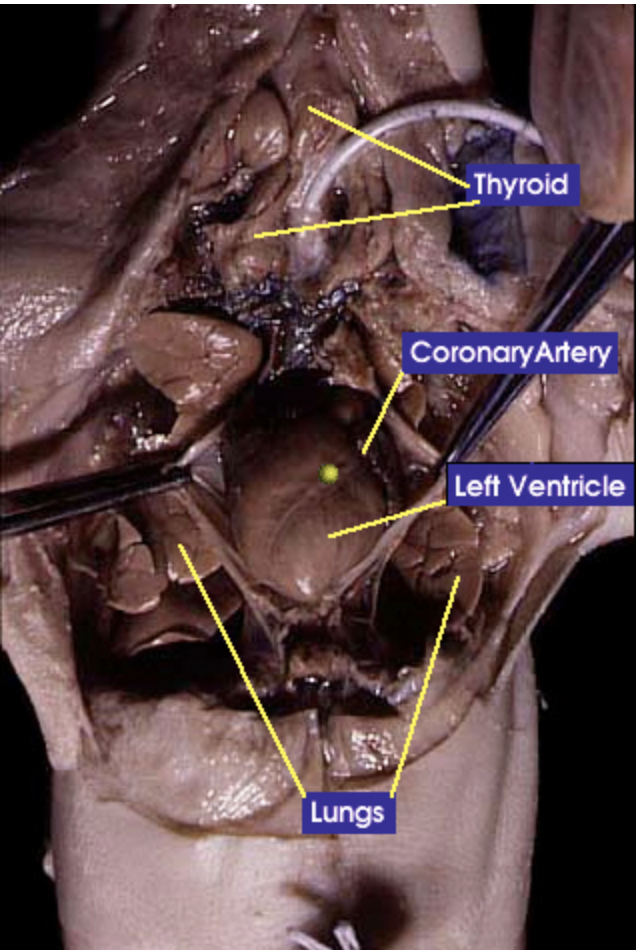 Lung: does gas exchange by inhaling oxygen and having it enter the bloodstream and at the same time carbon dioxide is exiting the bloodstream to he exhaled |
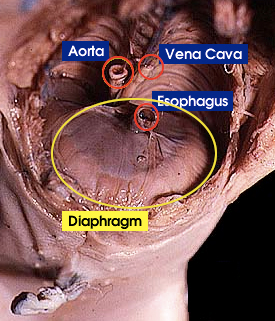 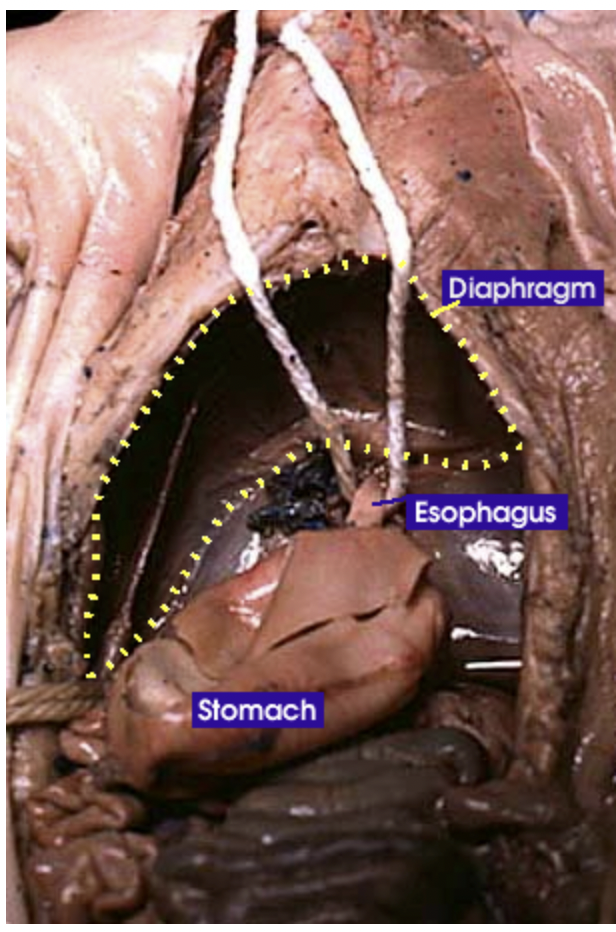 Diaphragm: Is a sheet-like muscle that lowers when inhaling and rises when exhaling. It plays a critical role in breathing |
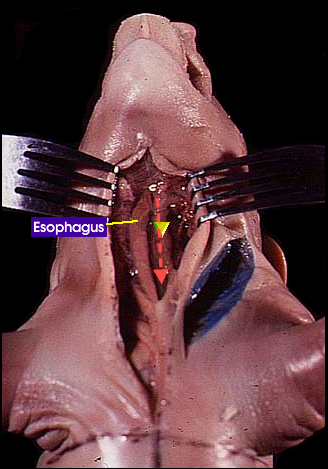 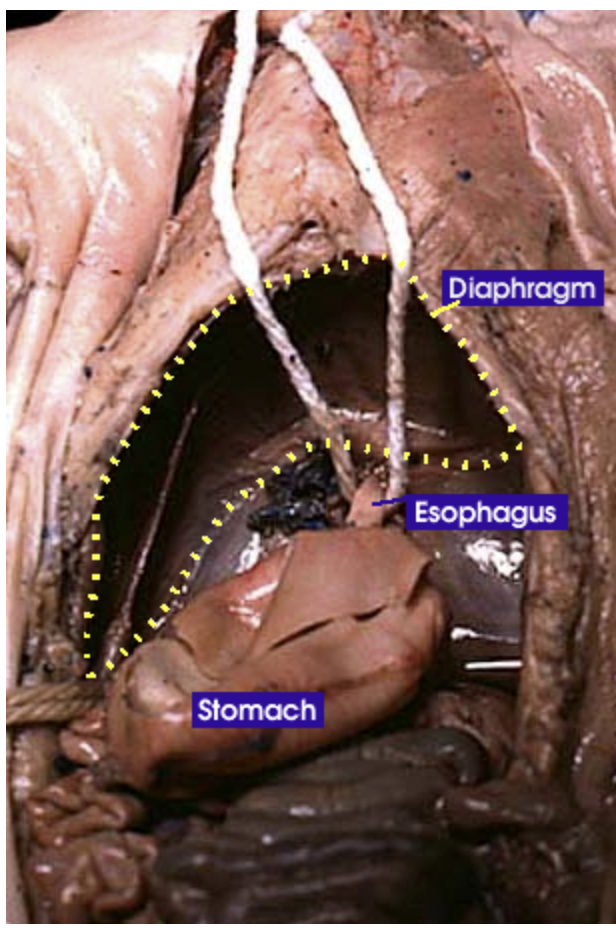 Esophagus: It is a tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach. It connects the oral cavity to the stomach |
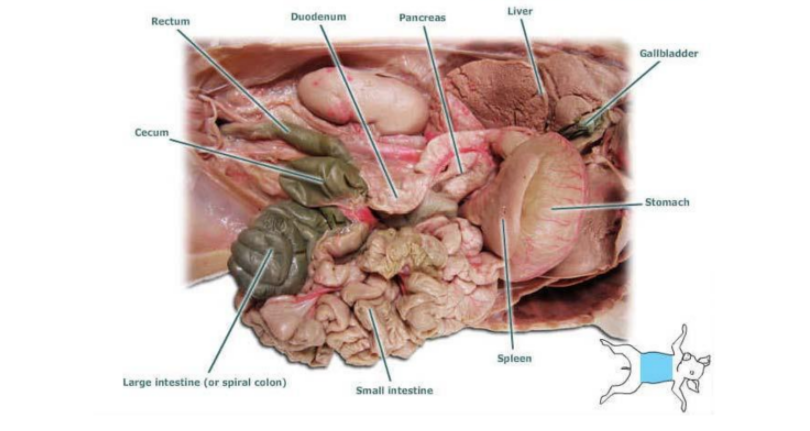
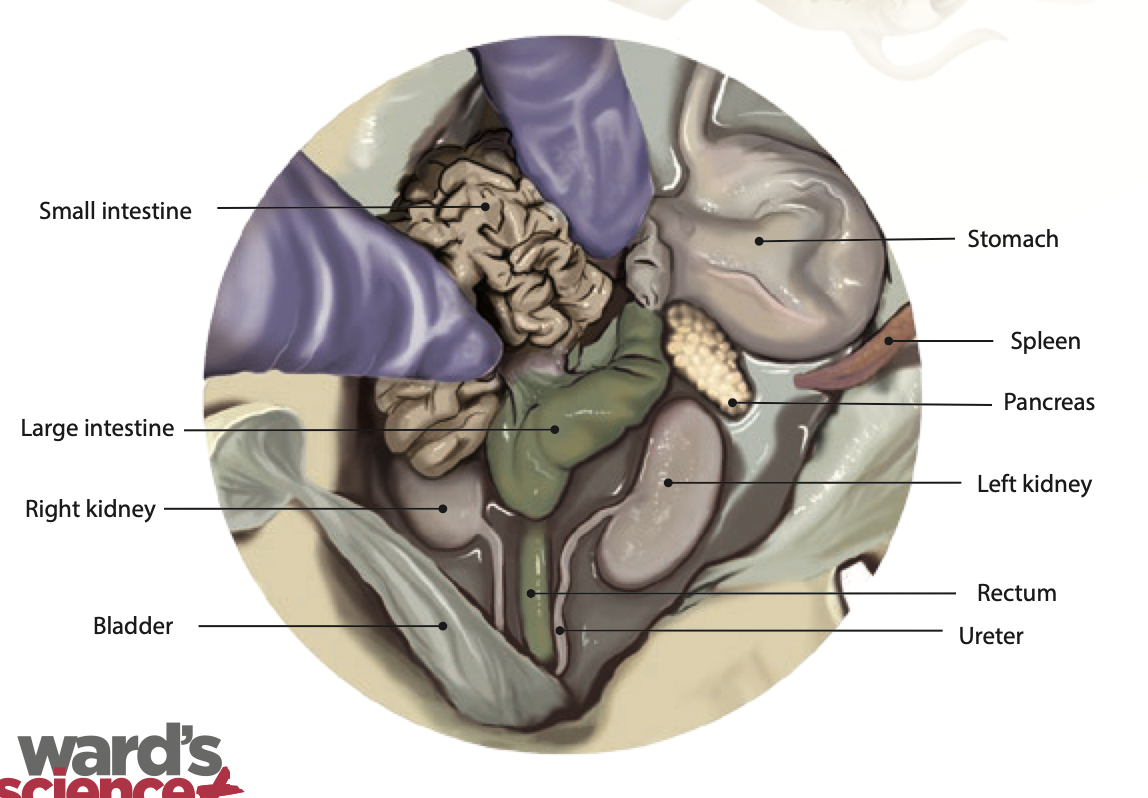
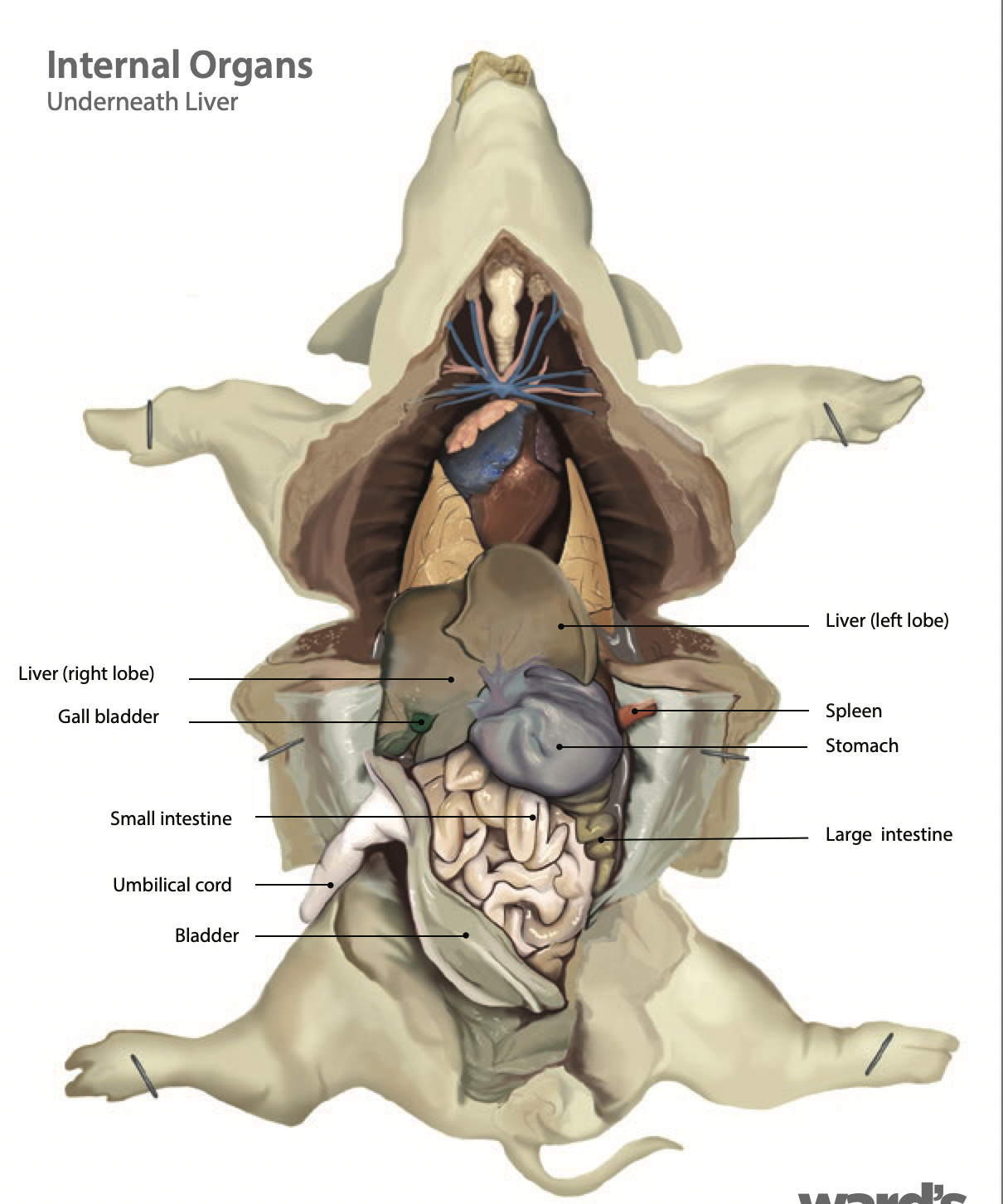
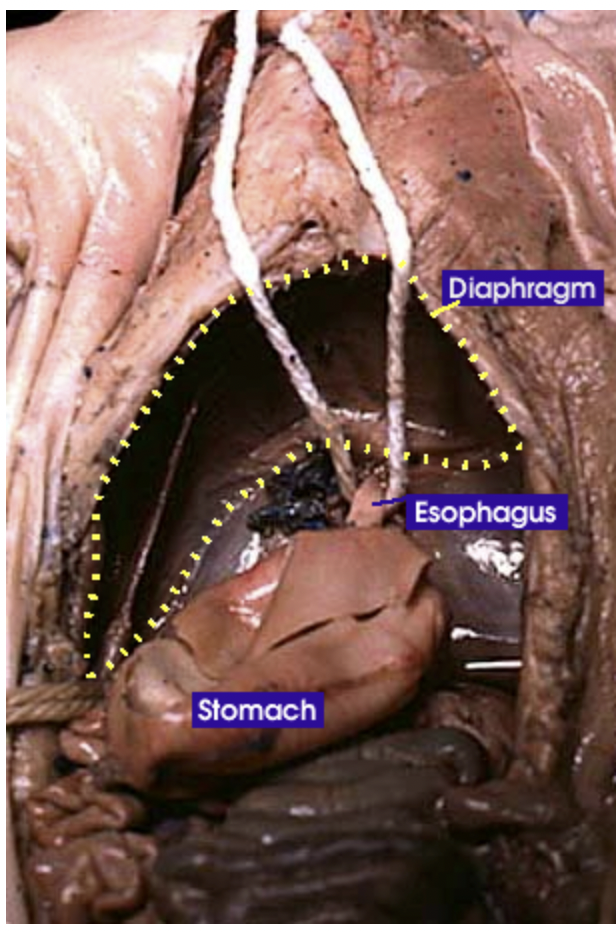 Stomach: Holds food and mixes it with acid and enzymes to break the food down |
Gastroesophageal sphincter: Valve that keeps food and stomach acid in the stomach. It prevents the contents in to stomach from going back up the esophagus |
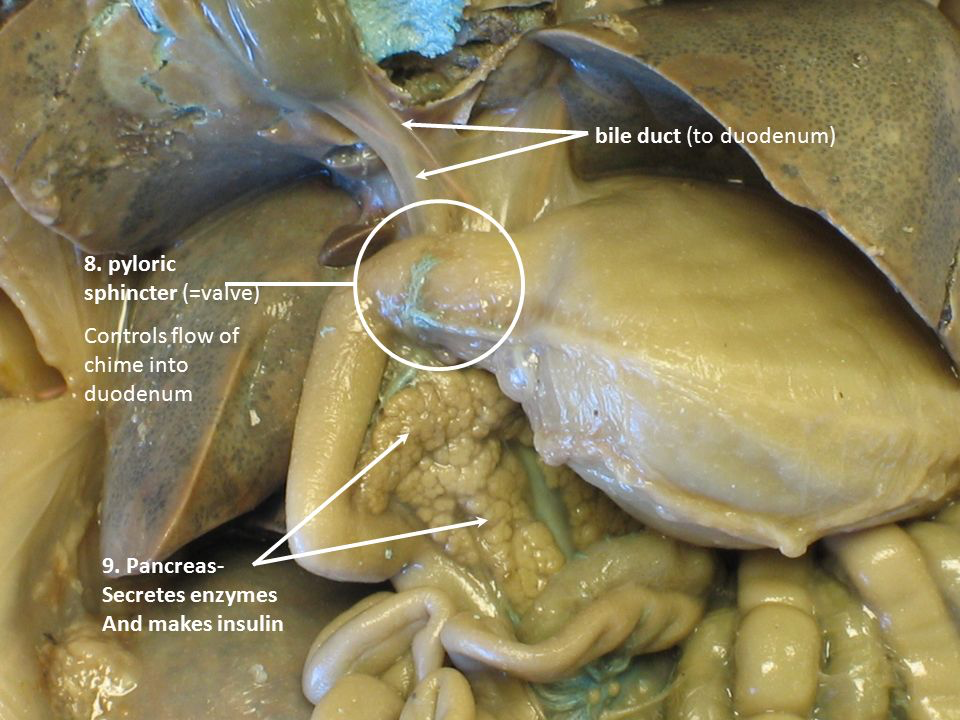 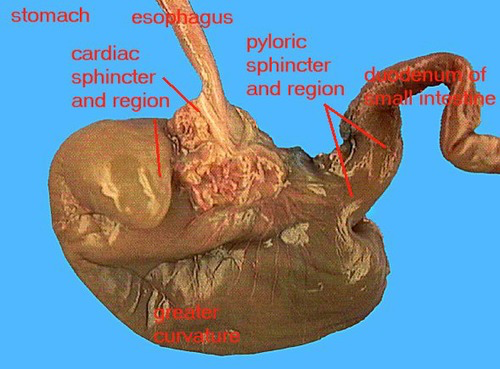 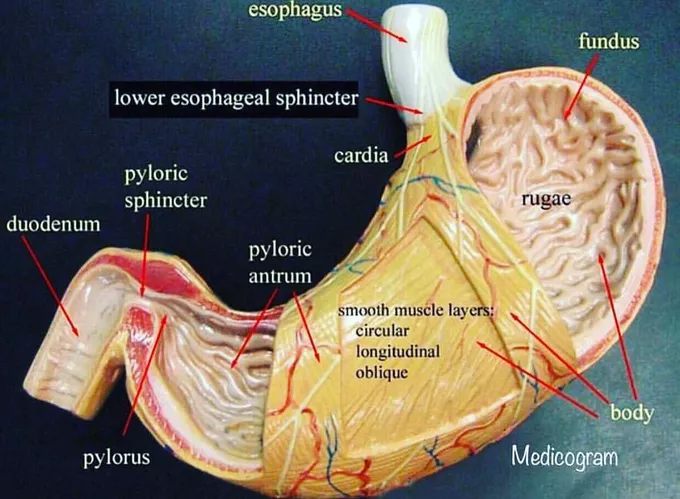 Pyloric sphincter: Is a ring like muscle that governs the passage of chyme from the stomach into the small intestine |
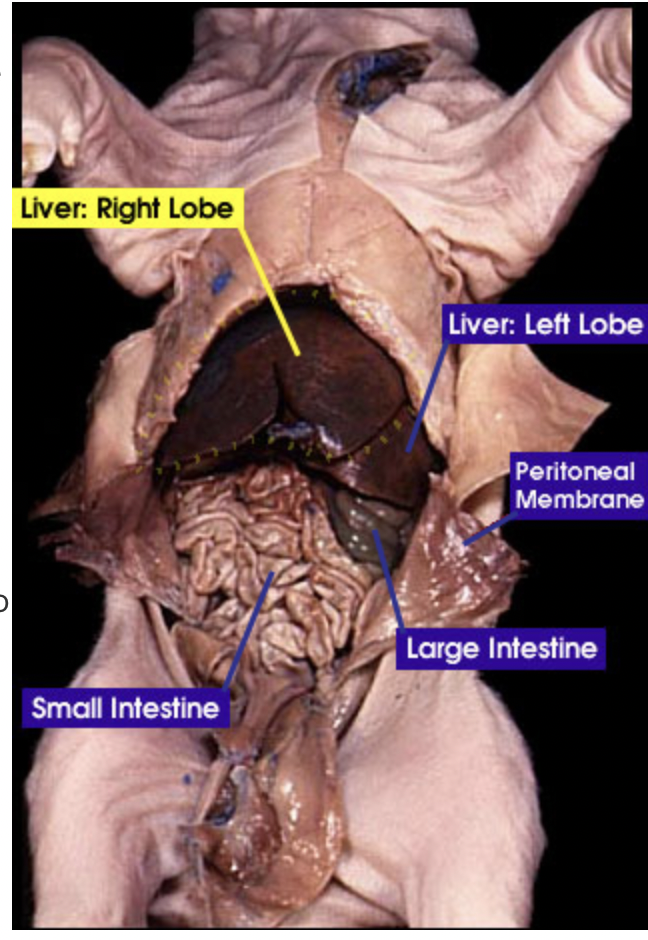 Small intestine: The small intestine is where digestion of food continues and absorption of nutrients occur |
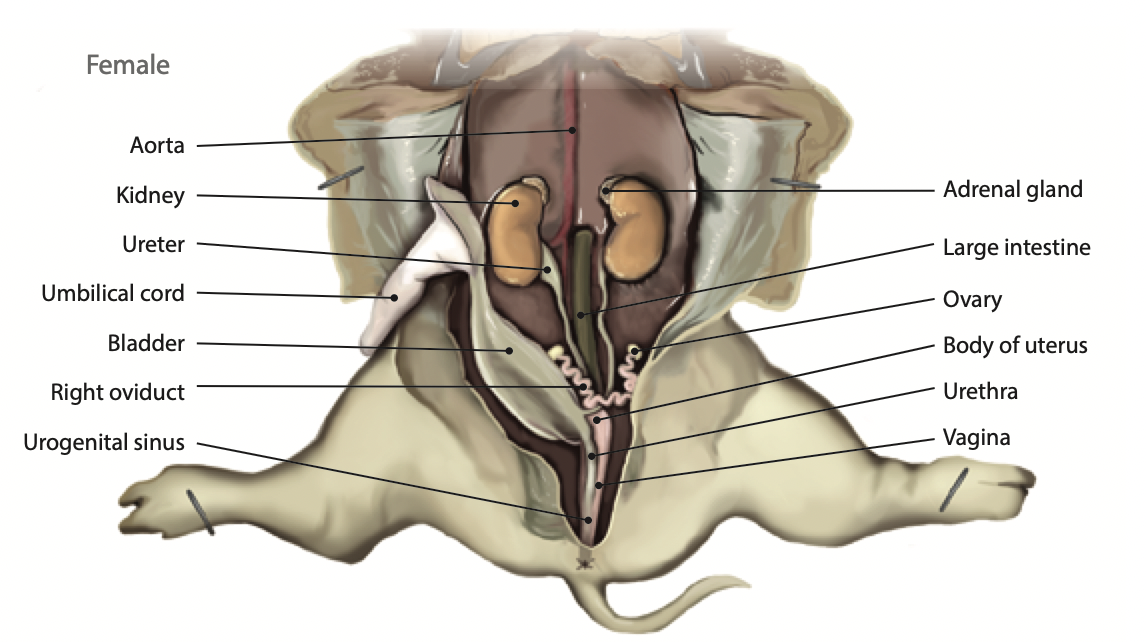
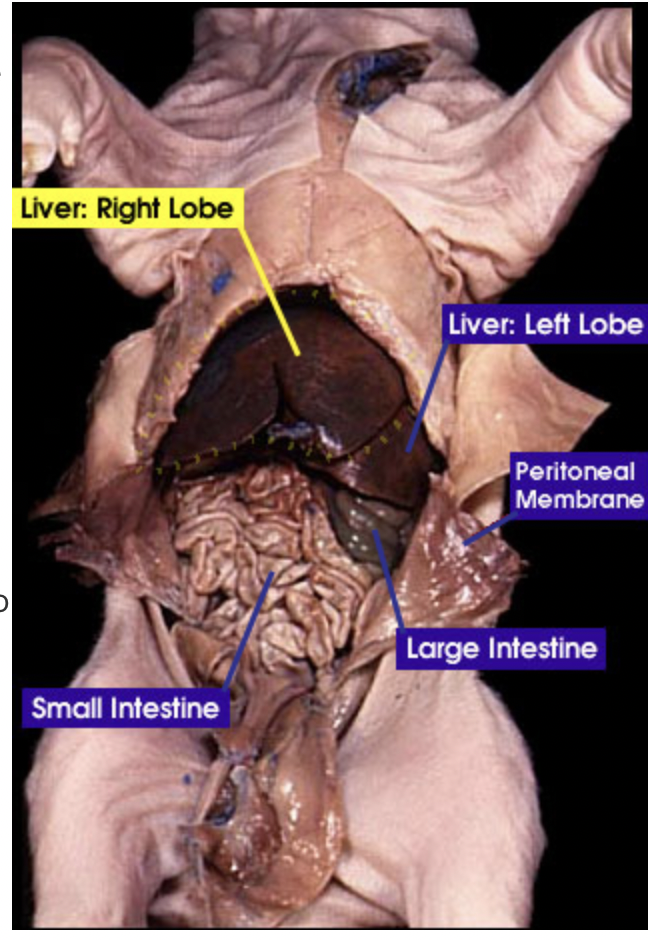 Large intestine: The large intestine absorbs water, salts and some vitamins. It also prepares the undigested materials for feces |
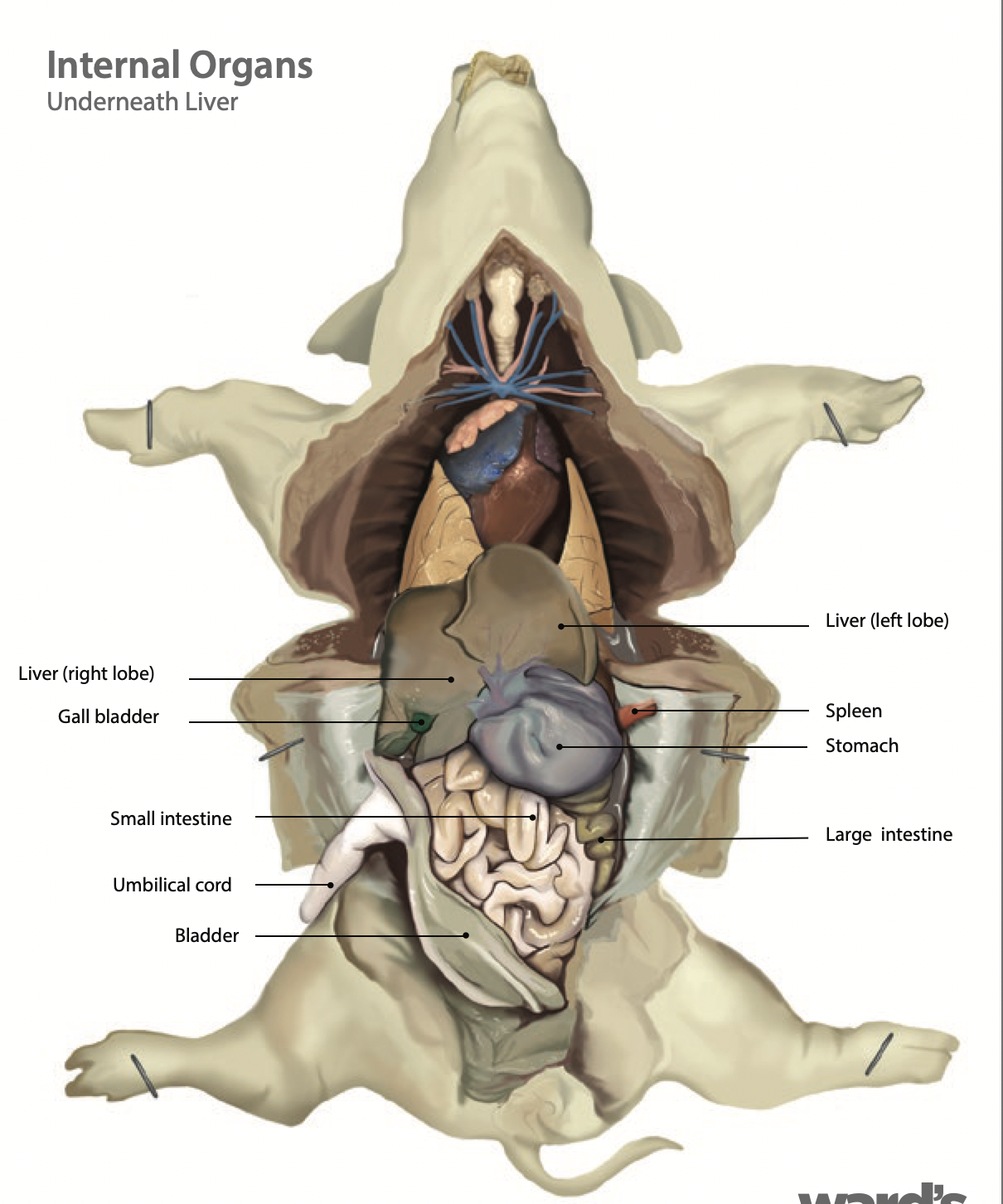 Spleen: It is an immune system organ that fights infection and breaks down expired red blood cells (Found along the left external margin of the stomach) |
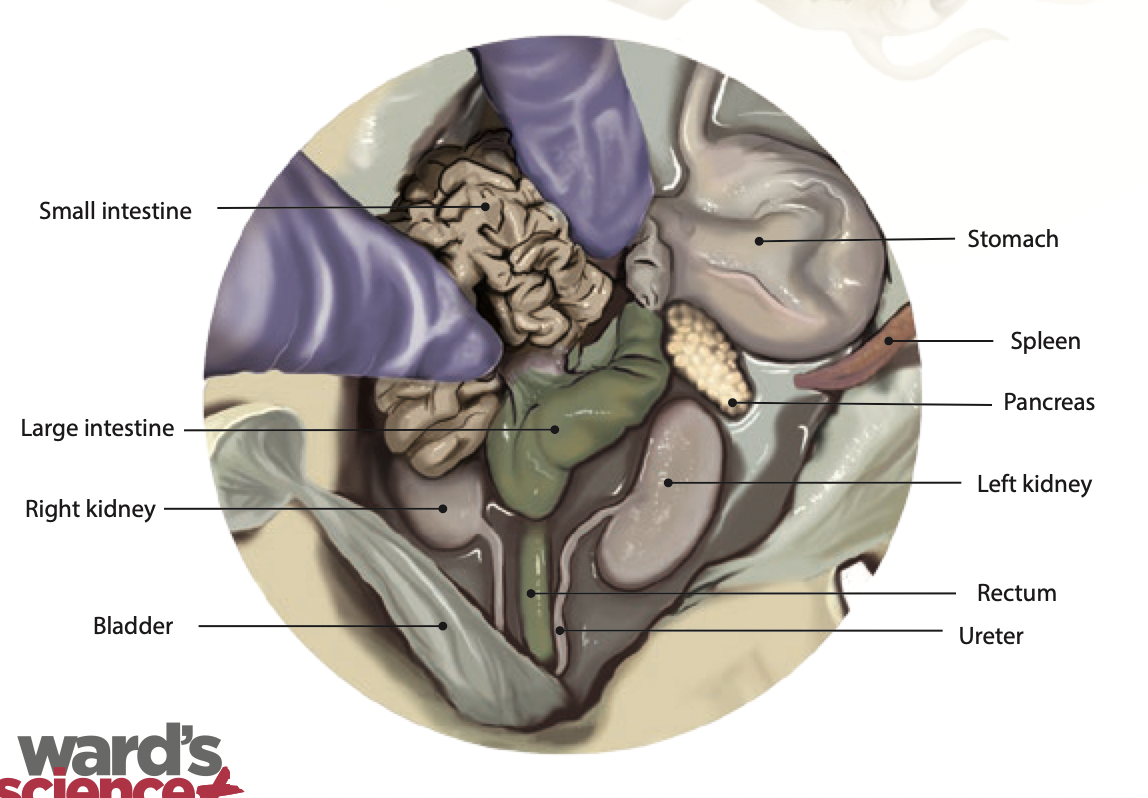 Pancreas: The pancreas secretes insulin and pancreatic juices to help with digestion |
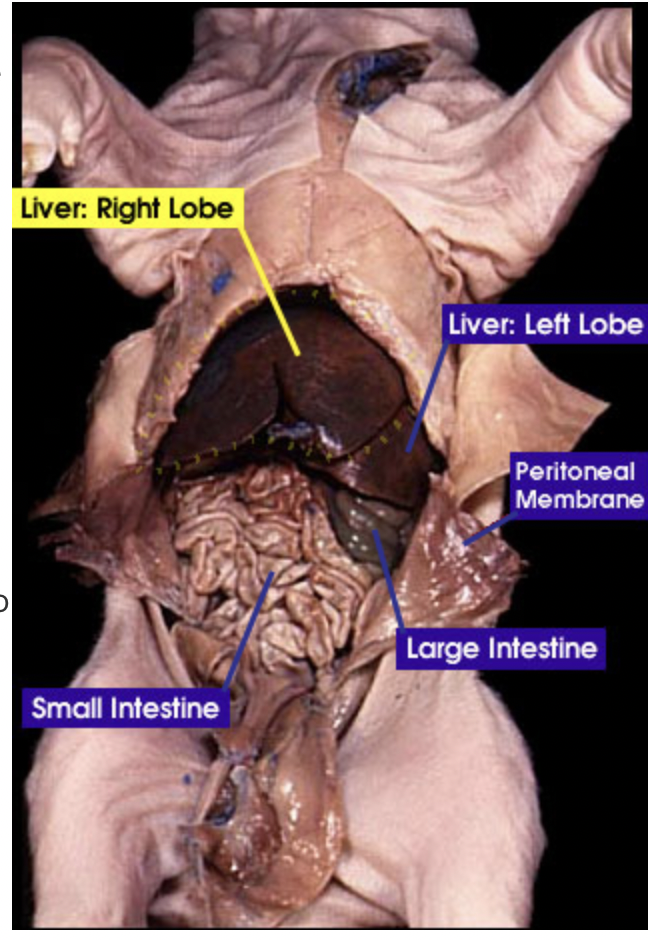 Liver: the liver makes bile and sends it to be stored in the gallbladder |
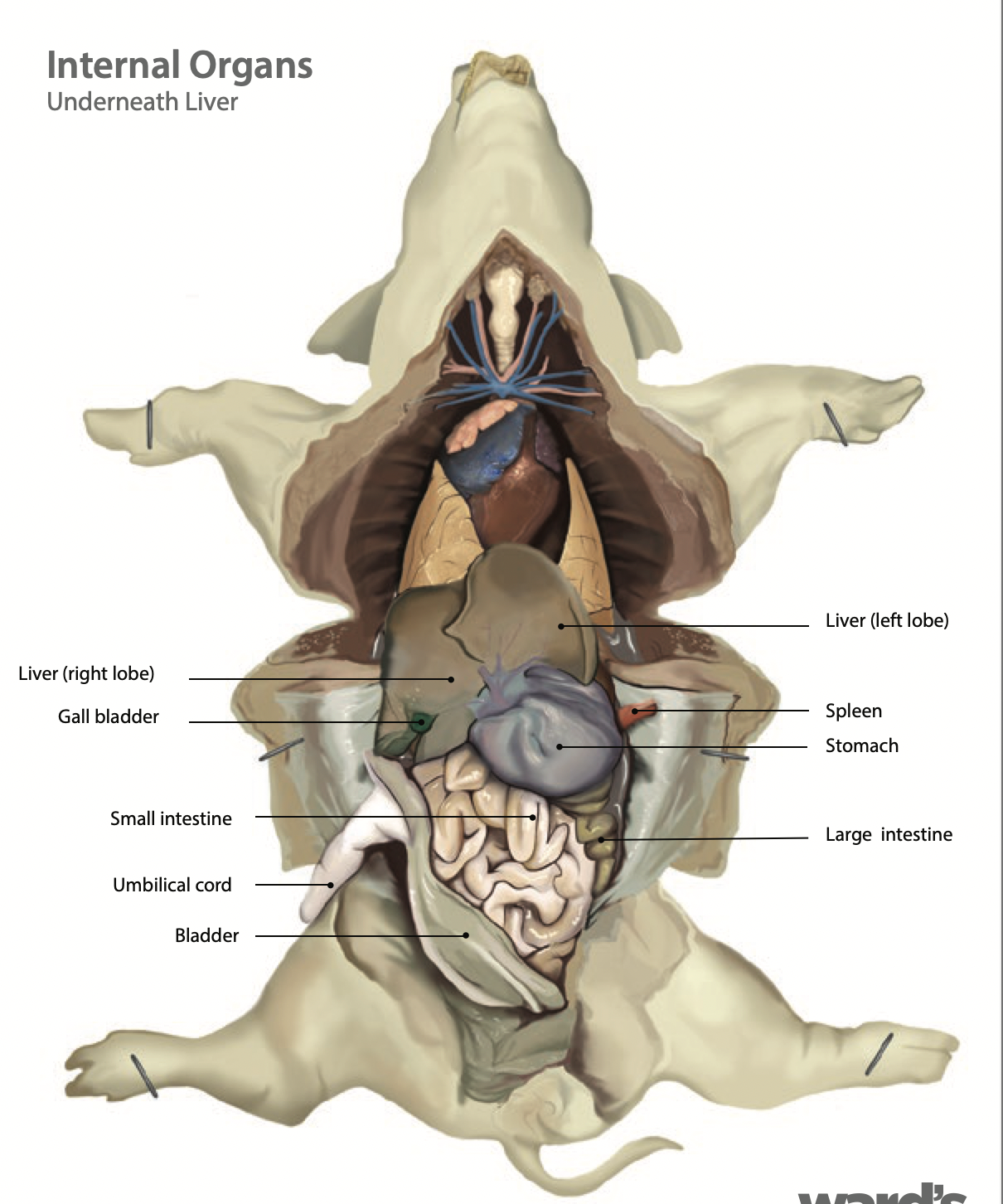 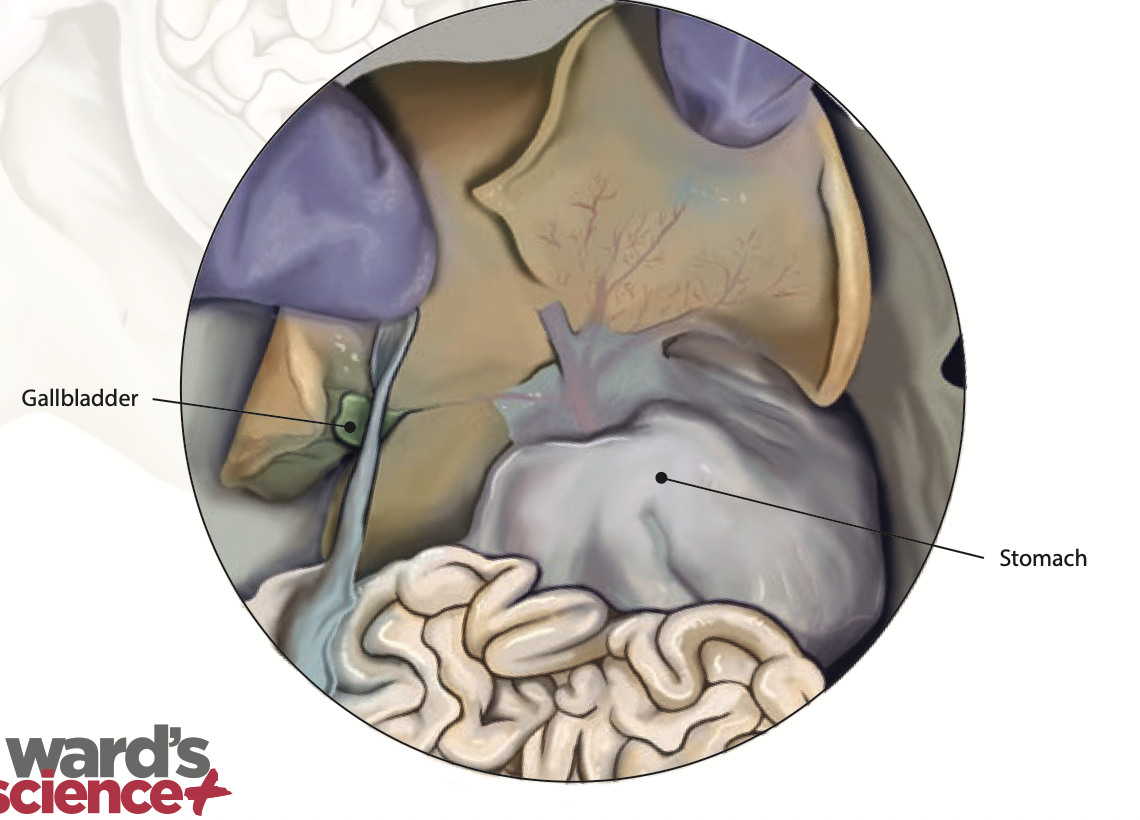 Gallbladder: The gallbladder stores and releases bile to aid in digestion |
 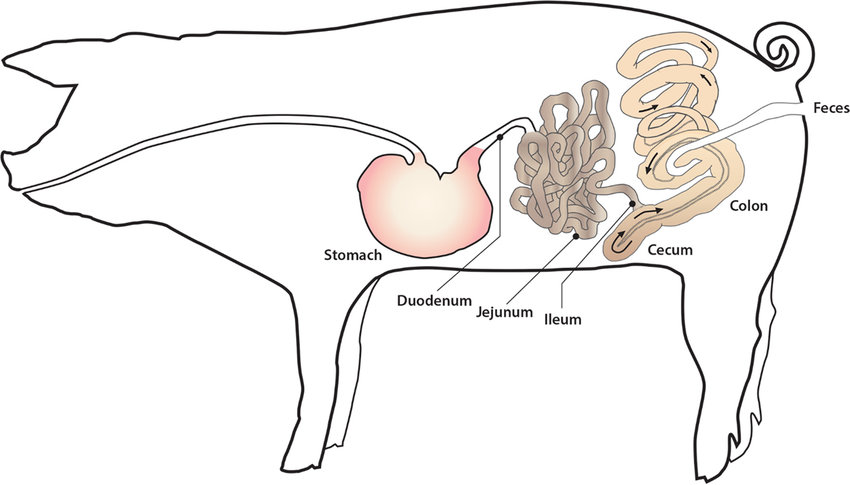 Caecum: Is a dead end that receives material from the small intestine |
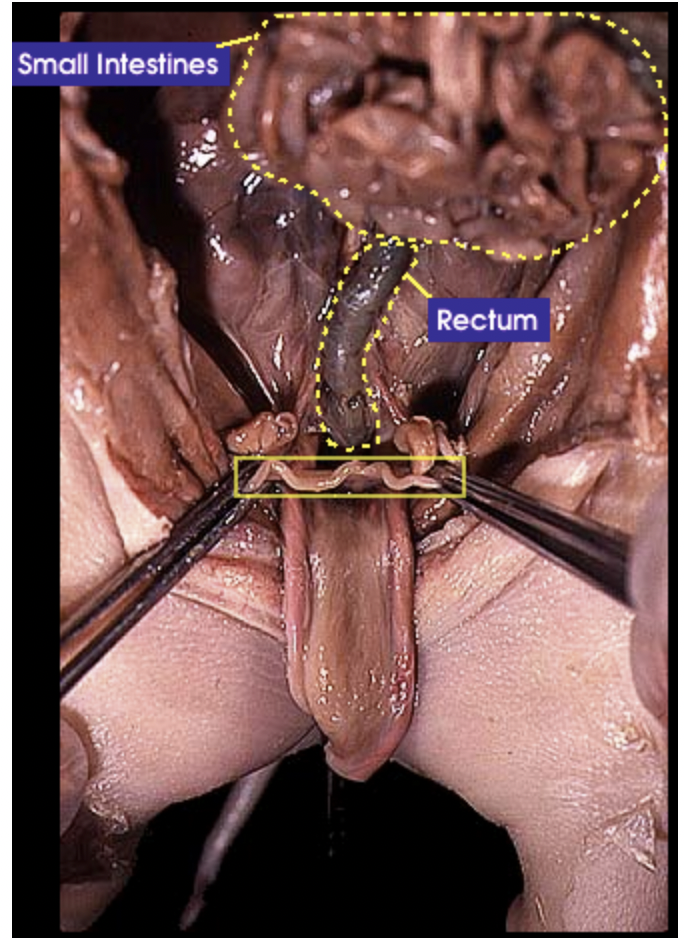
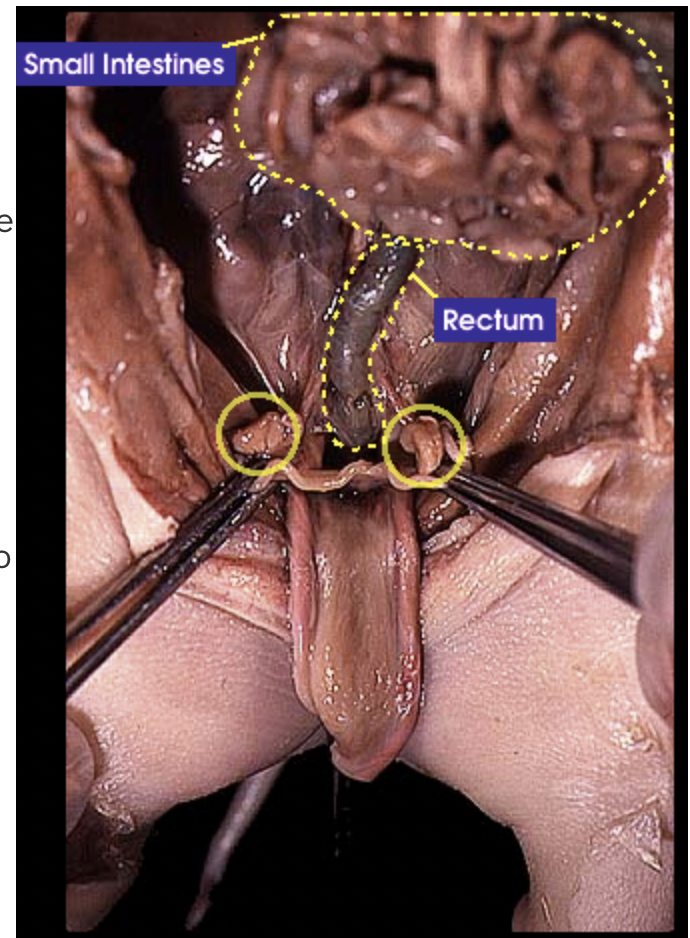 Rectum: Is where feces is stored before it is ready to be excreted |
 Heart: The heart pumps blood around the whole body through a series of veins and arteries |
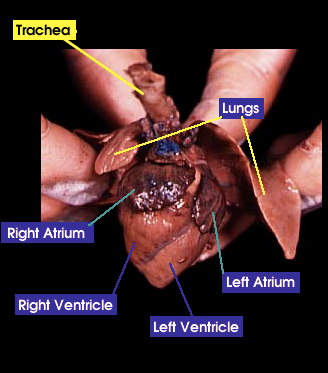 Atria: A chamber that receives blood from the body |
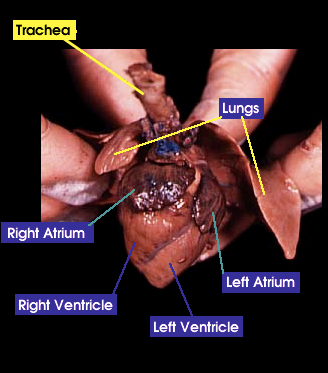 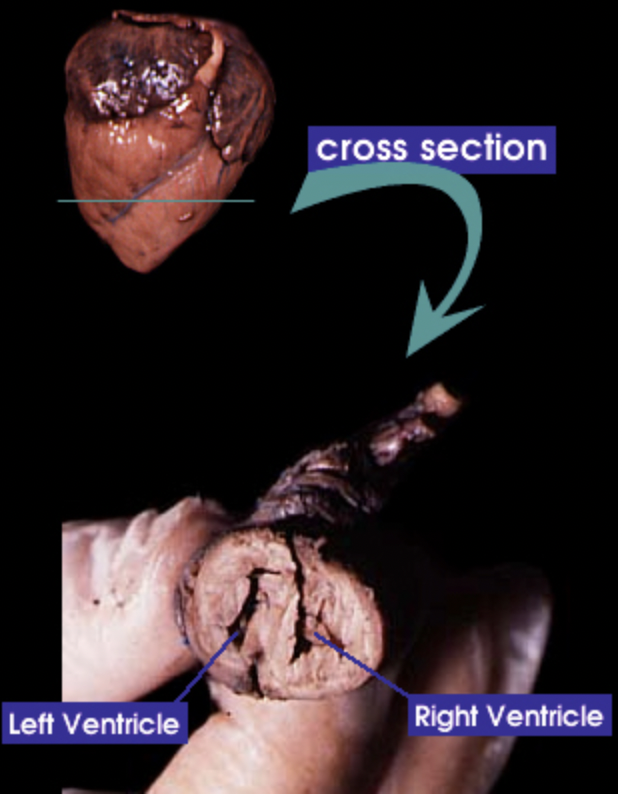 Ventricles: A chamber that pumps blood to the body |
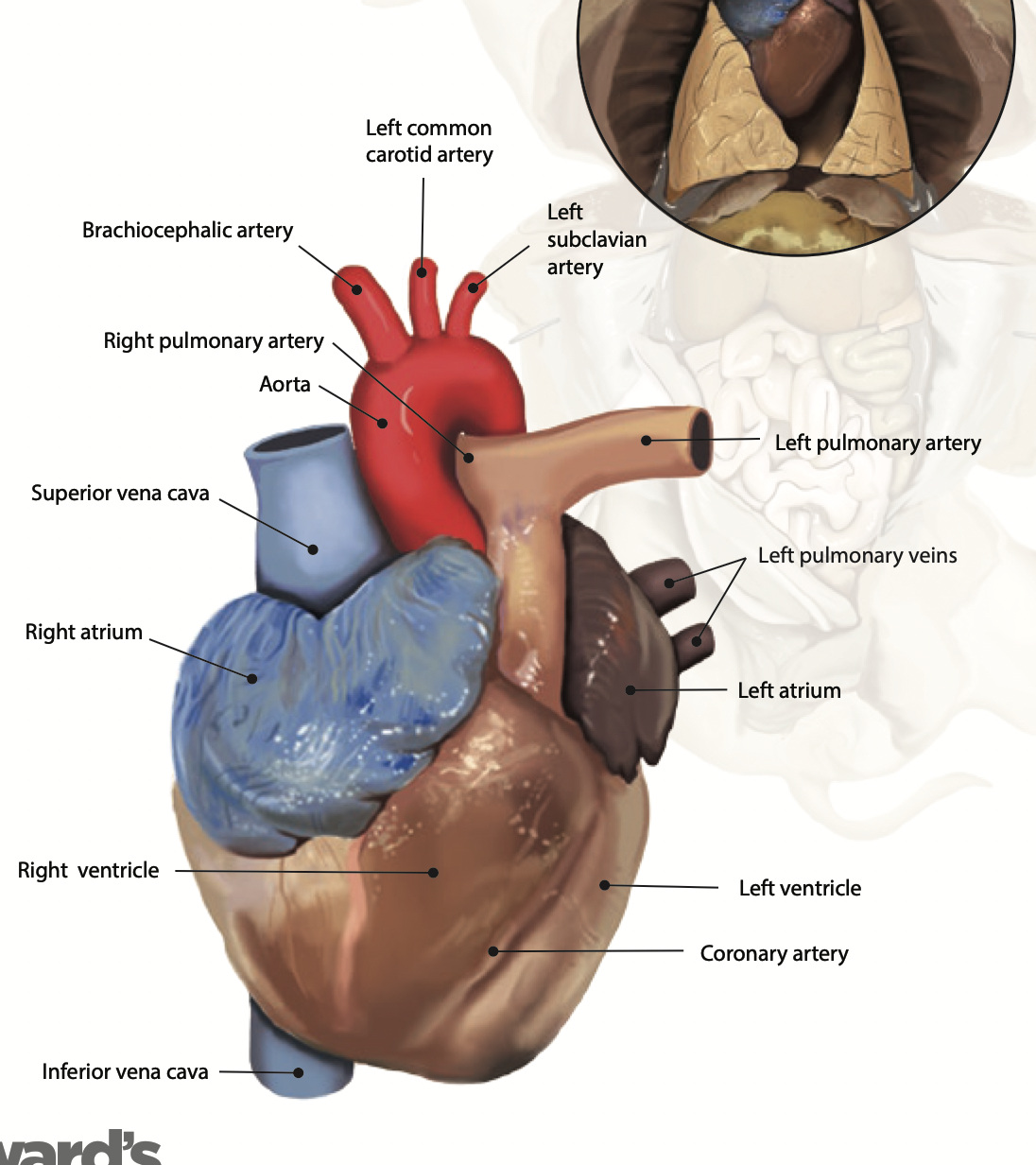 Aortic arch: Carries oxygenated blood under high pressure and distributes it to three main arteries |
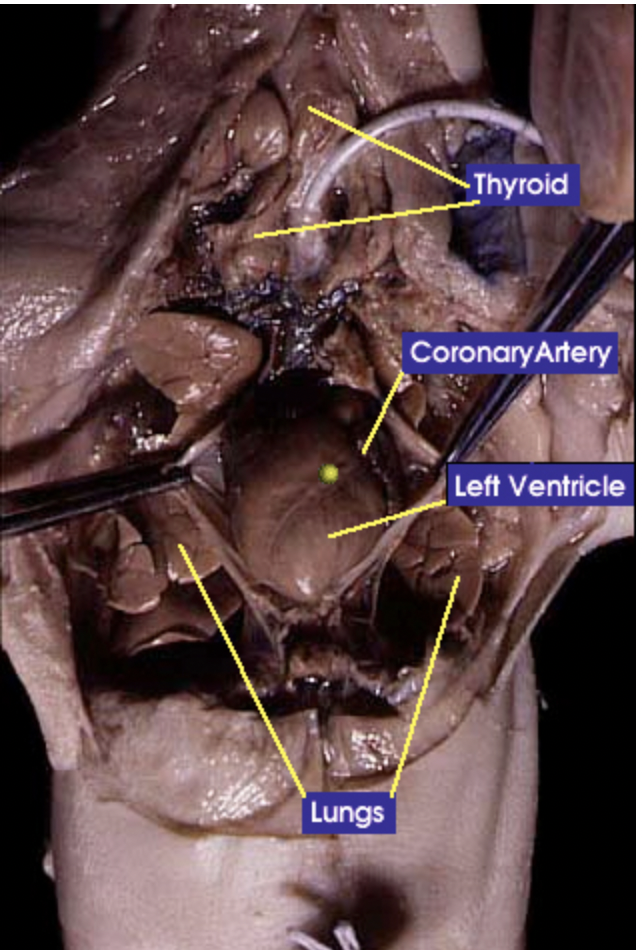 Coronary artery: Is the main supply of oxygenated blood to the heart |
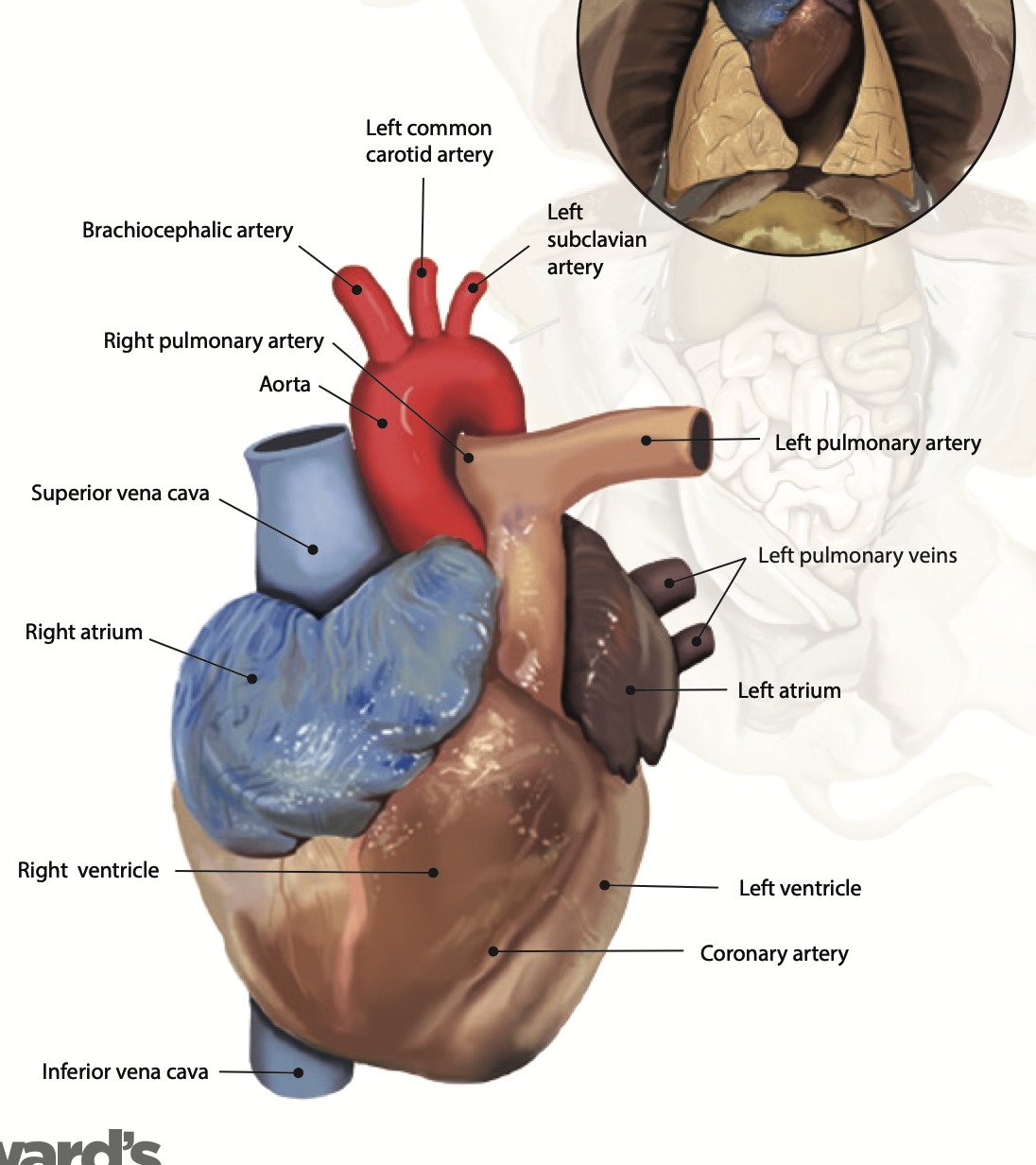 Pulmonary artery: Carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs |
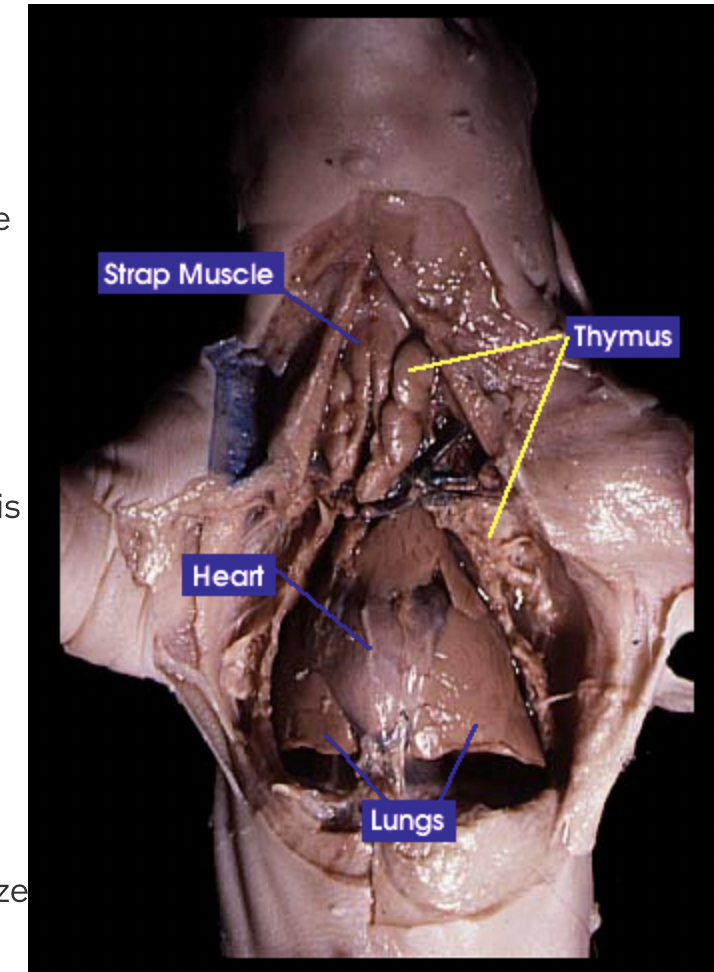 Thymus: The thymus is responsible for the production and maturation of immune cells |
 Kidney: kidneys removes waste from the blood and produces urine |
 Ureter: Urine passes through to reach the urinary bladder |
 Bladder: Stores urine until the fluid is eliminated |
 Urethra: It is a tube that allows urine to exit the body. (it is in the bladder) |
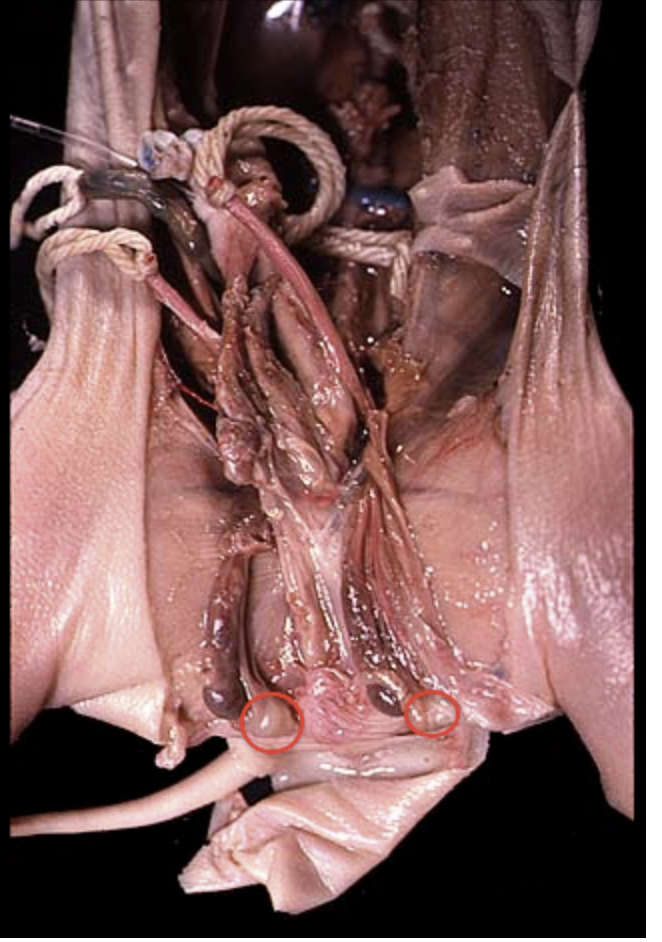 Epididymis: Is a storage place for sperm before it enters the ductus deferens |
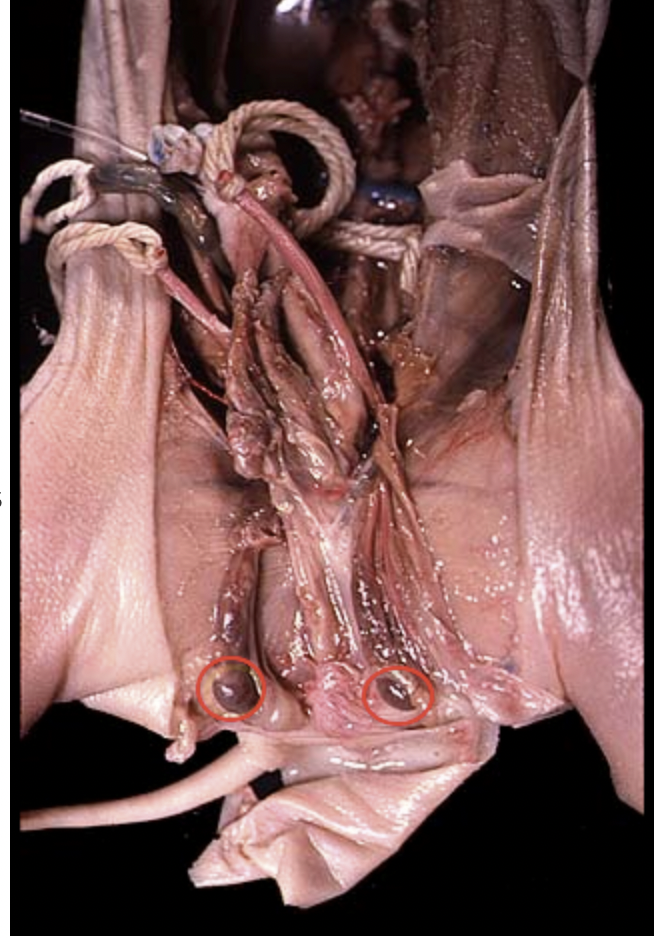 Testes: Is where sperm production takes place and where sex hormones are produced |
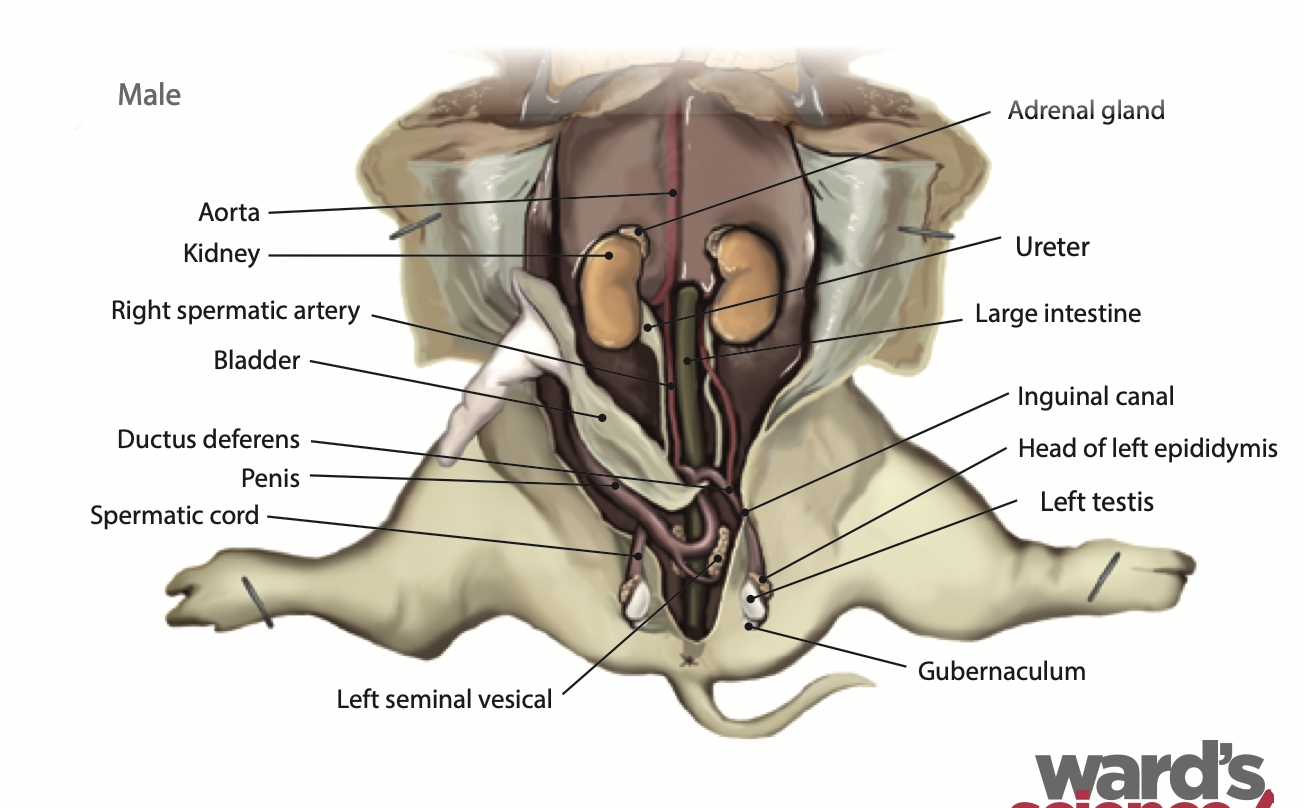 Gubernaculum: Guides the descent of the testes into the scrotum |
 Penis: It is used for urination and sexual intercourse |
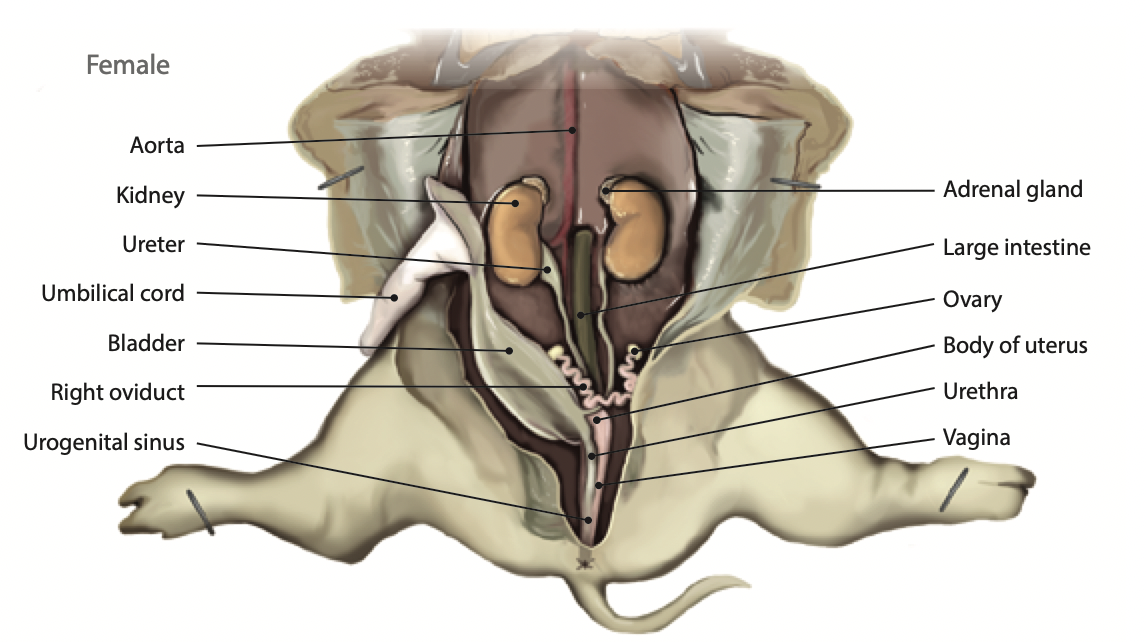 Ovary: The ovaries contain all the developing eggs a female pig will ever hav. They also produce hormones |
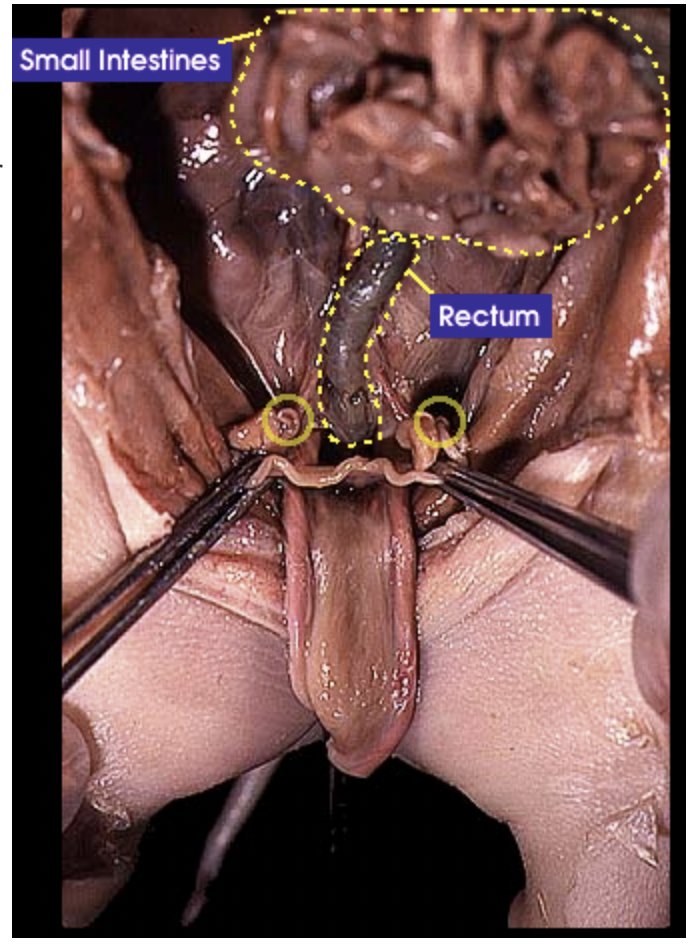 Oviduct/Fallopian tube: The oviduct receives the egg during ovulation and propels the eggs to the uterus |
 Uterus: Receives a fertilized egg and protects the fetus while is develops and grows |